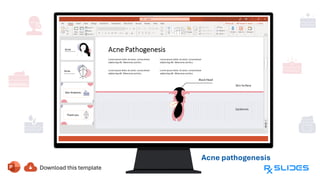
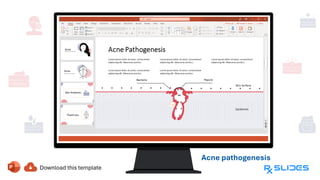
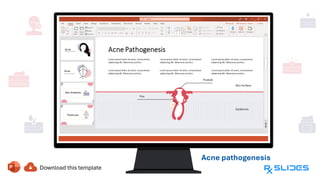
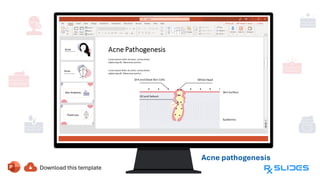
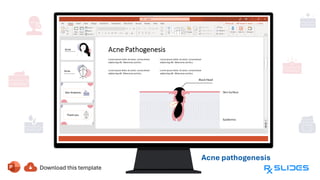
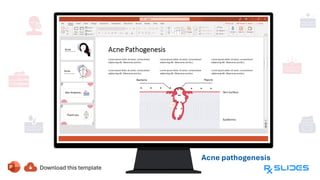
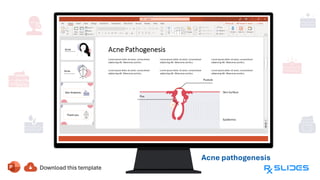
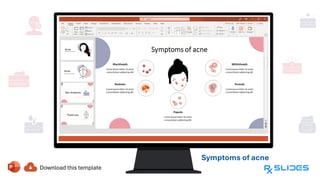
The document presents a detailed overview of acne, including its anatomy, causes, prevalence, types, and symptoms. It explores the pathogenesis of acne lesions and categorizes the severity from mild to severe. The document also discusses diagnosis methods, treatment options, and prevention strategies.