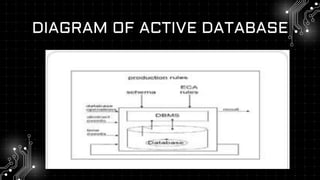
An active database automatically responds to data changes using triggers and rules, enhancing functionality beyond traditional databases. It features support for event-driven architectures, real-time data management, and automation but also introduces complexities in implementation and maintenance. While it provides benefits such as immediate updates and improved data integrity, it may also lead to performance overhead and potential over-automation issues.