Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times





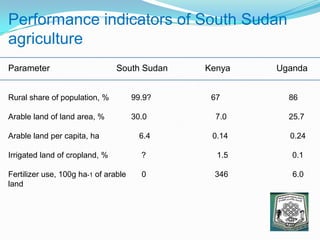






The document discusses research and technology options for increasing crop yields and soil fertility in South Sudan. It provides background on South Sudan's land use and challenges facing its agriculture sector. Specifically: - South Sudan has significant arable land but most agriculture is traditional and rain-fed, leading to low and unstable yields. - Two civil wars resulted in loss of seeds, farming skills, and interest in agriculture. Overall crop yields are very low across the country. - Options discussed to address this include on-farm research trials of techniques like intercropping and cover crops, providing agricultural inputs, improving infrastructure, and emphasizing applied research and extension services. The goal is to develop sustainable solutions to boost yields and soil health












