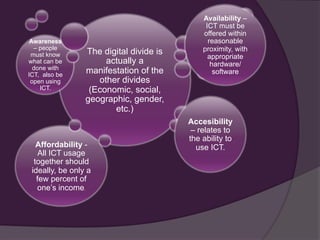
This document discusses the history and development of CALL (Computer Assisted Language Learning) in three phases: 1) Behavioristic CALL from the 1950s-1970s based on behaviorist learning theories using repetitive drills, 2) Communicative CALL from the 1970s-1980s focusing on using forms communicatively rather than explicitly teaching grammar, and 3) Integrative CALL from the 1990s onward allowing various multimedia and access to the internet. It also discusses the role of ICT in development as an enabler for efficiency, new business opportunities, and transparency, and issues around the digital divide between developing and developed nations related to connectivity, costs, language, and awareness of ICT capabilities.