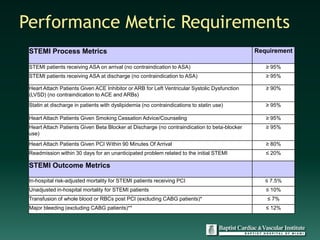
The document discusses accreditation for cardiovascular excellence (ACE) and provides information about the ACE accreditation process and its benefits. The 5 step ACE accreditation process involves: 1) reviewing ACE standards, 2) collecting data and preparing the application, 3) initial ACE review of the application, 4) an onsite review, and 5) ongoing reporting. The onsite review involves record reviews, policy reviews, facility tours, and interviews. Maintaining ACE accreditation requires ongoing data reporting and notifying ACE of any major program changes. While the accreditation process requires work, it is presented as the best tool to ensure hospitals are meeting quality standards for cardiovascular care.