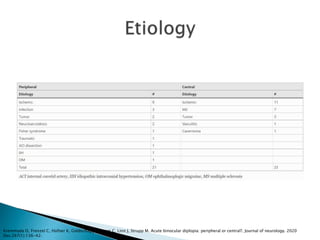
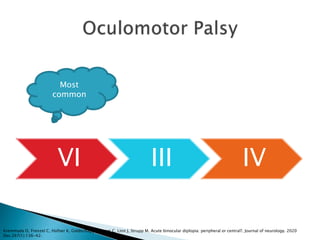
Binocular diplopia is the perception of two images of a single object that disappears when closing either eye. It is most commonly caused by an abducens nerve palsy. The most common etiology is microvascular ischemia. Ninety-eight percent of cases resolve spontaneously.