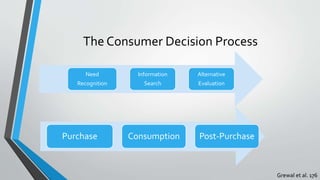
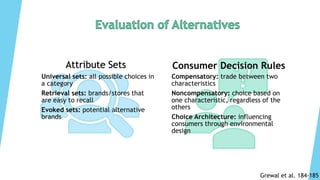
The document summarizes the consumer decision process, which consists of 5 stages: need recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, purchase/consumption, and post-purchase evaluation. It describes factors that influence each stage such as functional vs. psychological needs, external vs. internal information searches, attribute and decision rules for evaluation, and outcomes of satisfaction and loyalty. Recapping, the consumer decision process model outlines the comprehensive steps consumers go through in making purchase decisions.