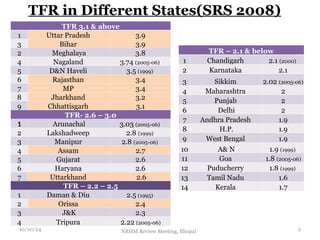
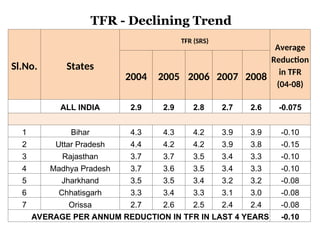
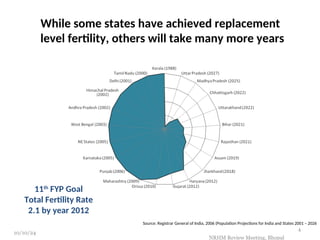
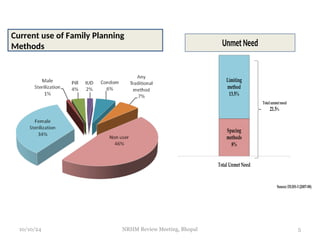
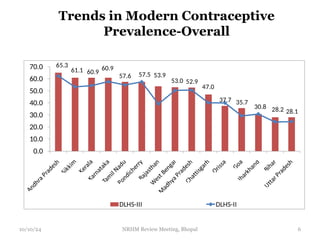
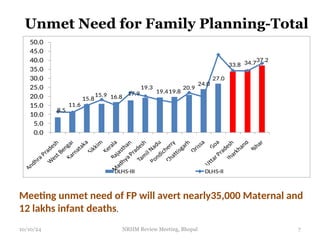
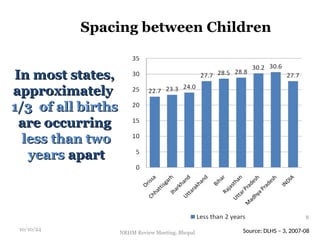
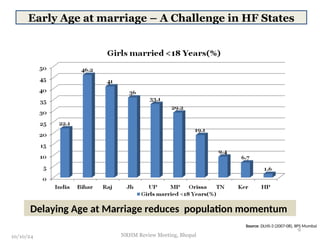
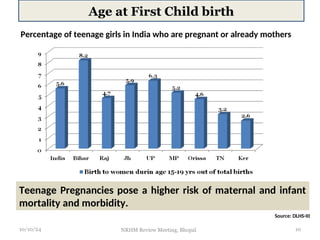
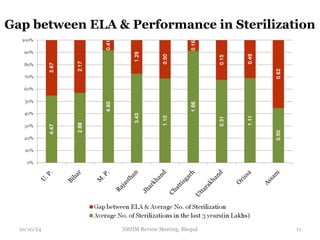
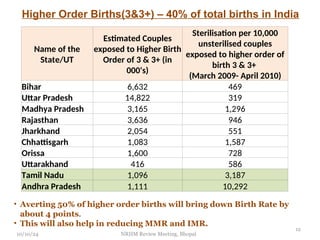
The document reviews India's family planning program, highlighting varied total fertility rates (TFR) across different states, with some achieving replacement levels while others lag significantly. It discusses the unmet need for family planning and the incidence of births occurring less than two years apart, emphasizing the importance of improving contraceptive use and delaying marriage to enhance maternal and infant health. Additionally, it outlines strategies and district-level action plans to bolster family planning initiatives and reduce higher-order births, aiming for overall population stabilization.