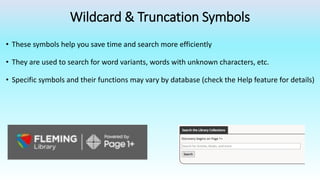
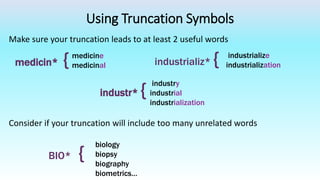
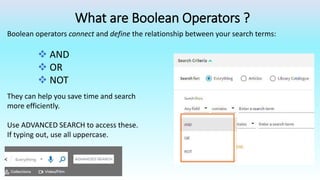
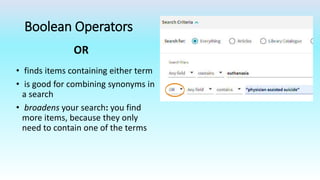
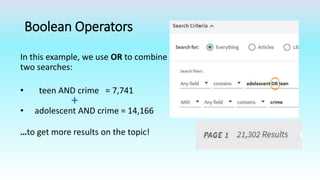
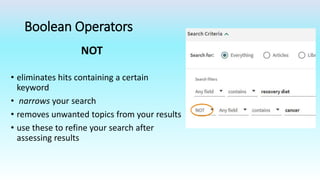
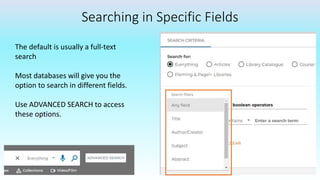
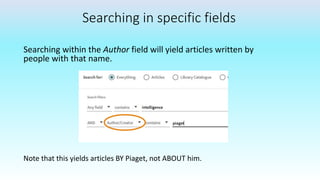
This document provides information on advanced search tools and strategies that can help users search more efficiently. It discusses wildcard and truncation symbols that can be used to search for word variants or unknown characters. Boolean operators like AND, OR and NOT are explained, which can connect search terms and refine results. The document also recommends searching specific fields like title, abstract, or author to find more targeted results.