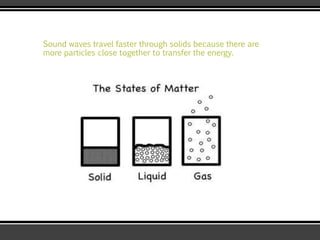
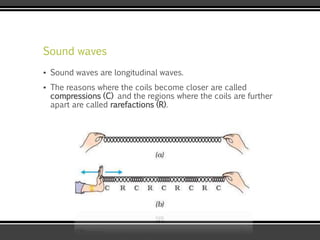
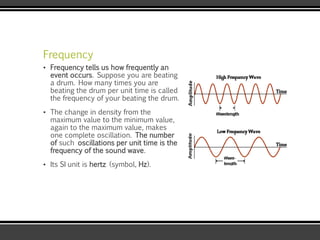
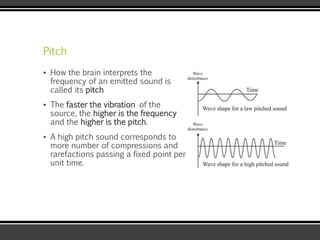
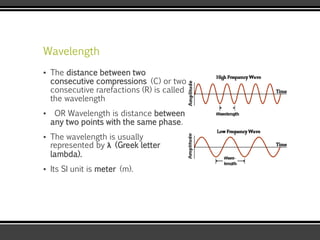
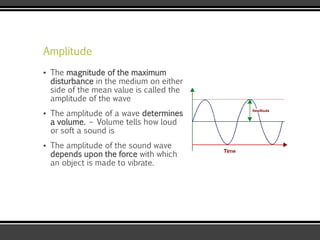
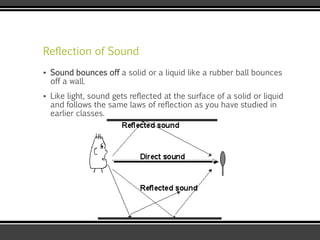
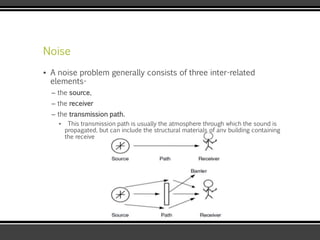
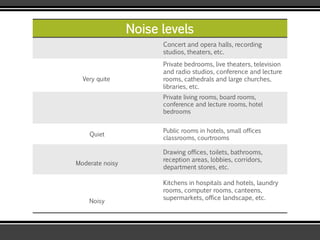
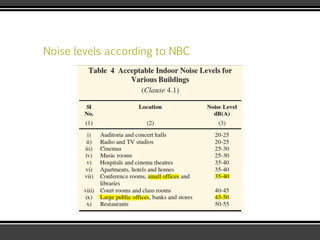
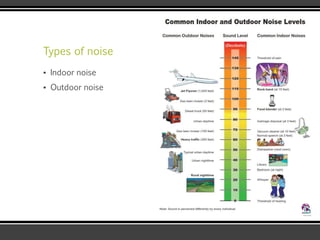
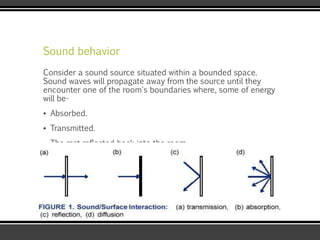
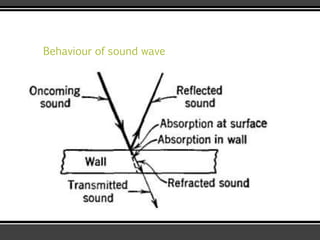
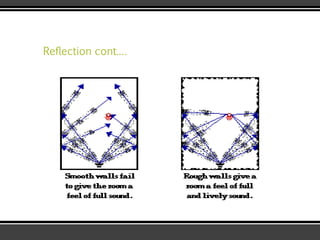
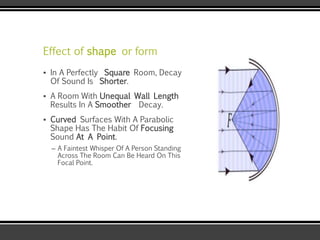
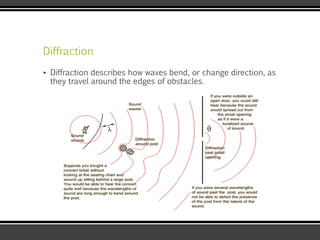
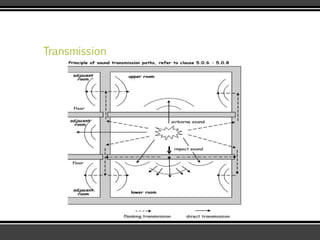
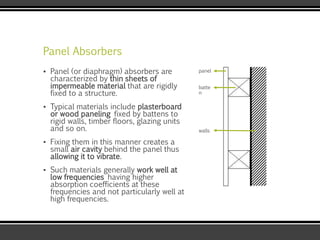
The document discusses the physics of sound. It defines sound as a pressure wave that travels faster through solids than liquids or gases. Sound waves are longitudinal waves that create compressions and rarefactions. The key characteristics of a sound wave are its frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed. Frequency is measured in Hertz and determines the pitch of a sound. Amplitude determines loudness. Wavelength is the distance between compressions or rarefactions. Sound waves can be reflected, transmitted, absorbed, or cause diffraction or reverberation when interacting with surfaces. The range of normal human hearing is between 20-20,000 Hz. Different materials are used to absorb sound like porous absorbers, panel absorbers, and resonators