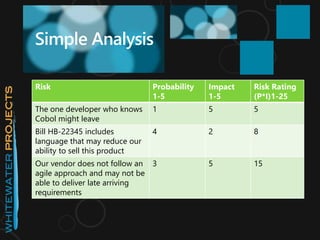
The document discusses advanced agile risk management, highlighting the importance of identifying, evaluating, prioritizing, and responding to risks in agile projects. It outlines key risks such as delivering the wrong product or delays and emphasizes strategies for managing these risks through incremental delivery and customer involvement. Additionally, it provides frameworks for analysis, including SWOT and Ishikawa diagrams, to facilitate risk assessment and decision-making.