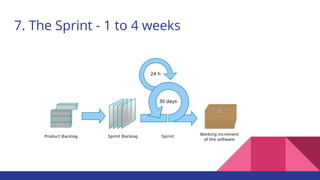
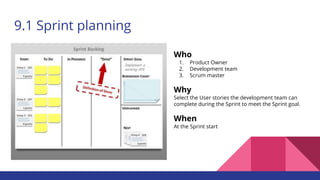
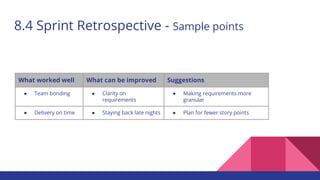
The document outlines the Agile philosophy as an alternative to traditional project management, emphasizing incremental development, collaboration, and adaptability through the Scrum methodology. It details the roles within a Scrum team, the significance of the sprint process, and various Scrum events that facilitate project management. Additionally, it touches on performance measurement, agile transformation, and essential practices for successful Agile project execution.