Embed presentation
Download to read offline




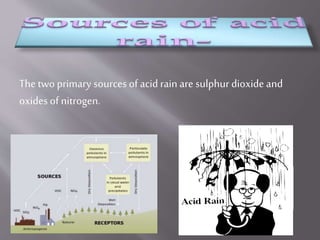















Acid rain is rainfall with a pH level below 5.6, formed when oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere combine with moisture to produce nitric and sulfuric acids. It is deposited through wet deposition via precipitation or dry deposition by sticking to surfaces through dust and smoke. Acid rain pollutes water bodies by increasing pH levels, damages forests by affecting flora and fauna, and corrodes certain materials in architecture and art.


















