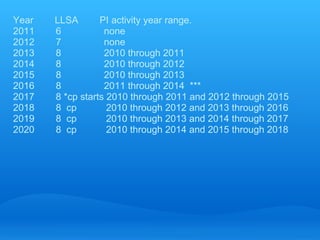
The document provides information about the requirements for maintaining emergency medicine board certification through the American Board of Emergency Medicine's Emergency Medicine Continuous Certification (EMCC) program. It discusses the four components of EMCC - professional standing, lifelong learning and self-assessment, assessment of cognitive expertise through examination, and assessment of practice performance. It provides details on the lifelong learning, examination, and practice performance requirements, including acceptable types of activities to fulfill the practice performance component.