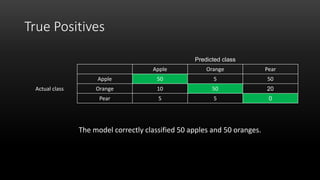
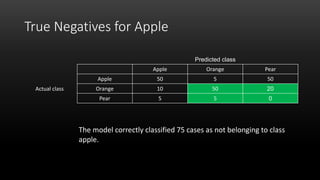
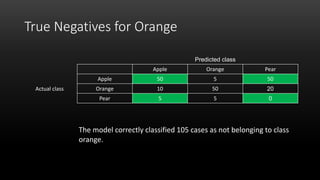
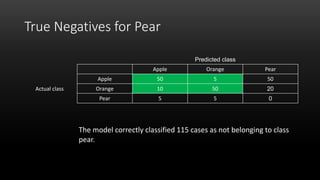
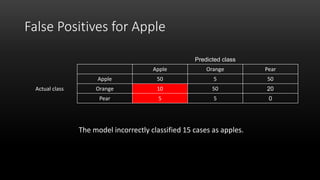
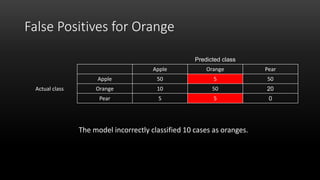
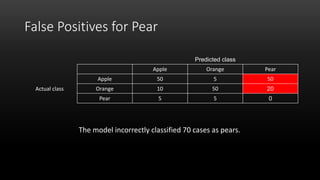
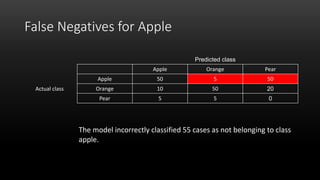
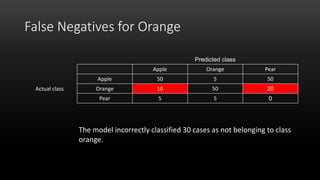
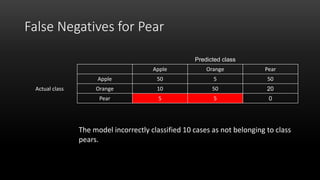
A confusion matrix is a table that shows the performance of a classification model by listing the true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives. It displays how often the model correctly or incorrectly classified observations into their actual classes. The document provides an example confusion matrix for a model classifying apples, oranges, and pears, showing the number of observations the model correctly and incorrectly classified into each class.