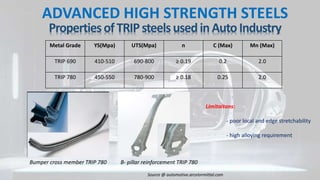
This document provides information on advanced high strength steels (AHSS) used in the automotive industry. It defines AHSS as steels with yield strengths over 550 MPa and discusses various strengthening mechanisms employed. Different types of AHSS are described, including dual phase steels, ferritic bainitic steels, and complex phase steels. Their microstructures and properties are summarized. Key factors for material selection like crash performance, stiffness, and formability are also outlined. The document provides an overview of the evolution of steels in the automotive industry to enable lightweight design through improved strength-ductility combinations realized by AHSS.