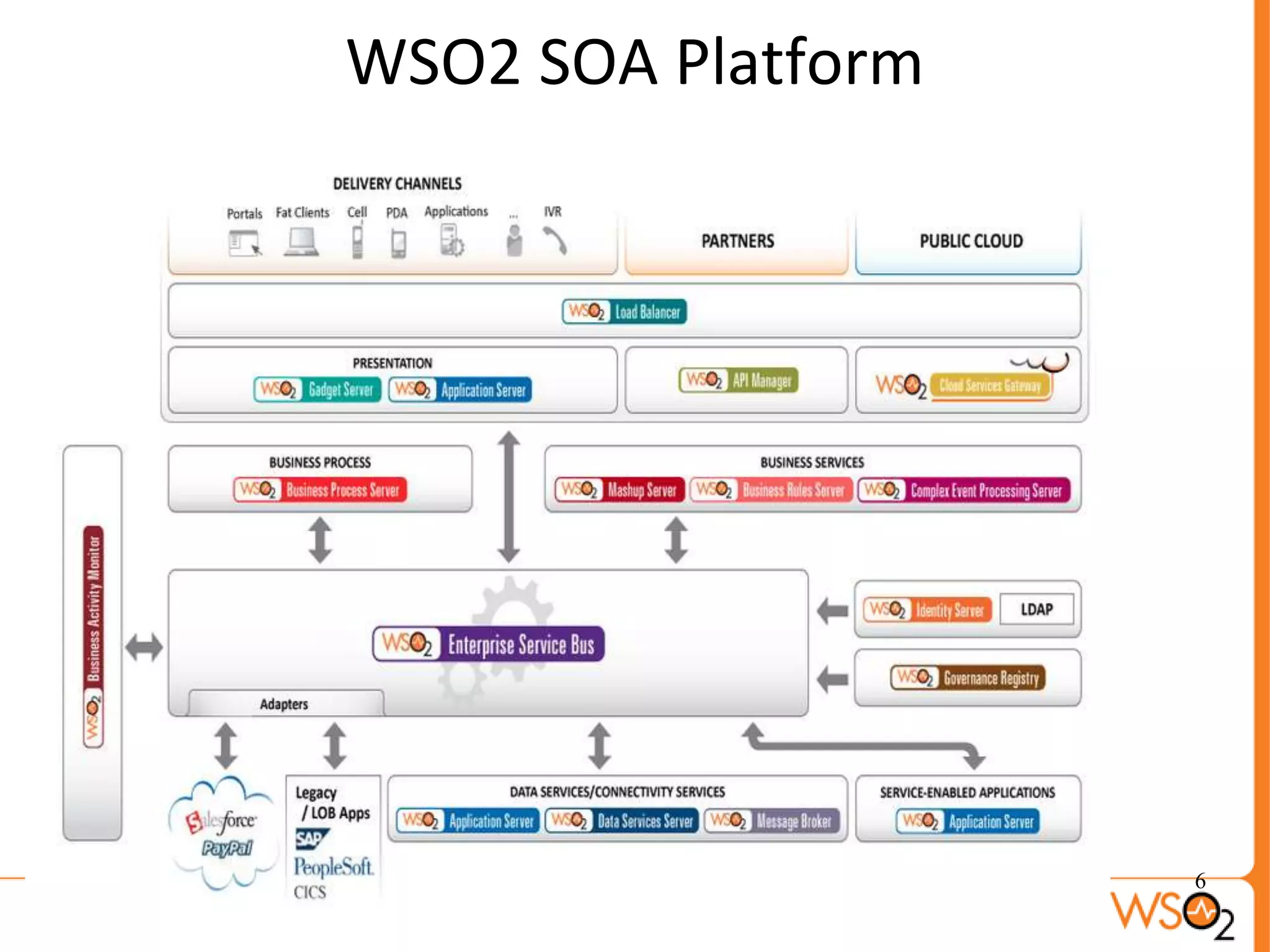
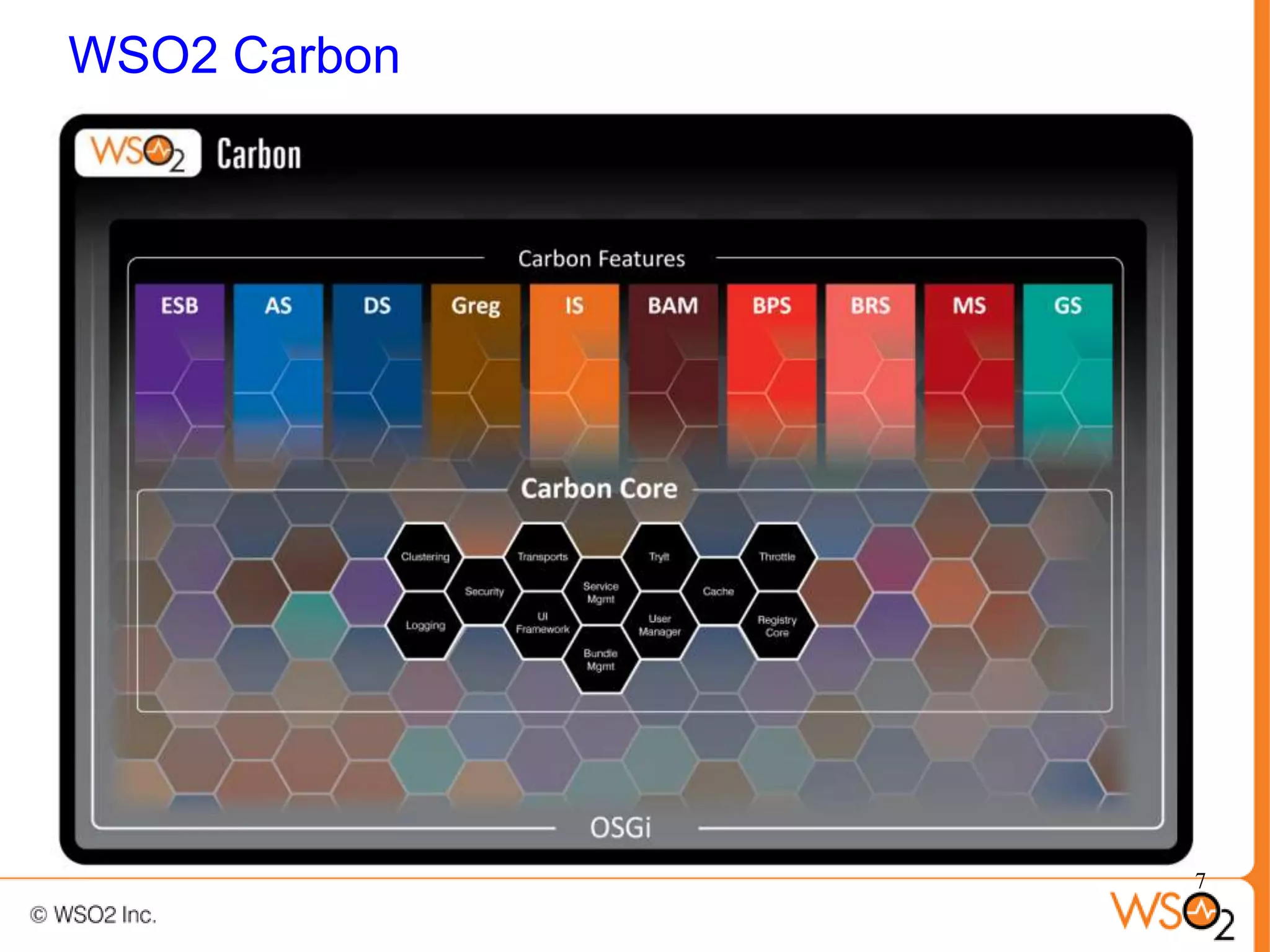
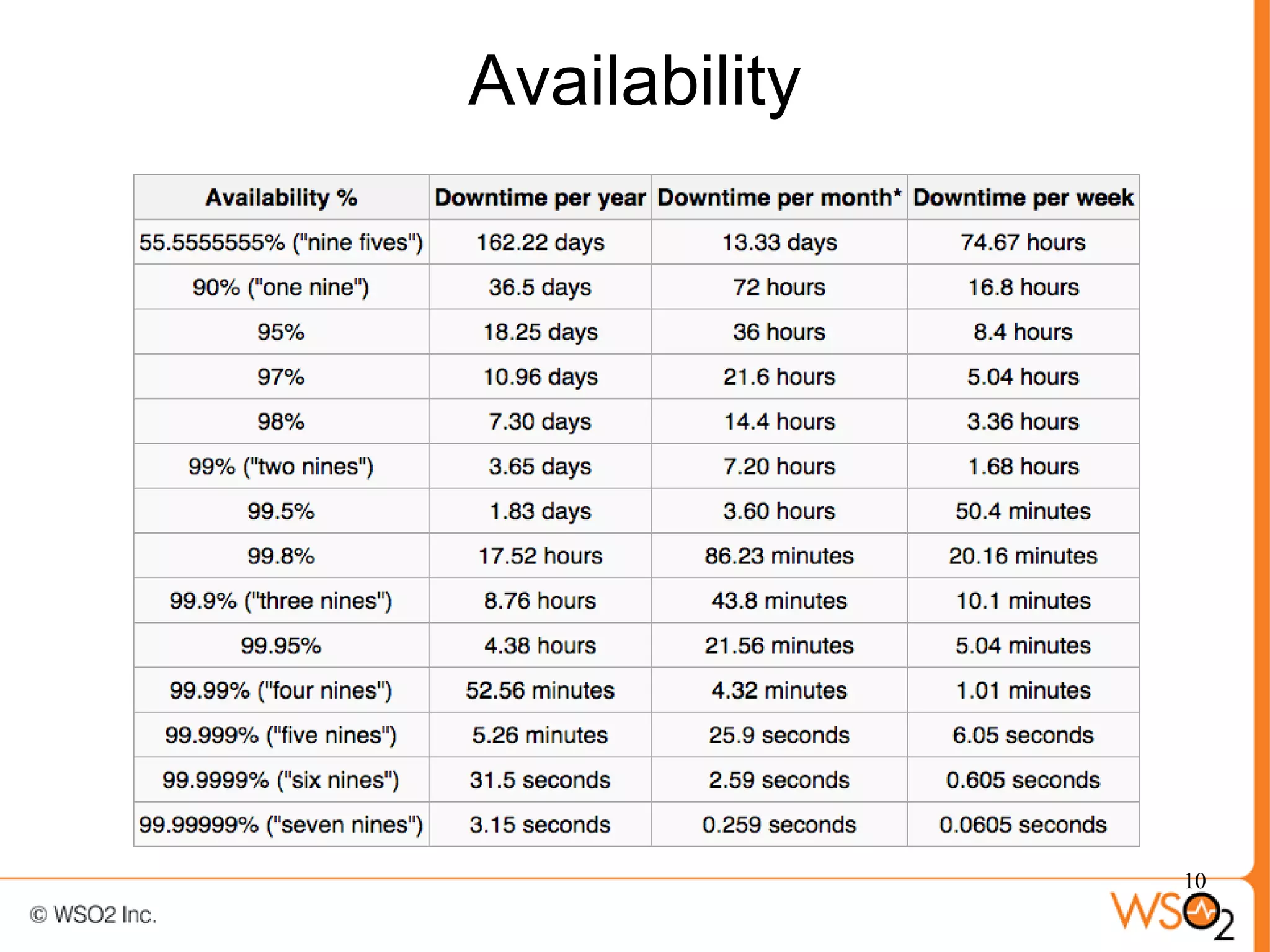
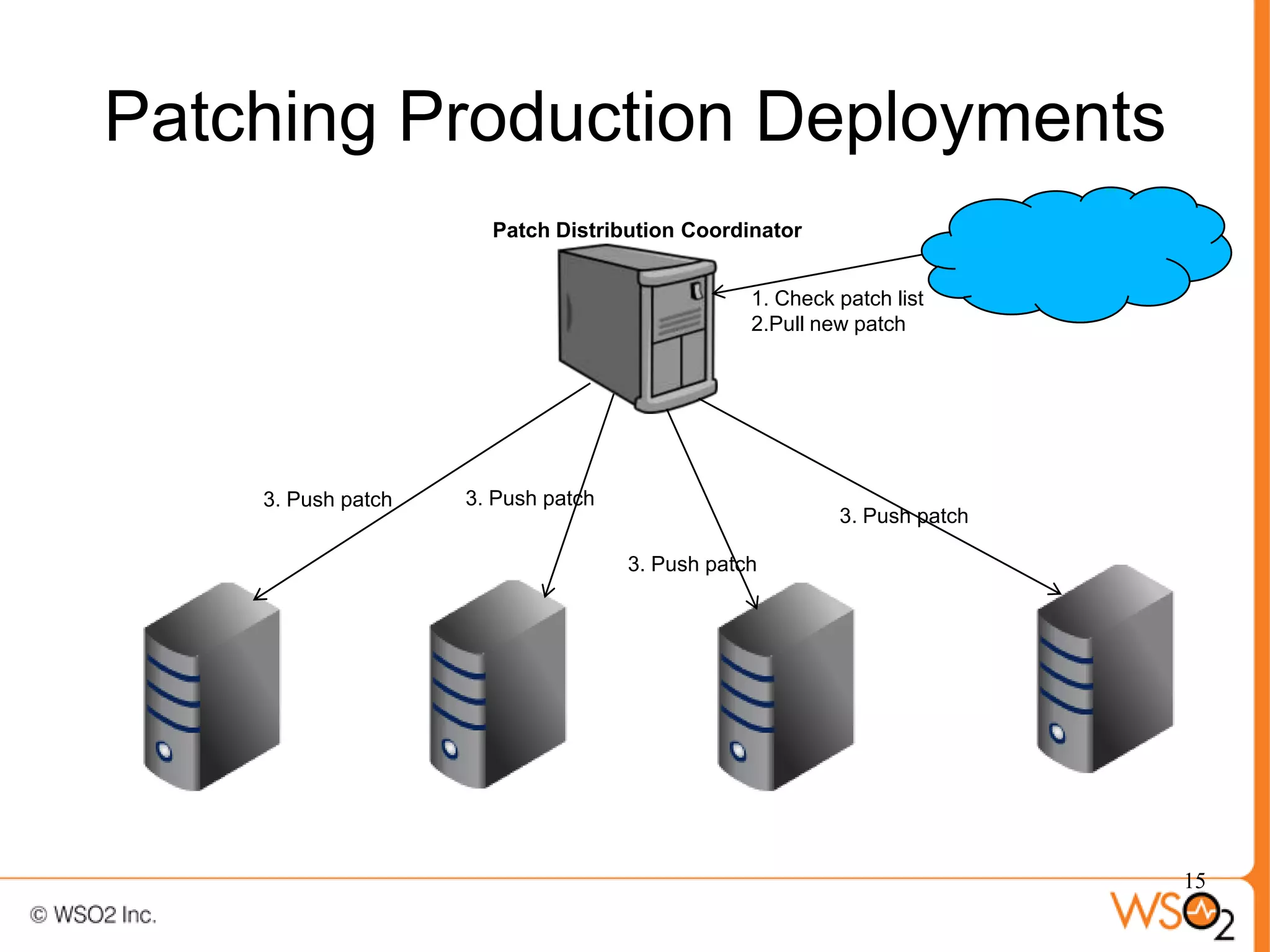
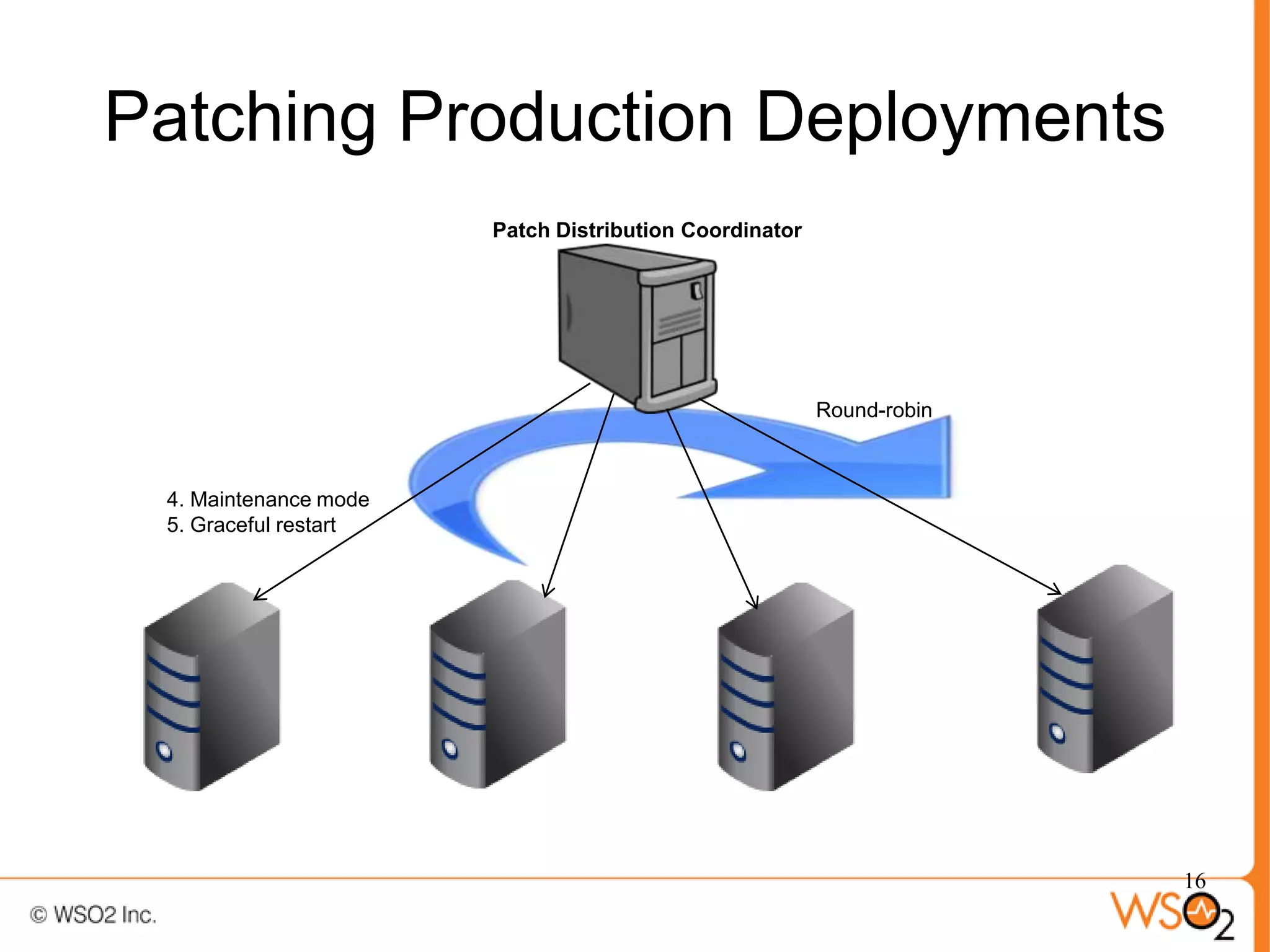
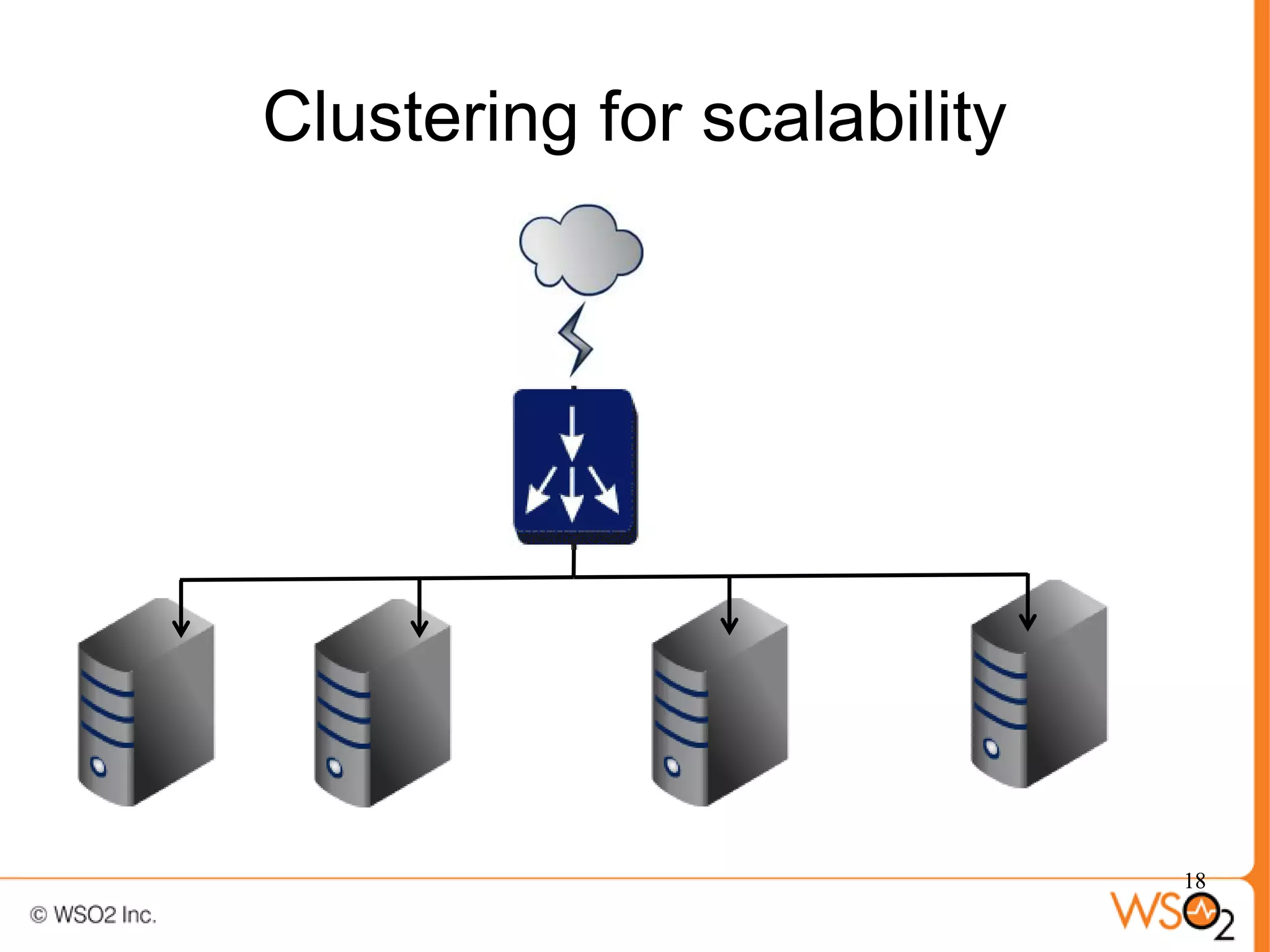
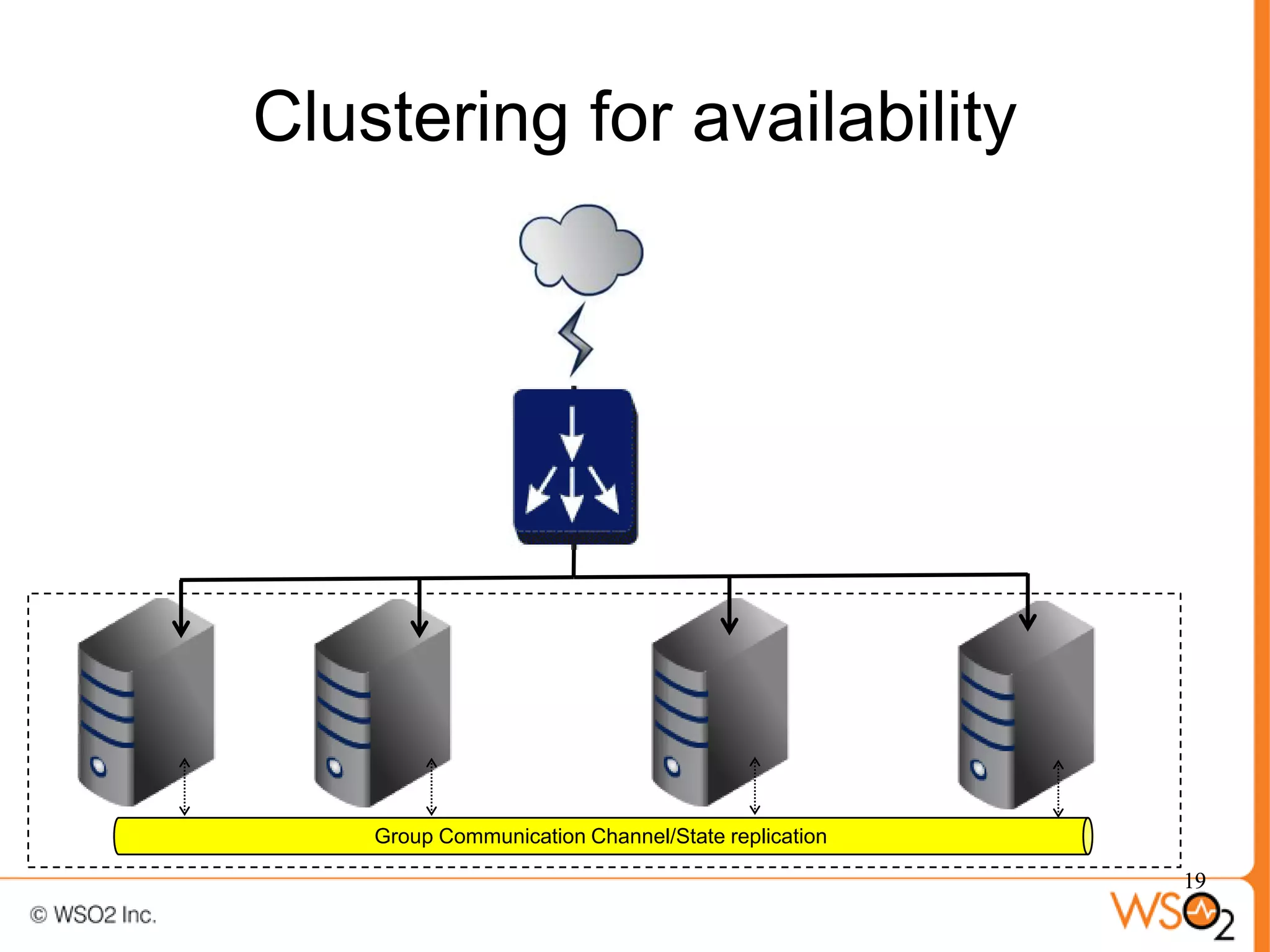
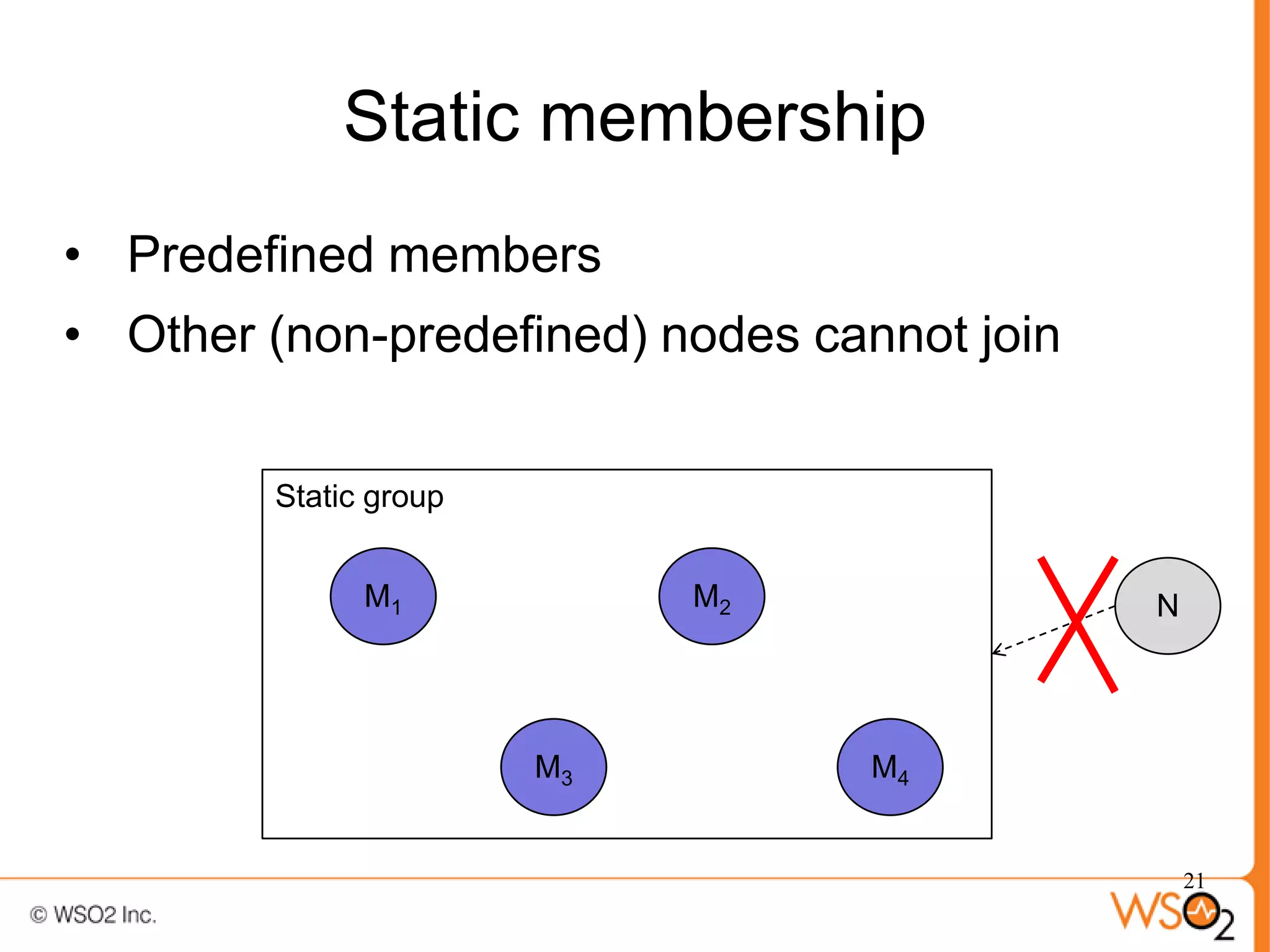
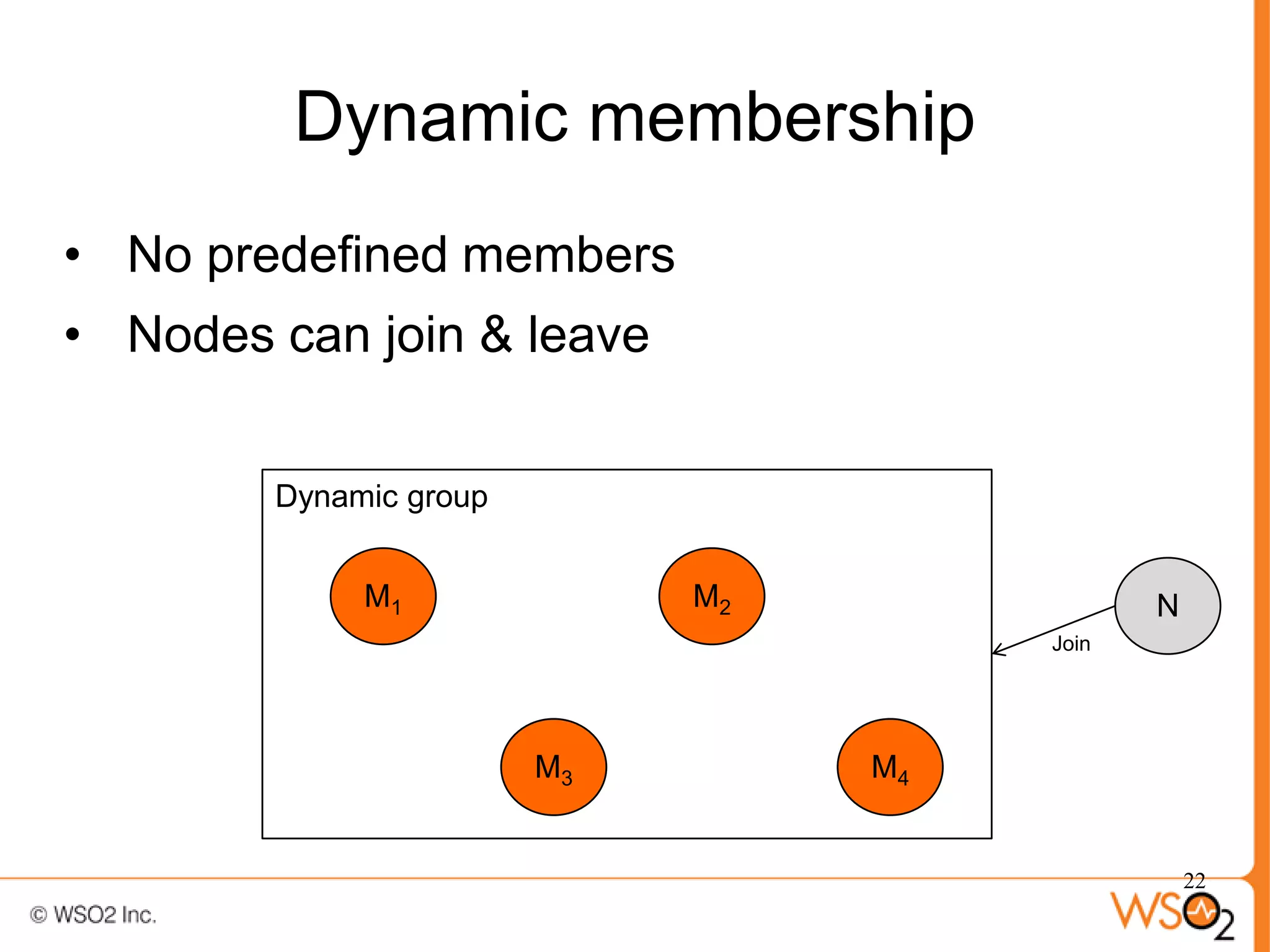
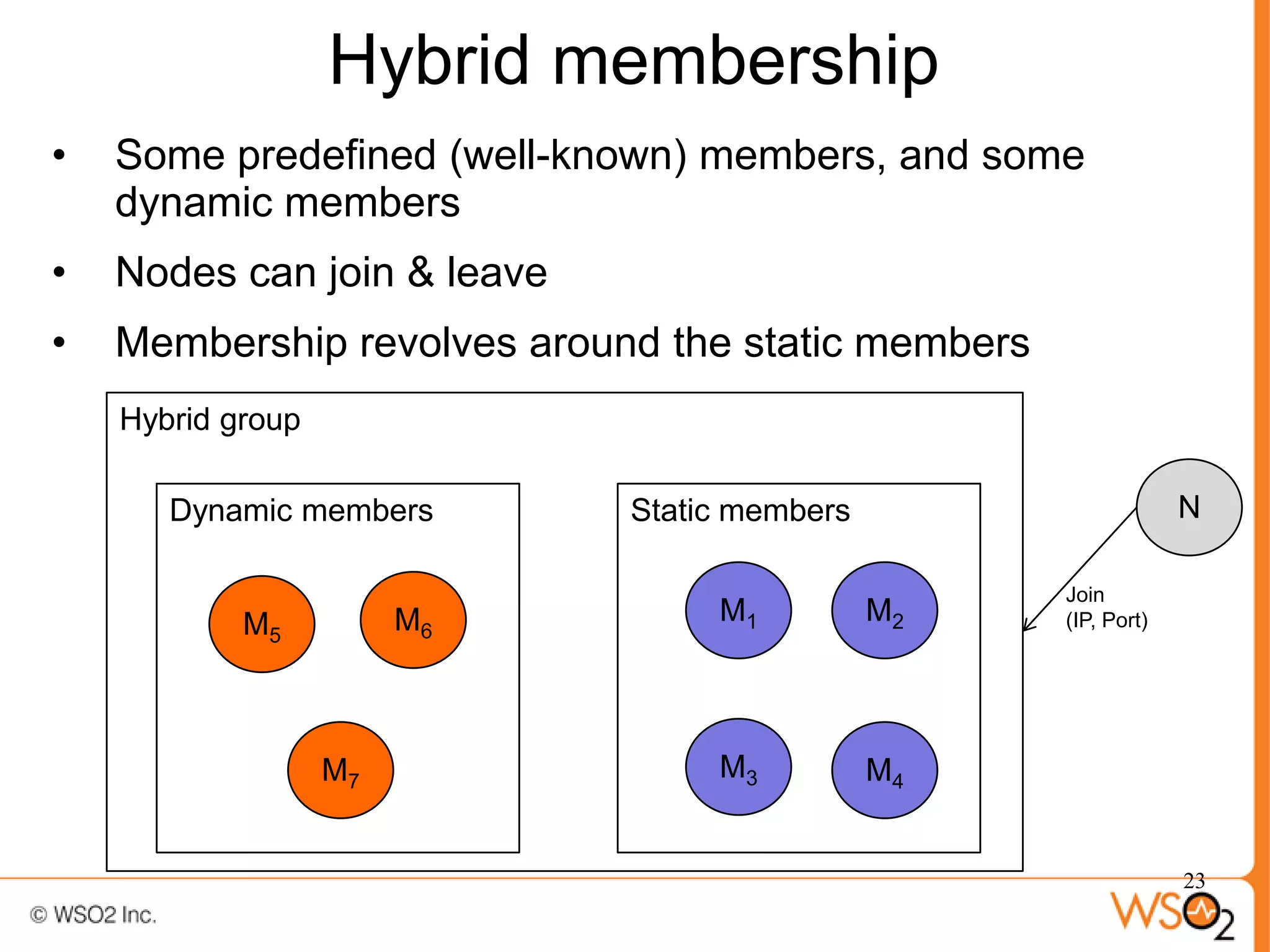
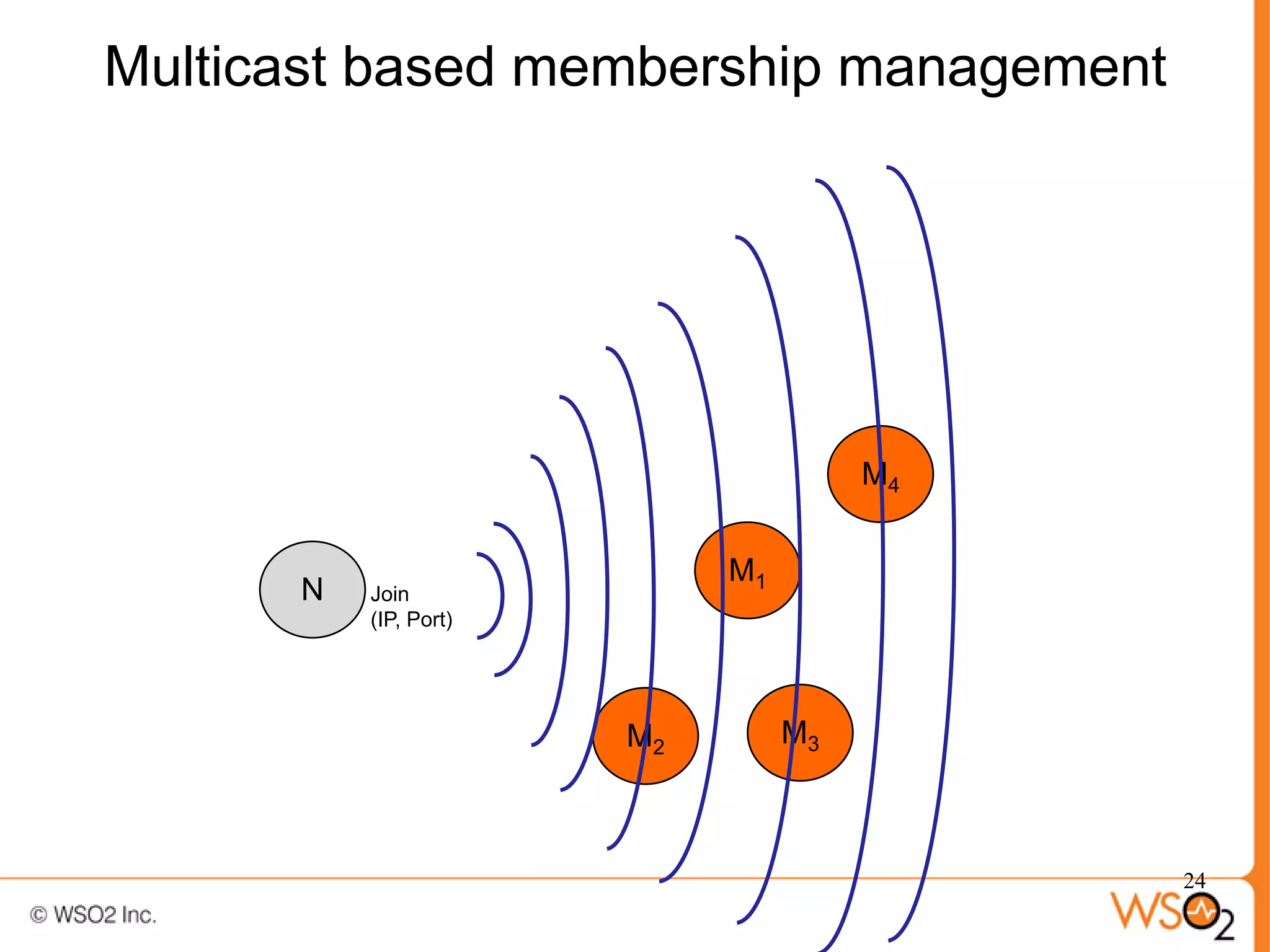
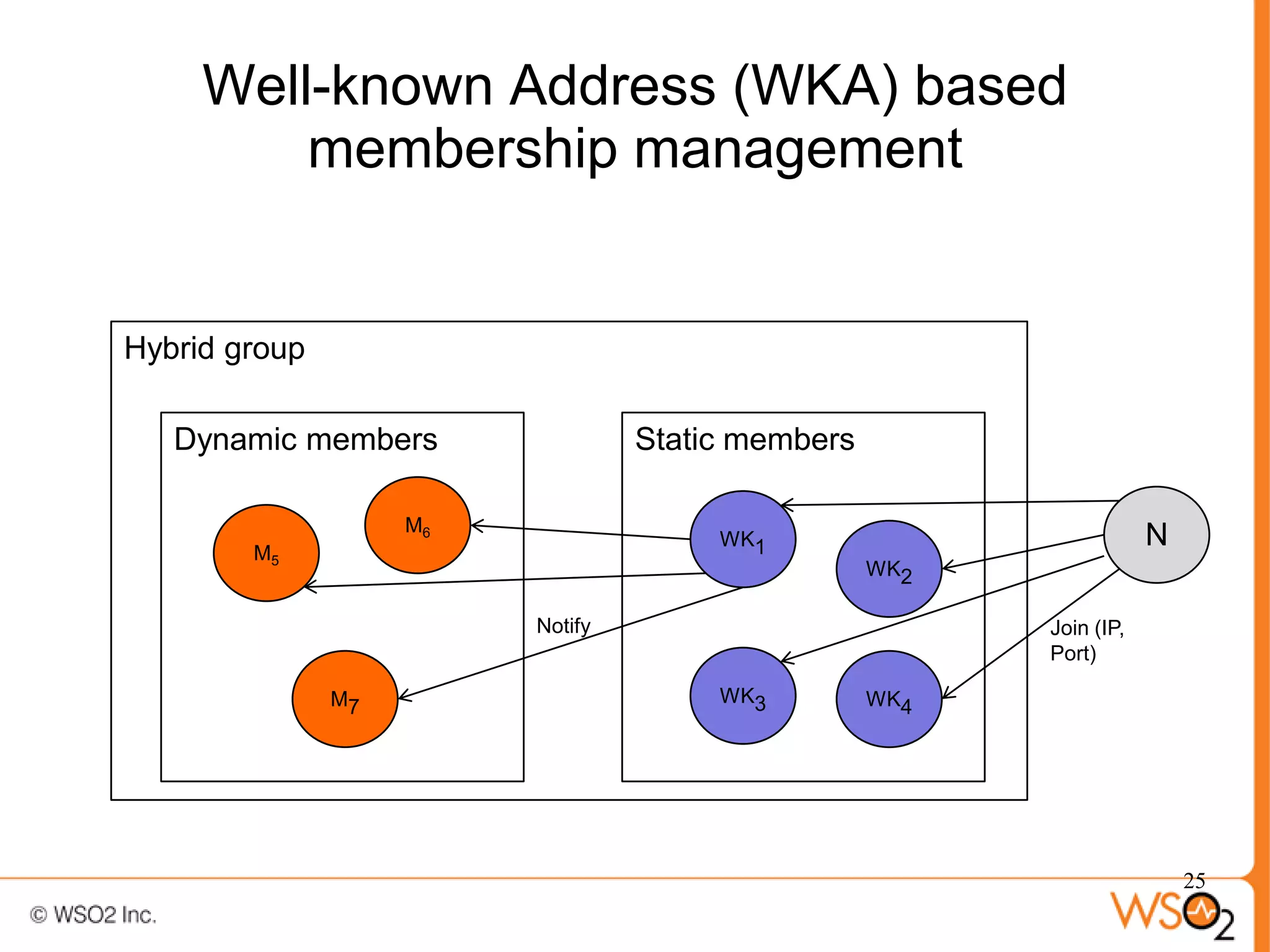
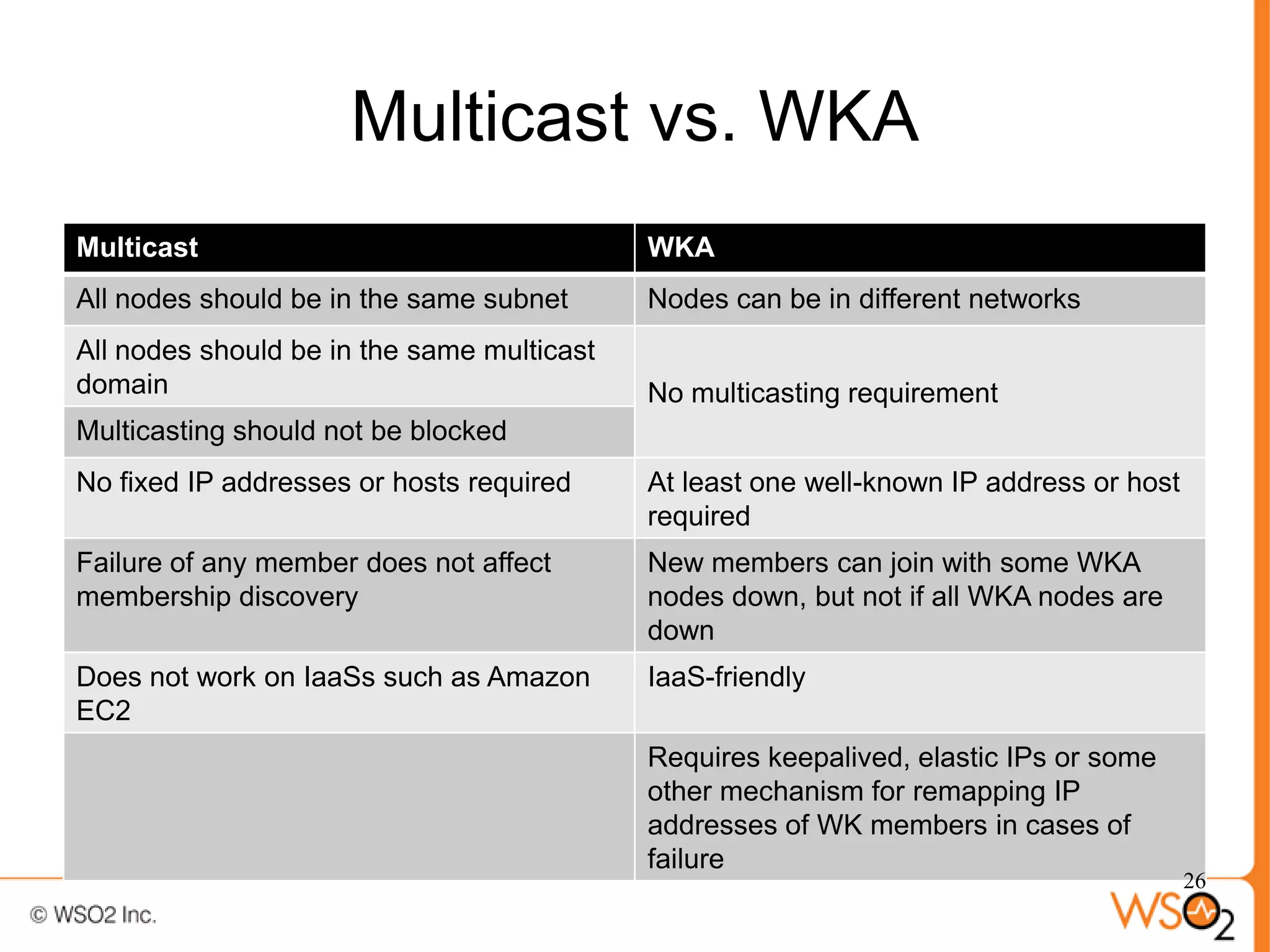
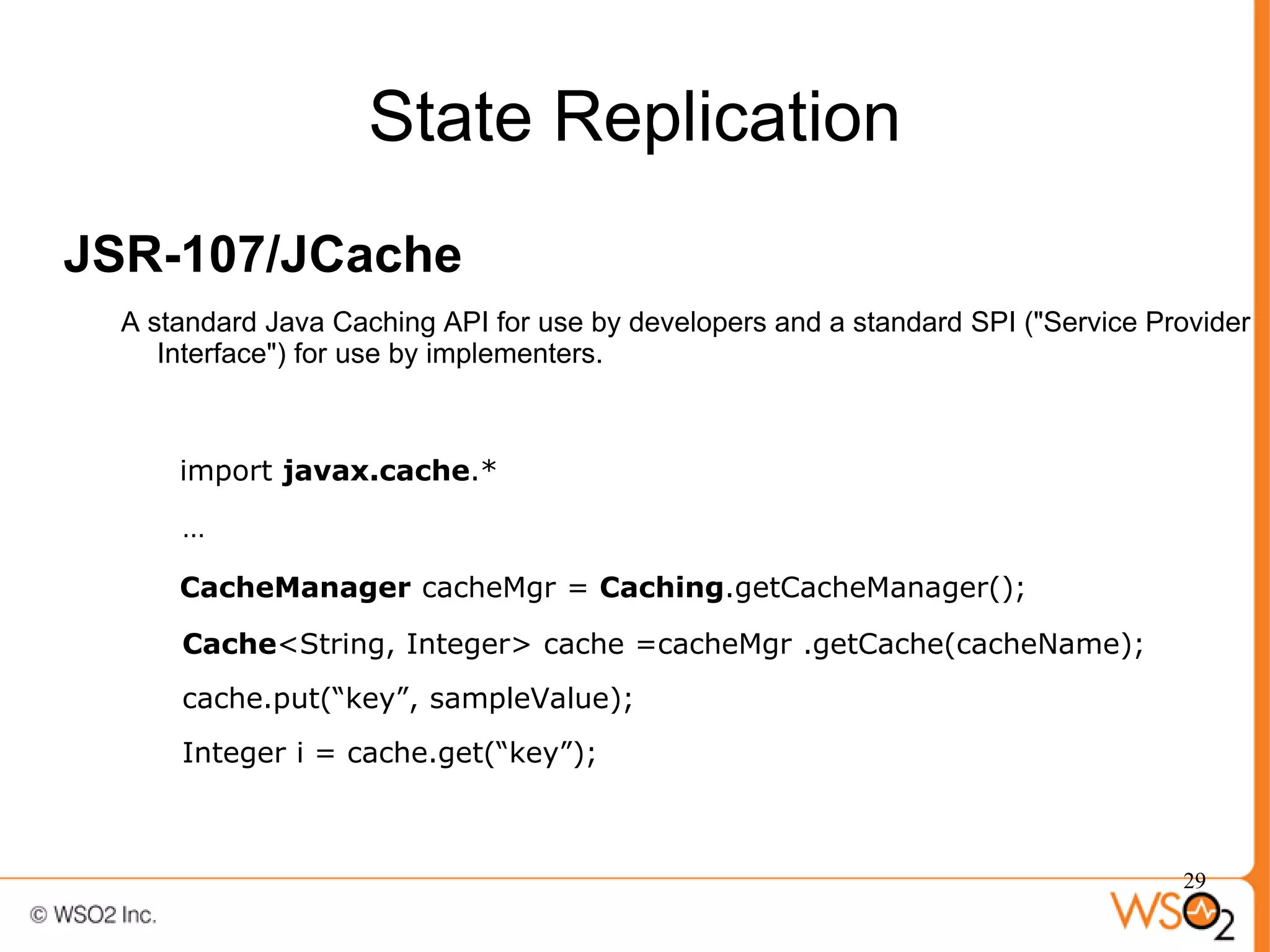
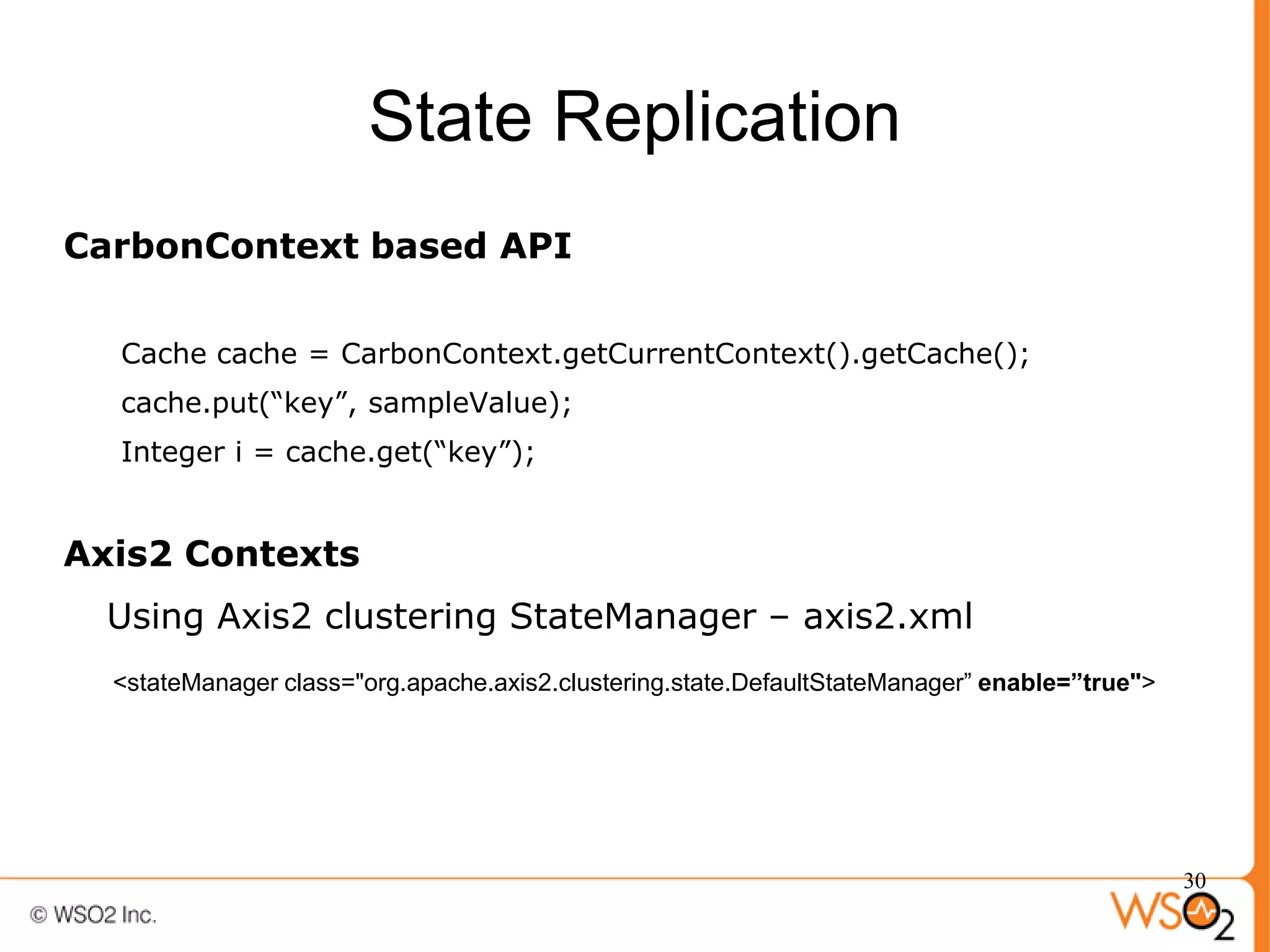
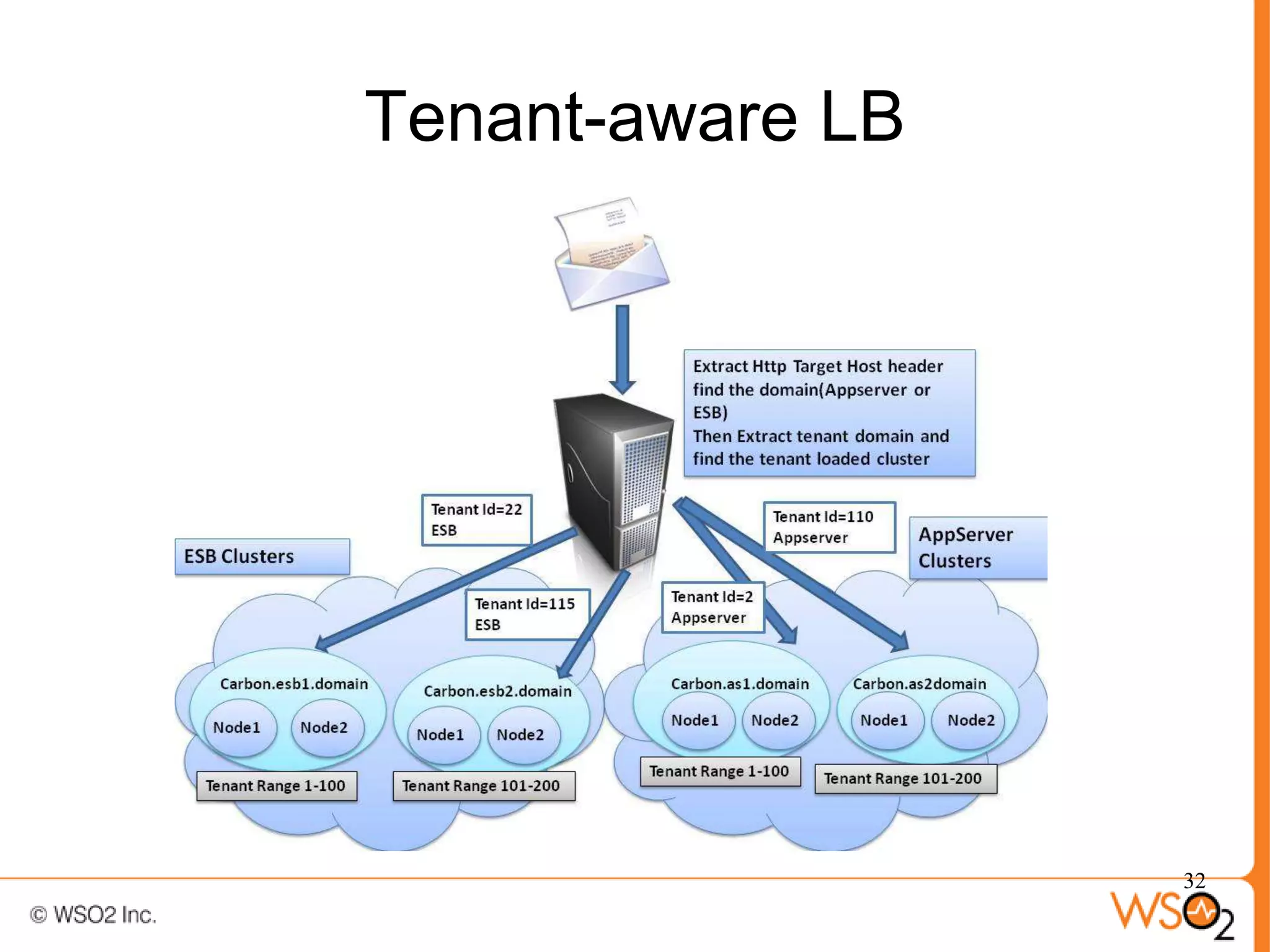
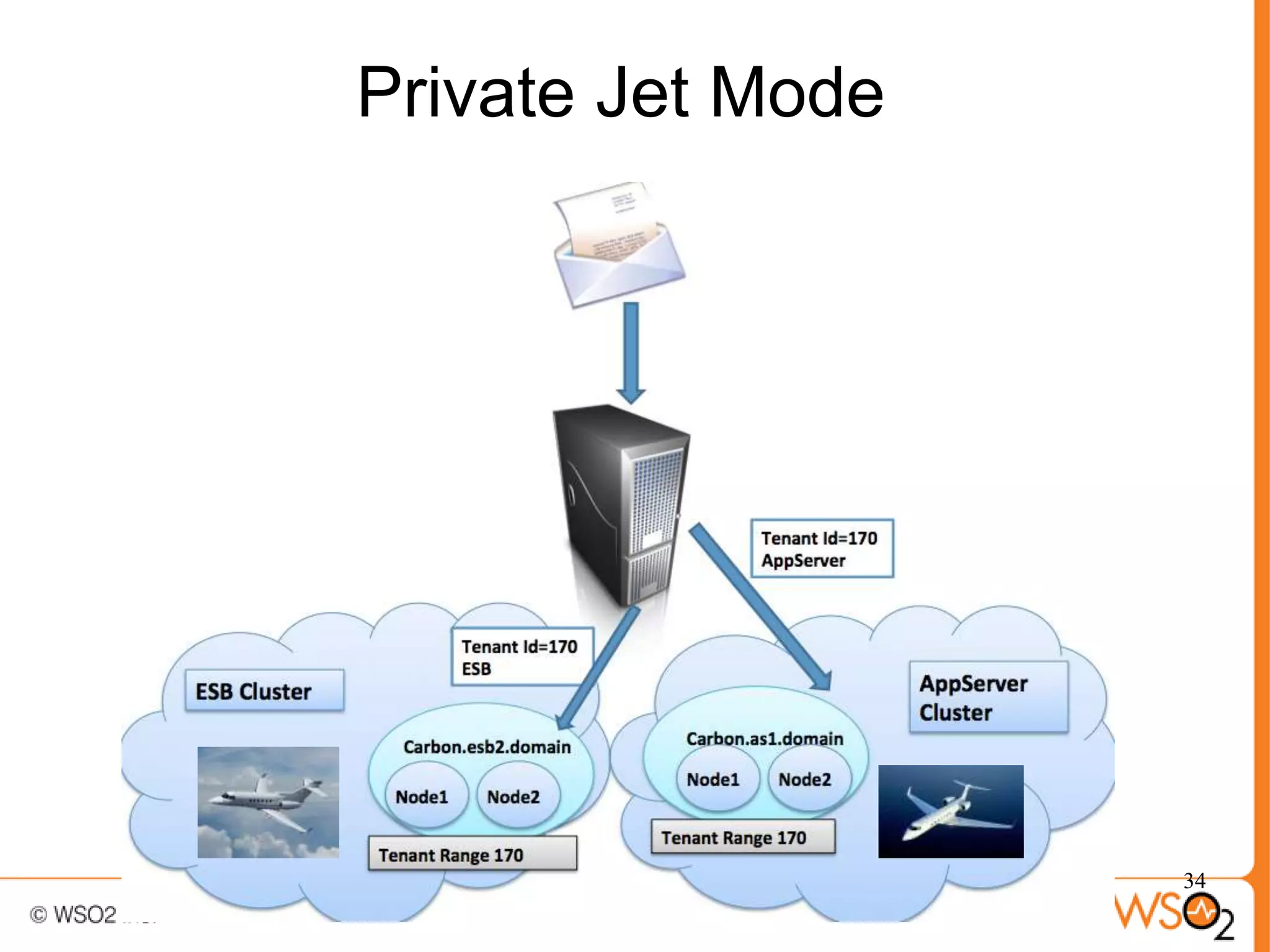
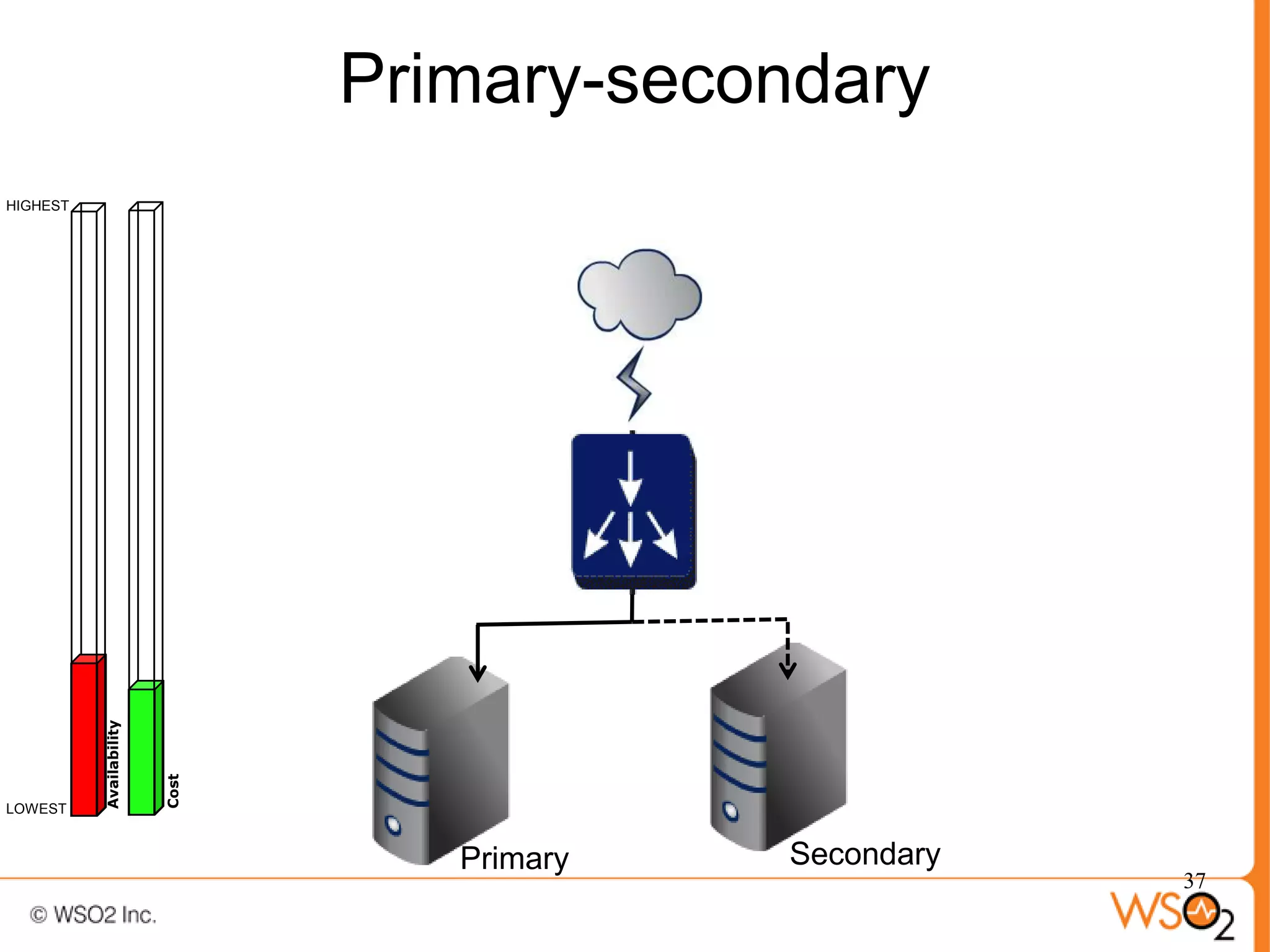
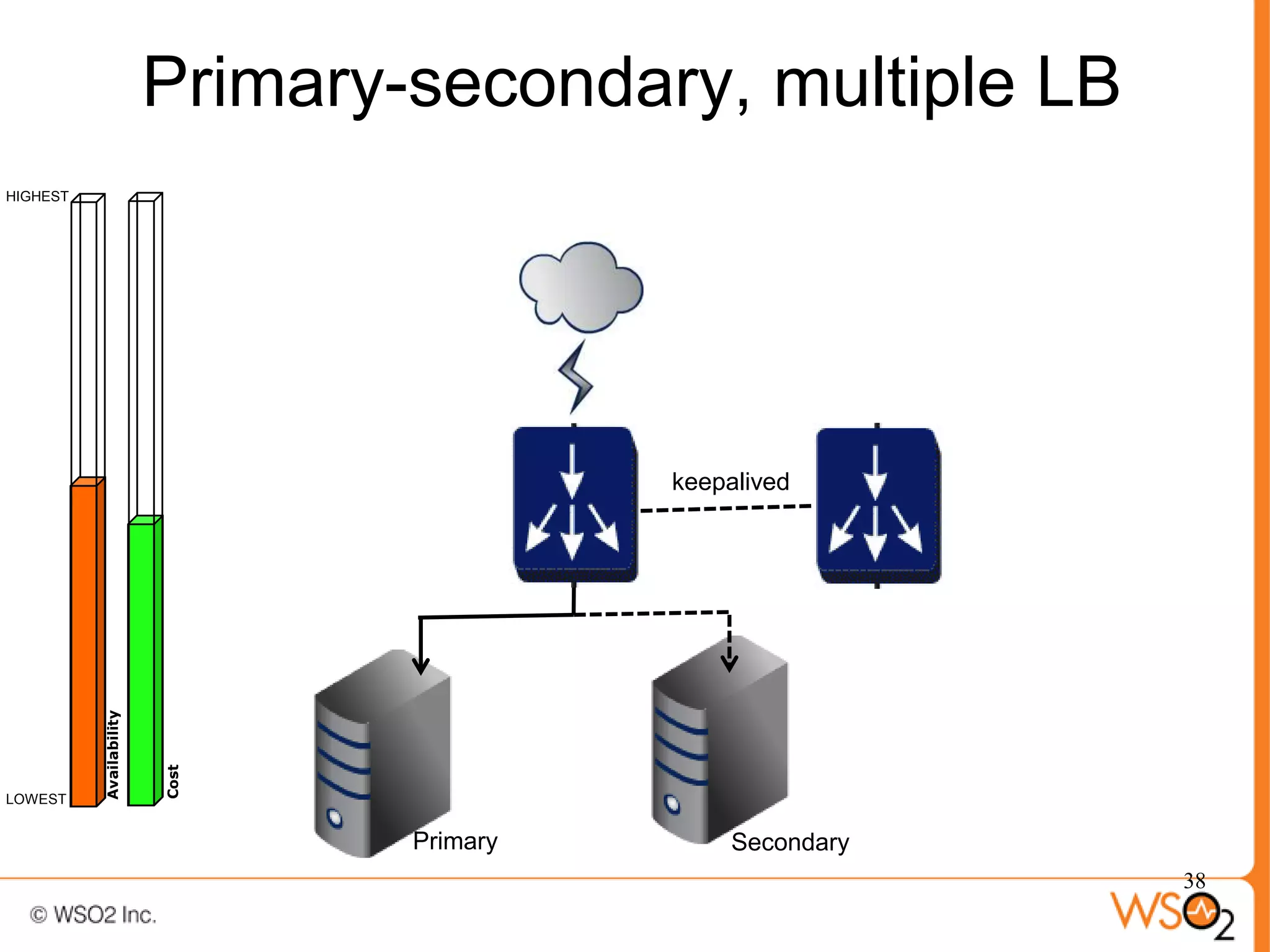
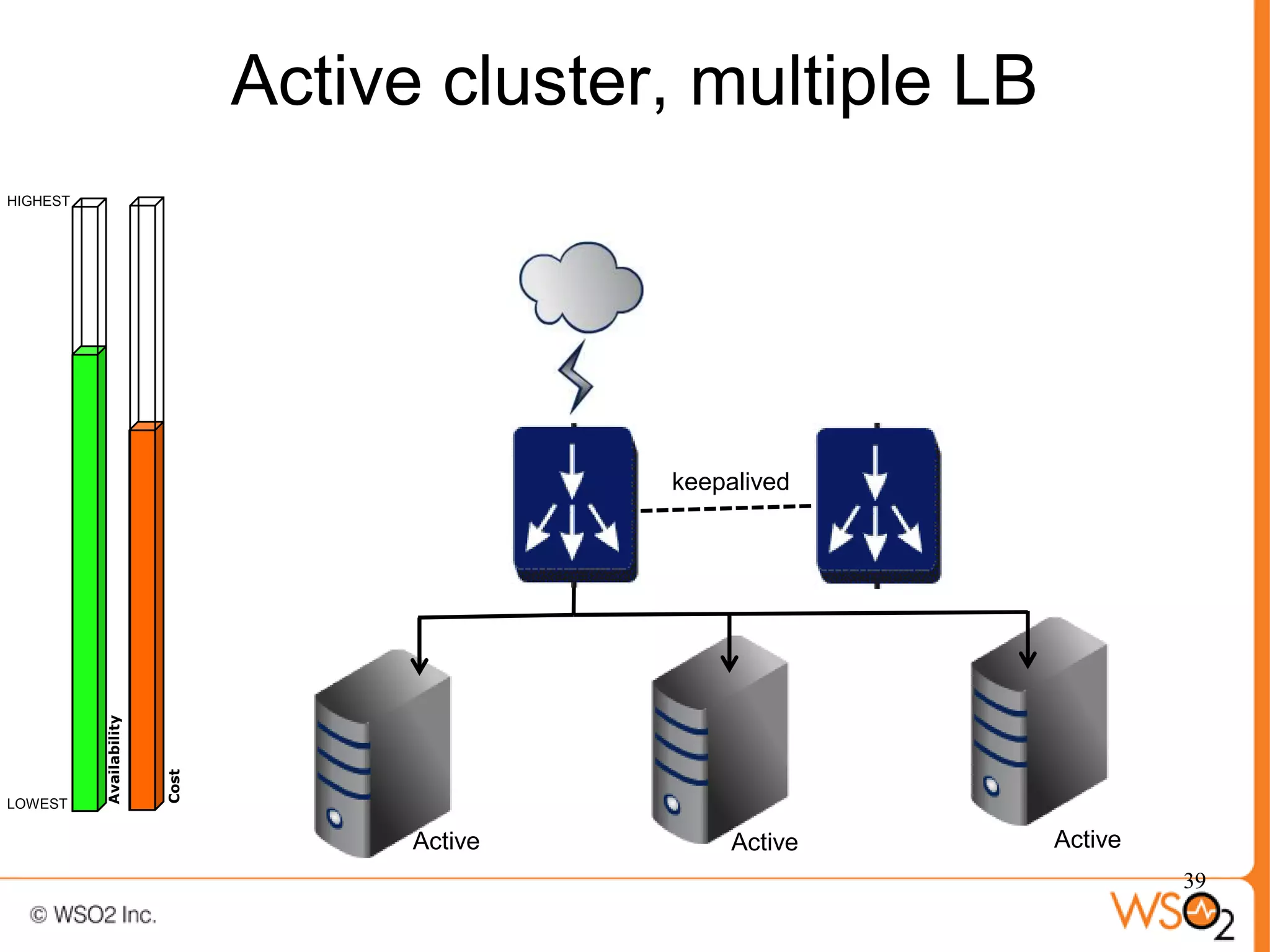
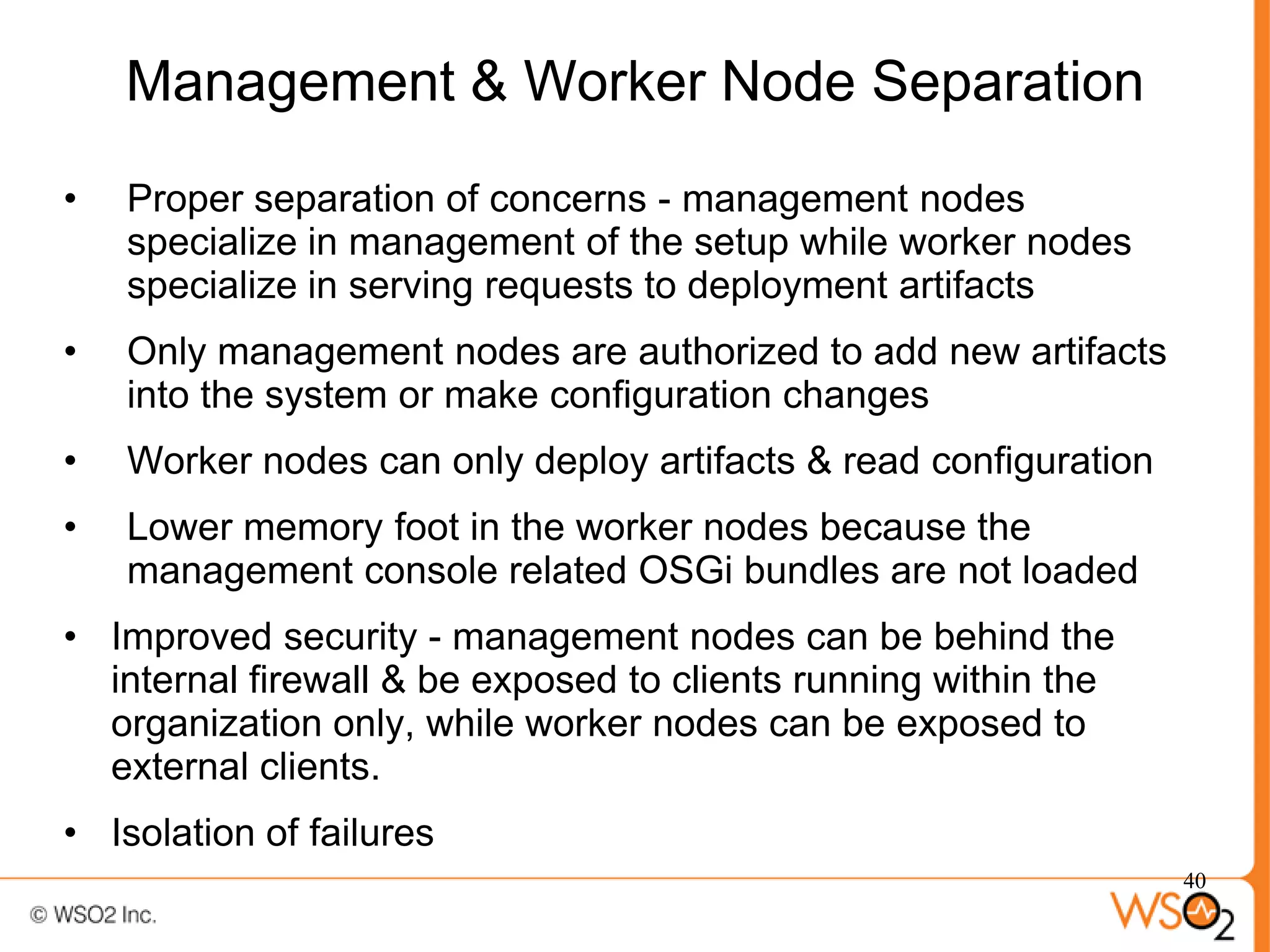
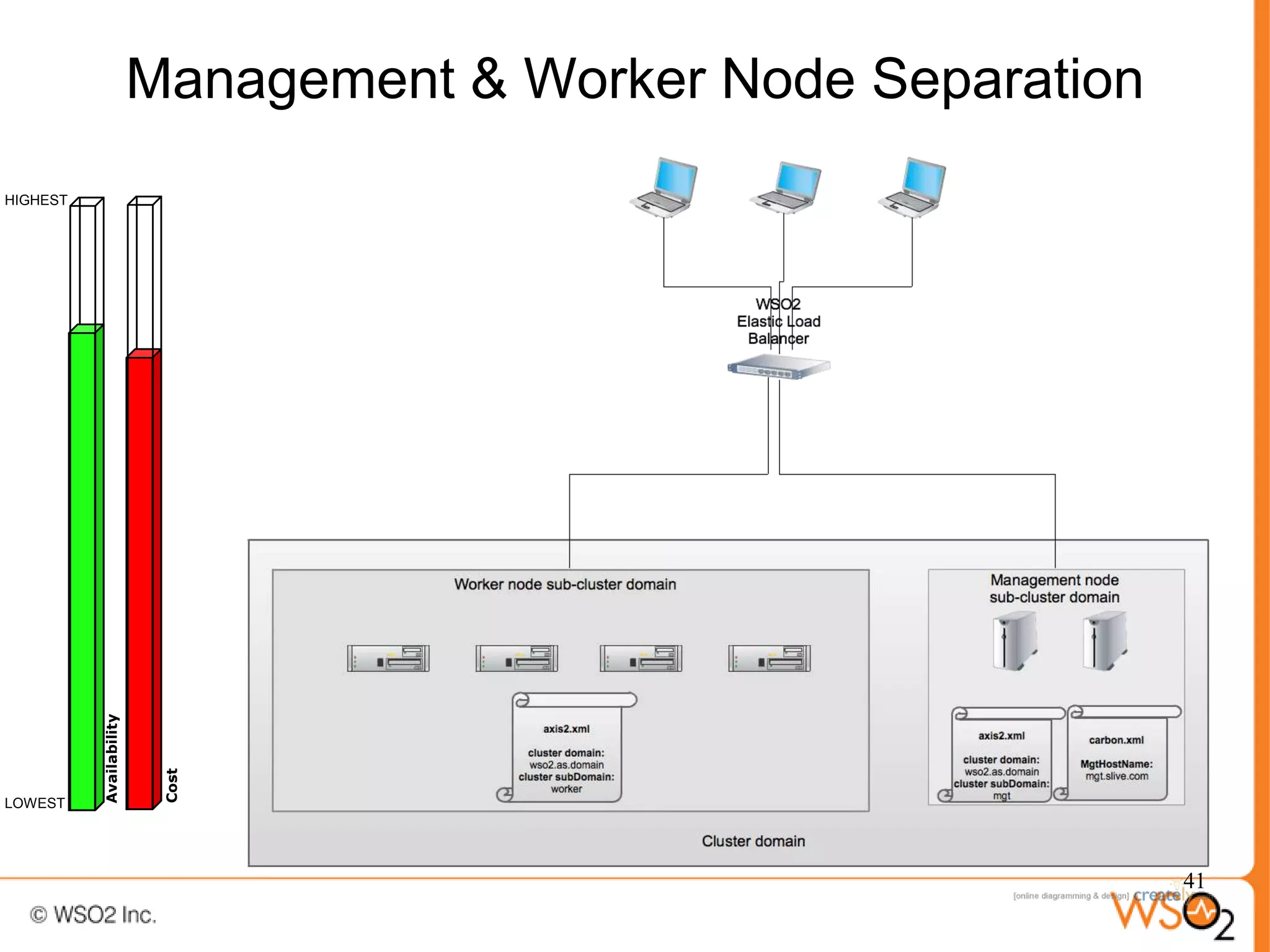
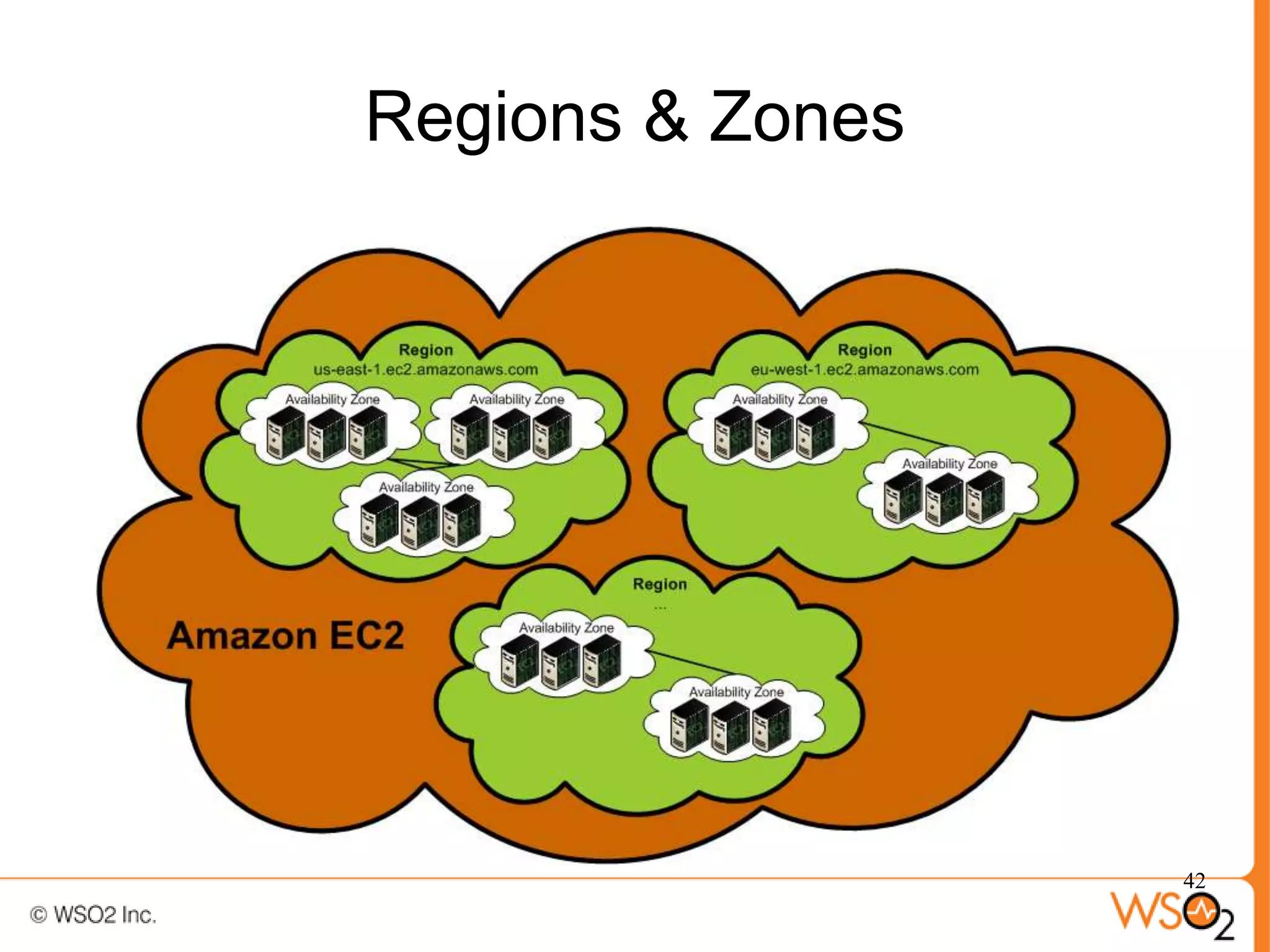
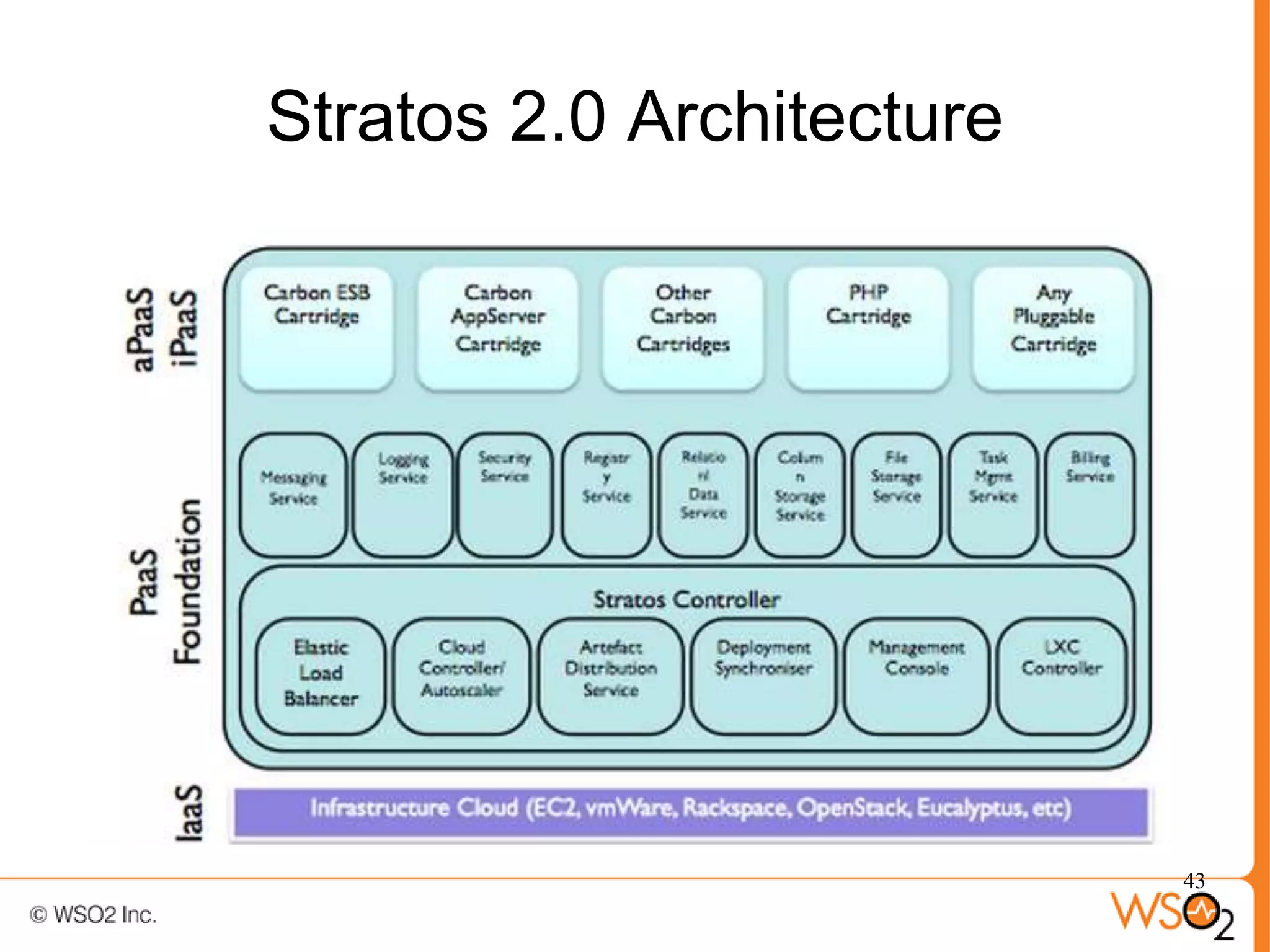
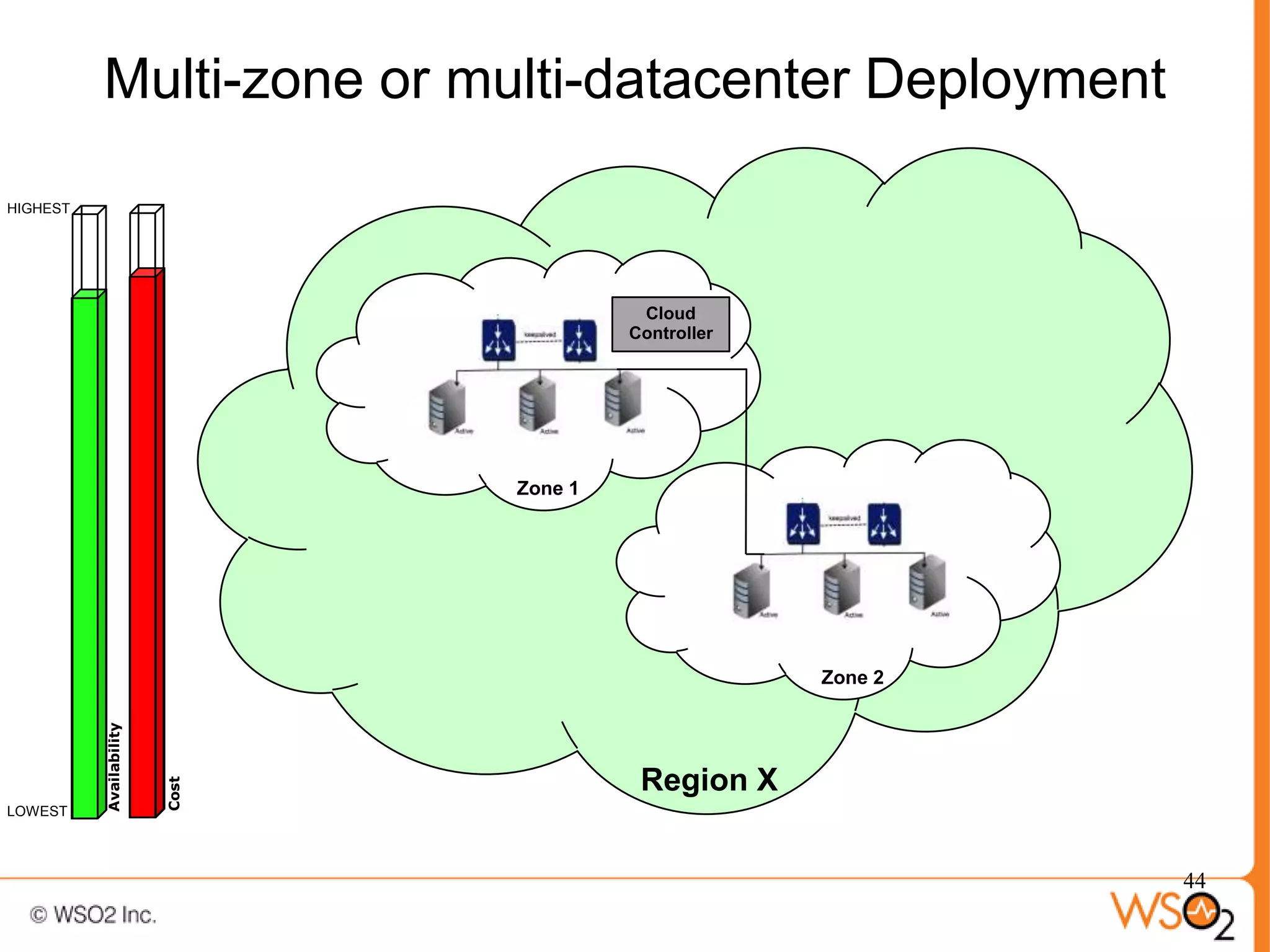
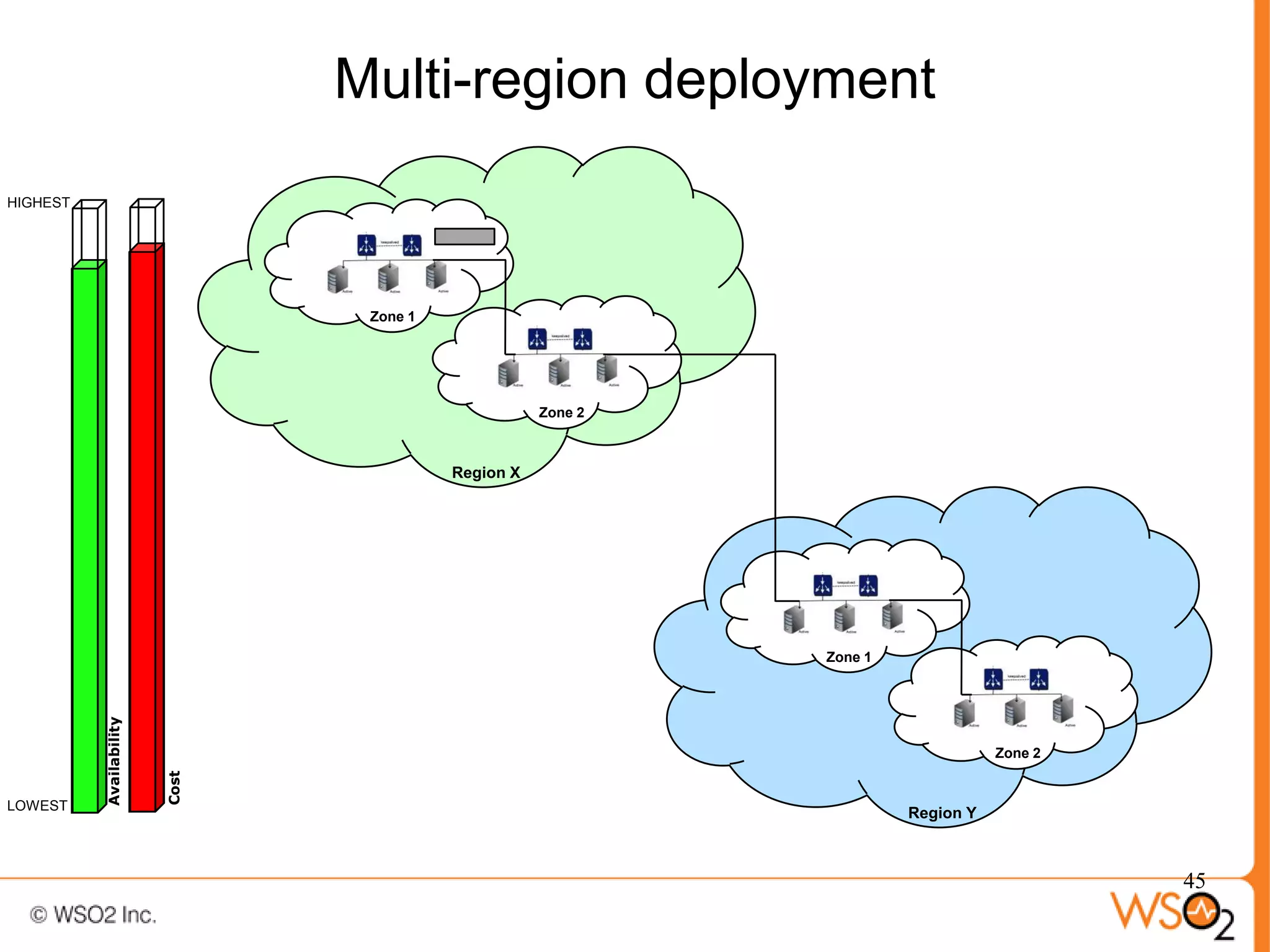
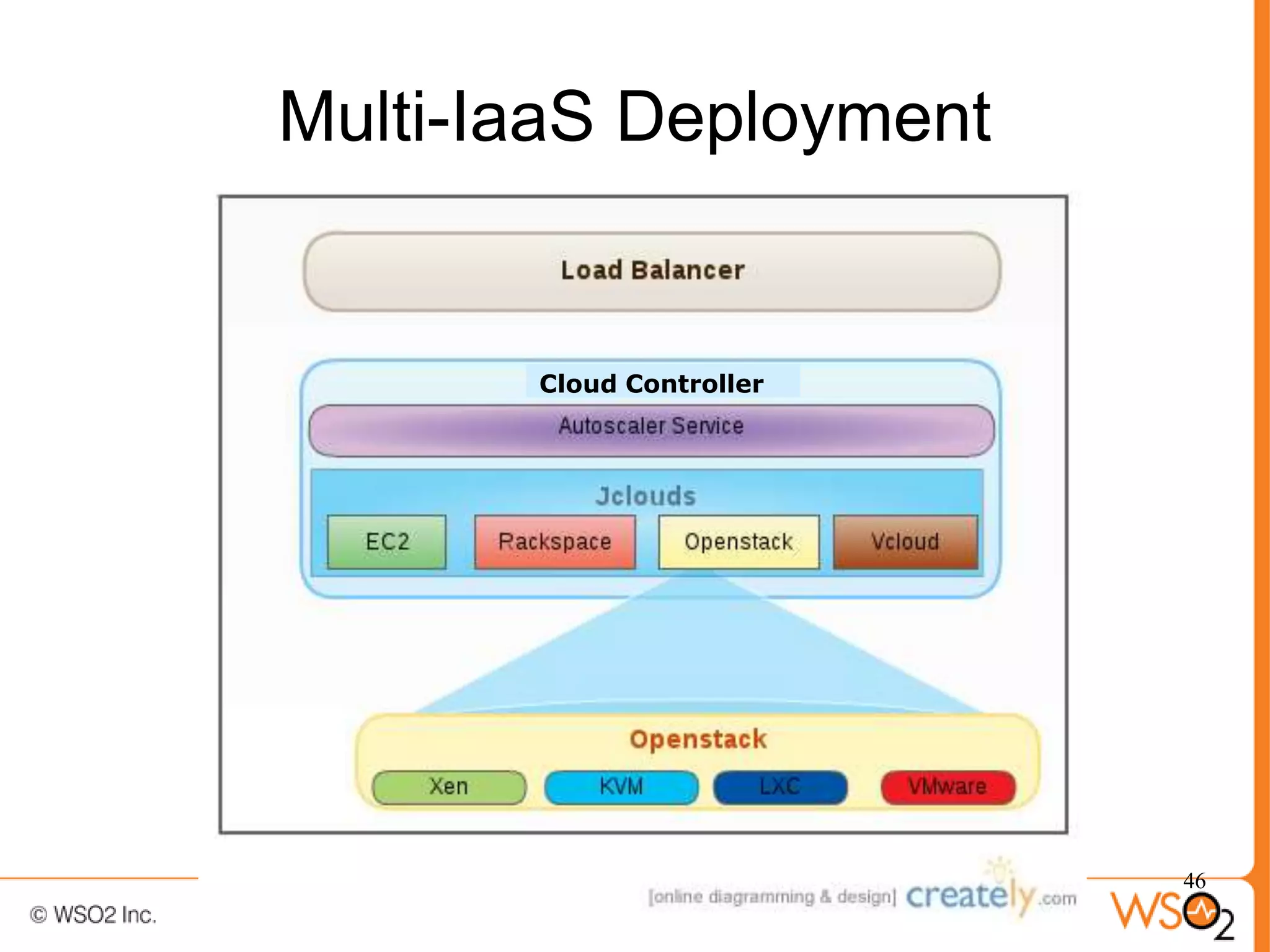
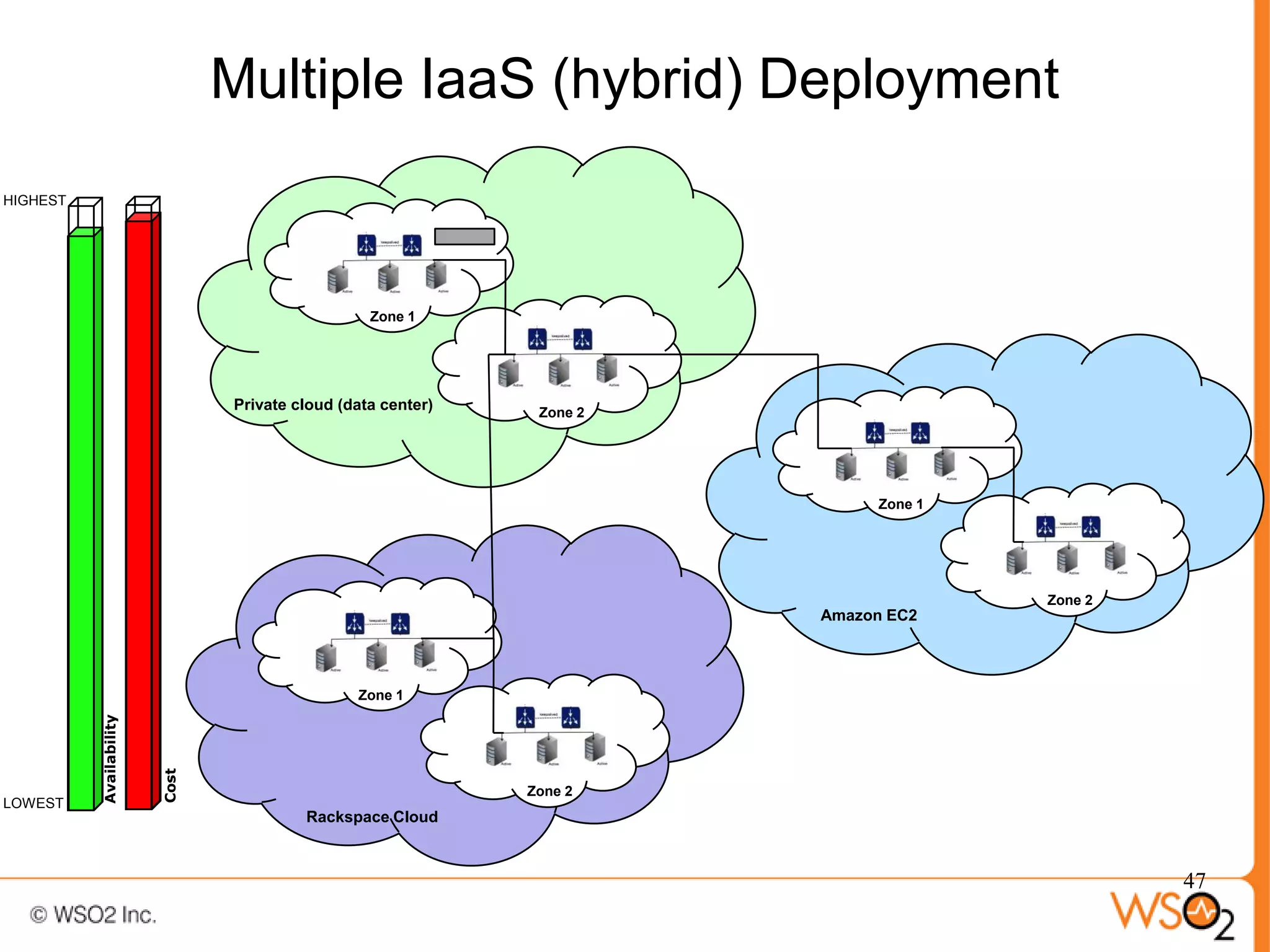
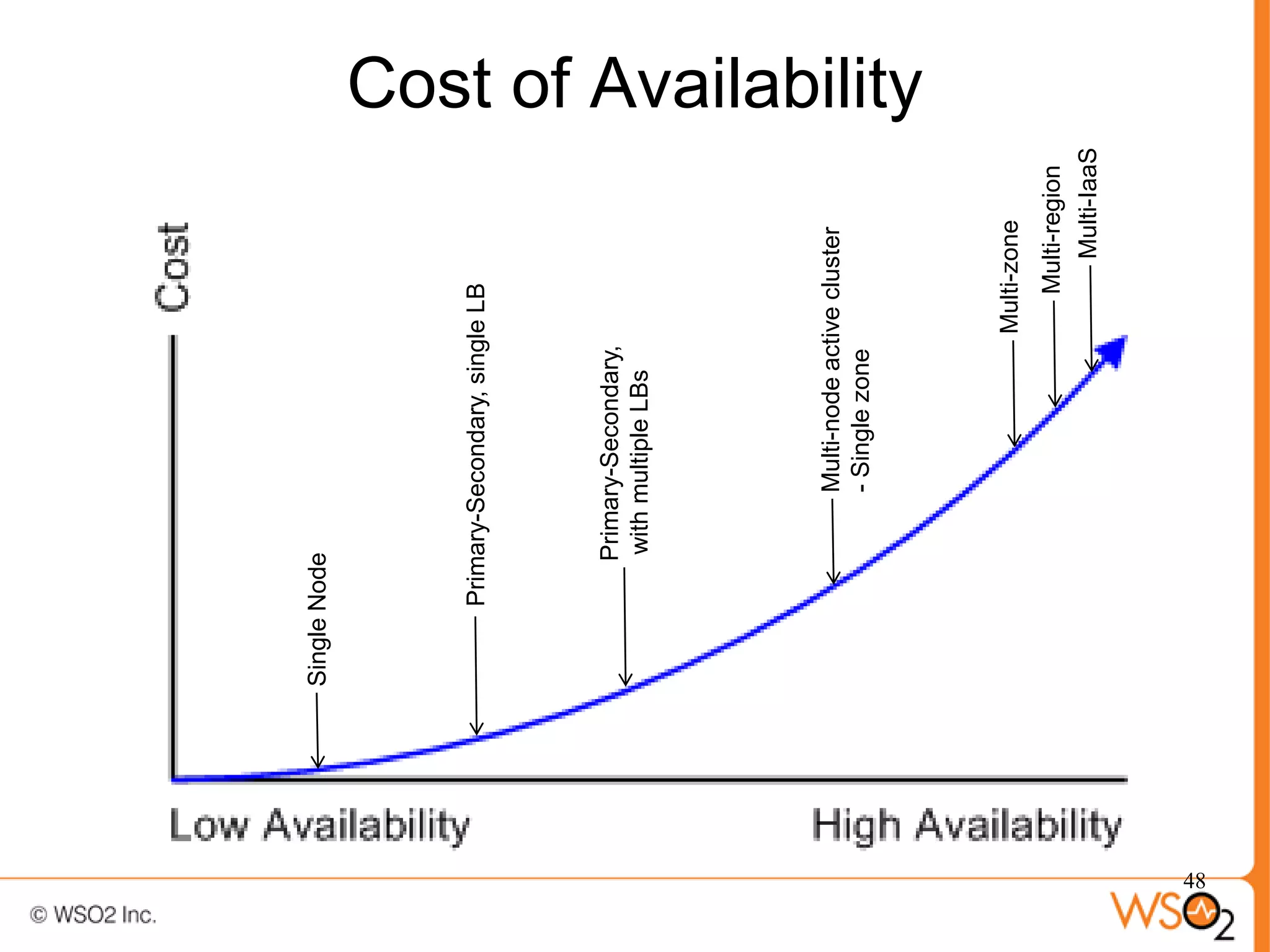
The document discusses strategies for achieving high availability in WSO2 architecture, addressing the importance of continuous operation and redundancy techniques. It describes WSO2 offerings, including Carbon and Stratos platforms, which provide a consistent architecture for both on-premise and cloud deployments, emphasizing the elimination of single points of failure. The presentation also covers clustering methods, load balancer configurations, and the cost versus benefit tradeoffs concerning system availability.