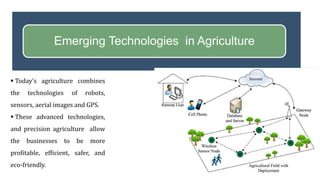
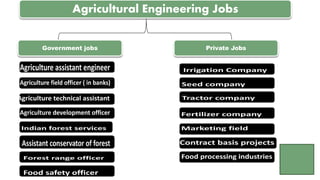
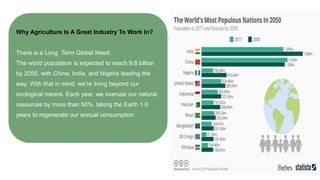
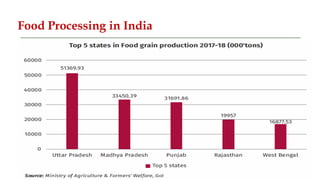
The presentation by Surjeet Singh Rana discusses the evolution of agriculture engineering and its integration with Industry 4.0 technologies, emphasizing advancements from historical innovations to precision agriculture using AI and IoT. It outlines the importance of agricultural robotics, vertical farming, and farm automation in modern practices. Additionally, the document highlights the career prospects and significance of the agricultural industry in meeting the increasing global food demands as the population rises.