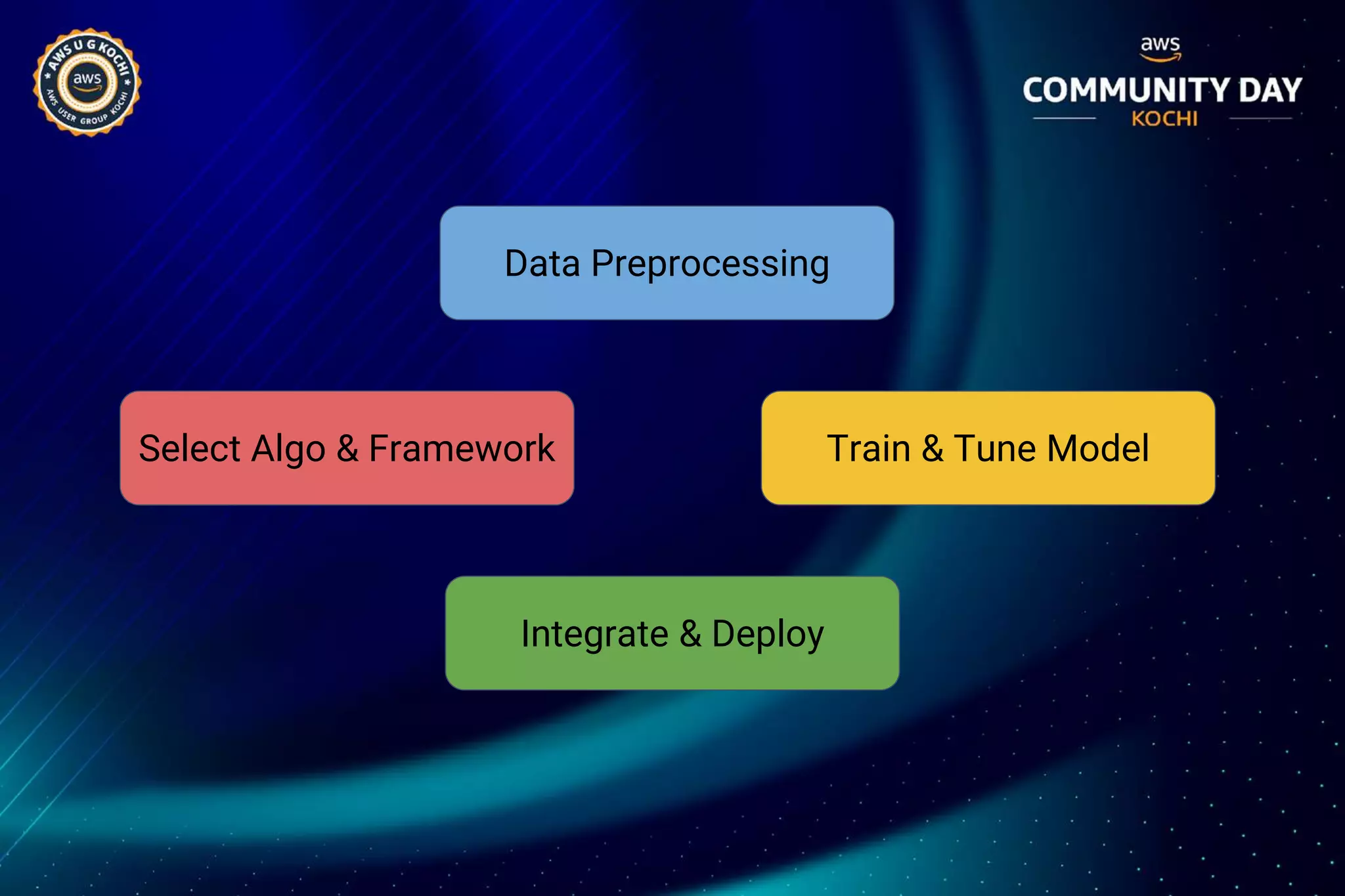
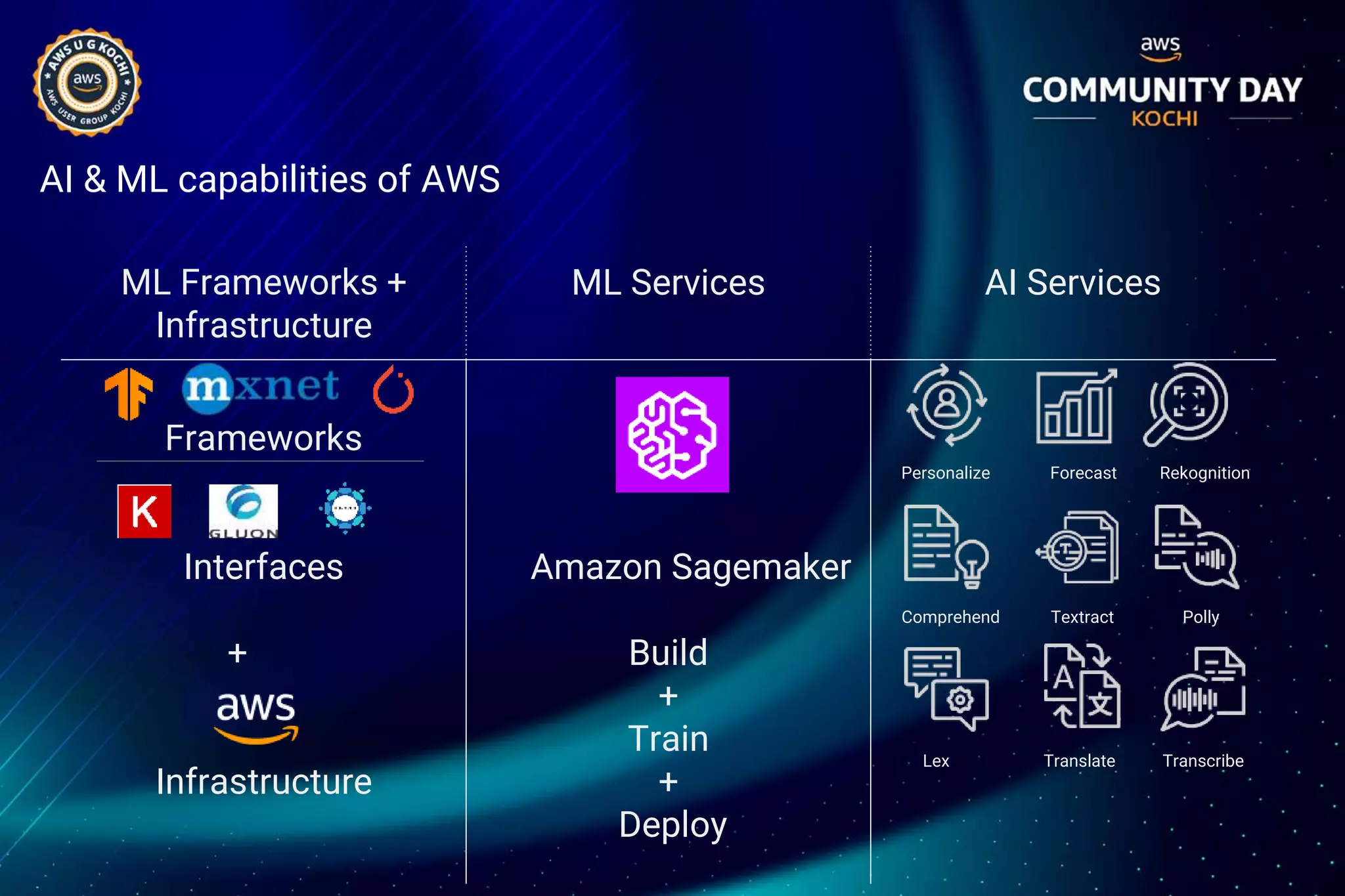
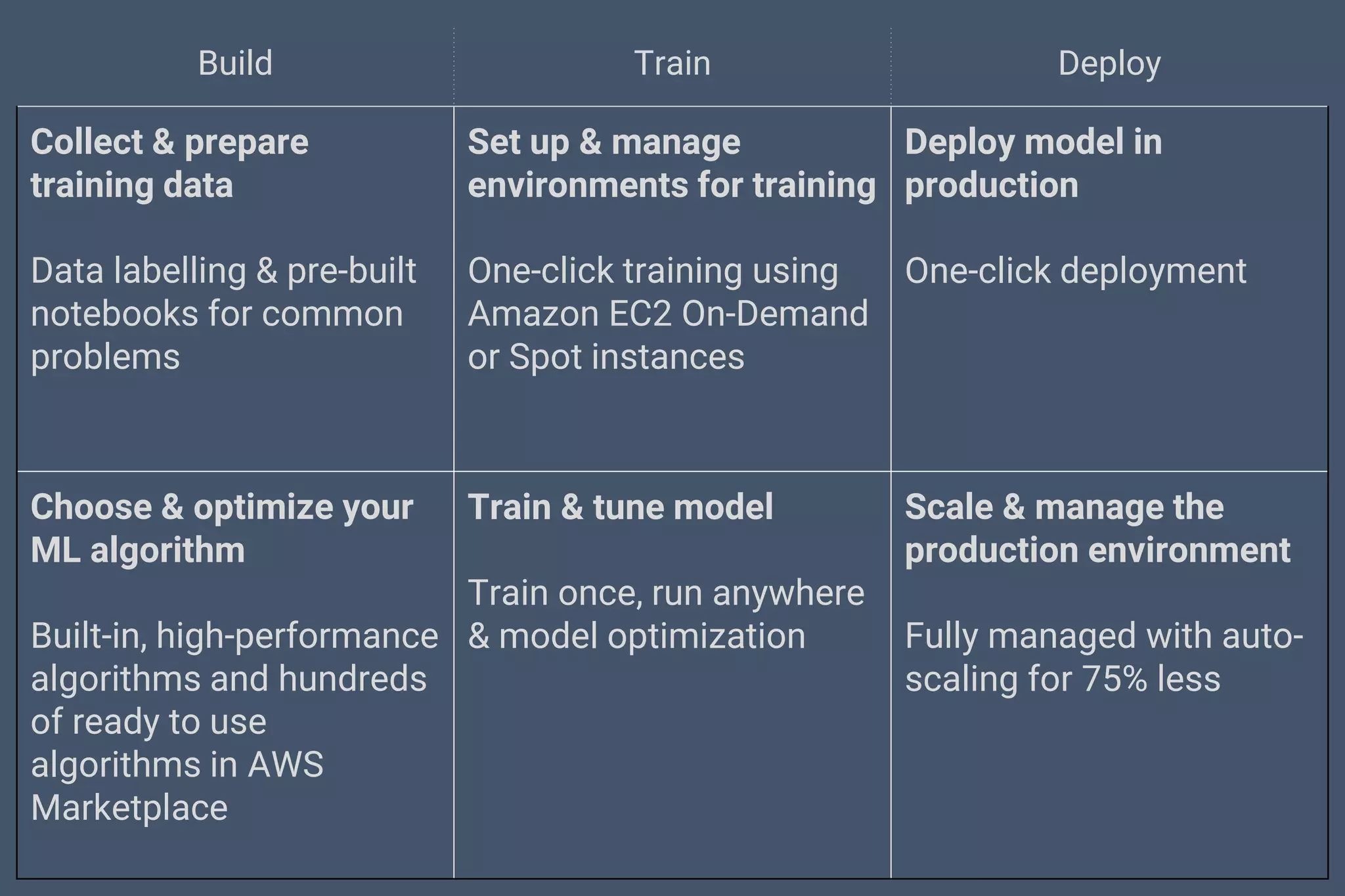
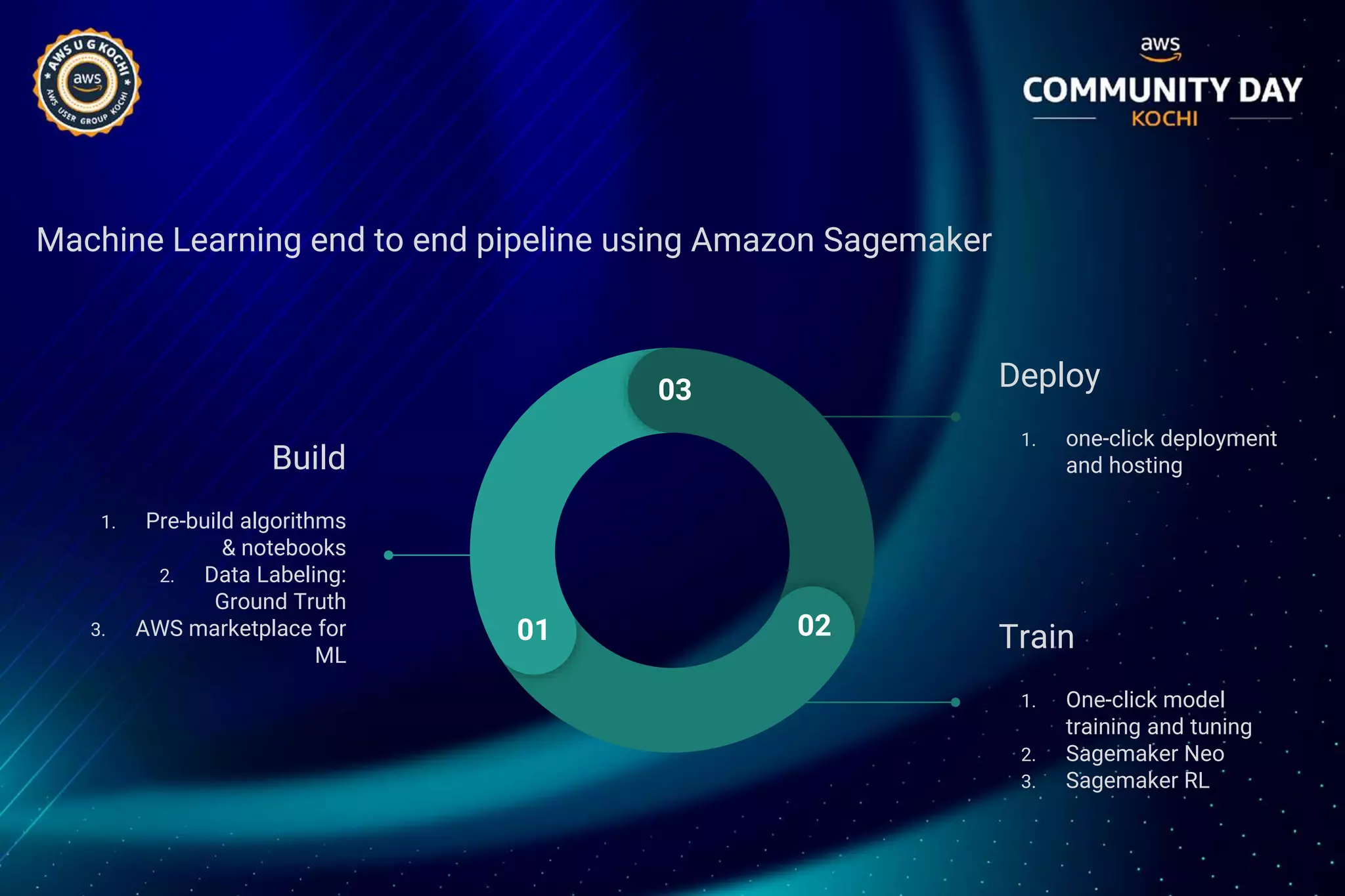
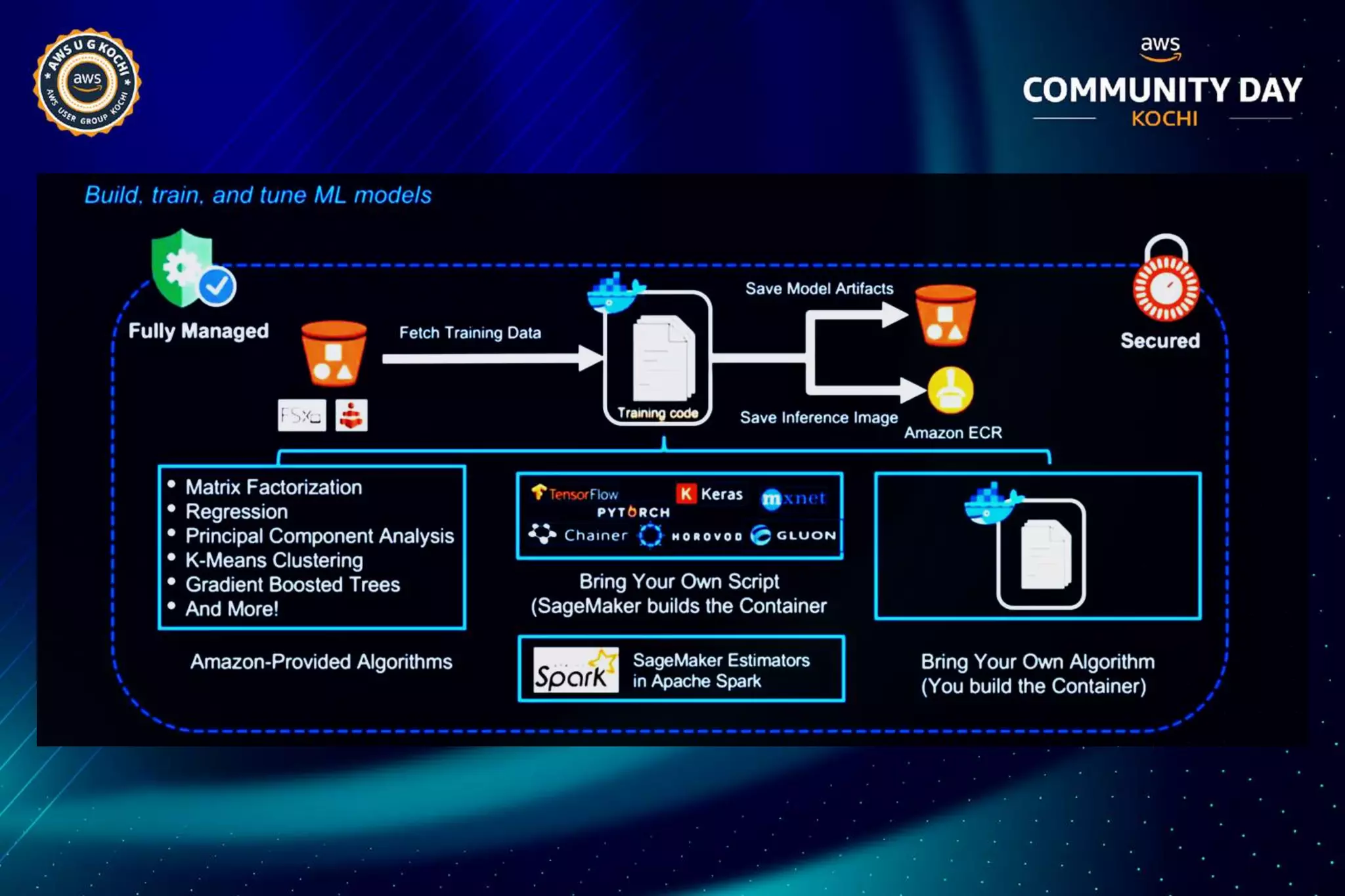
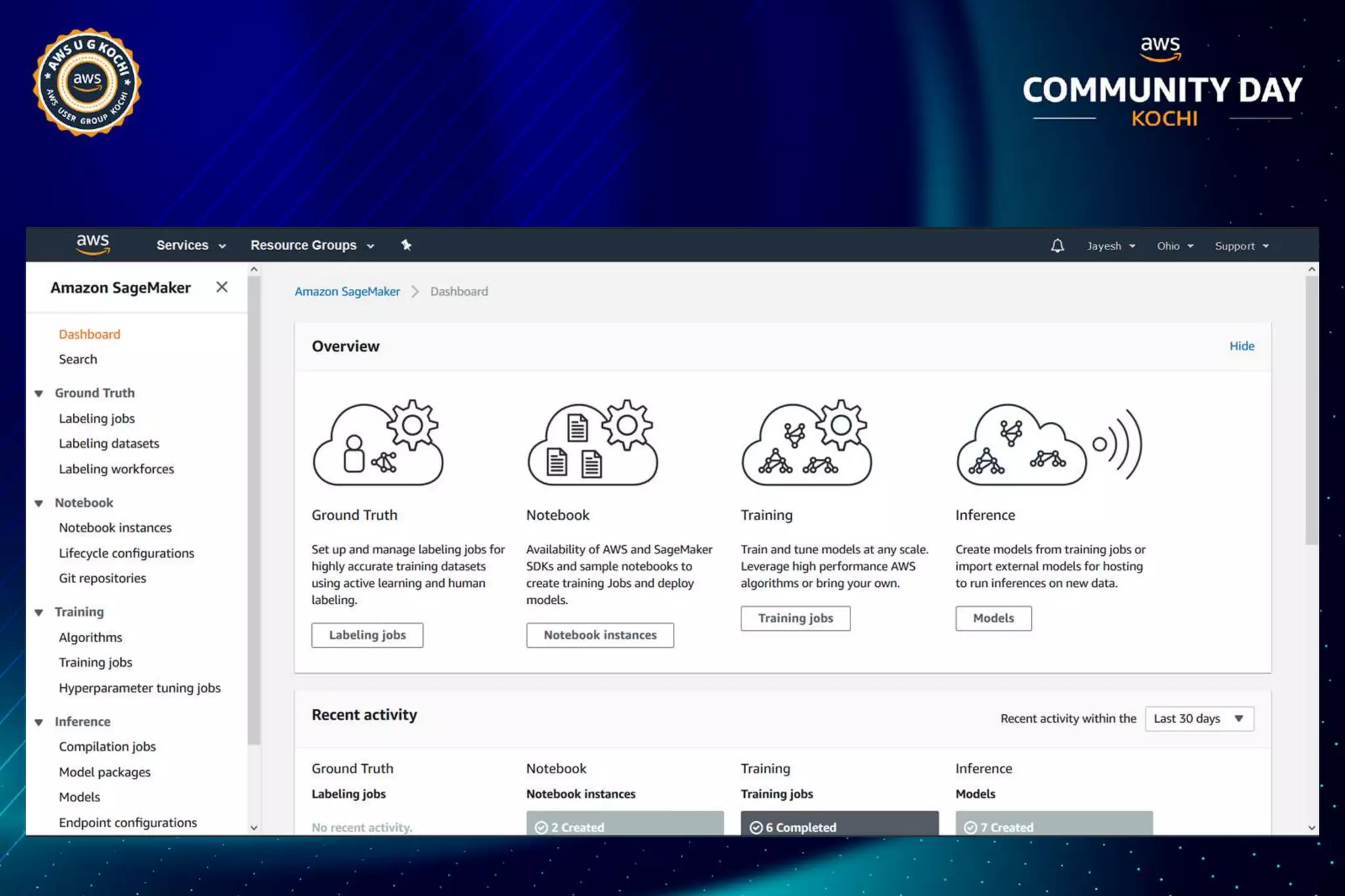
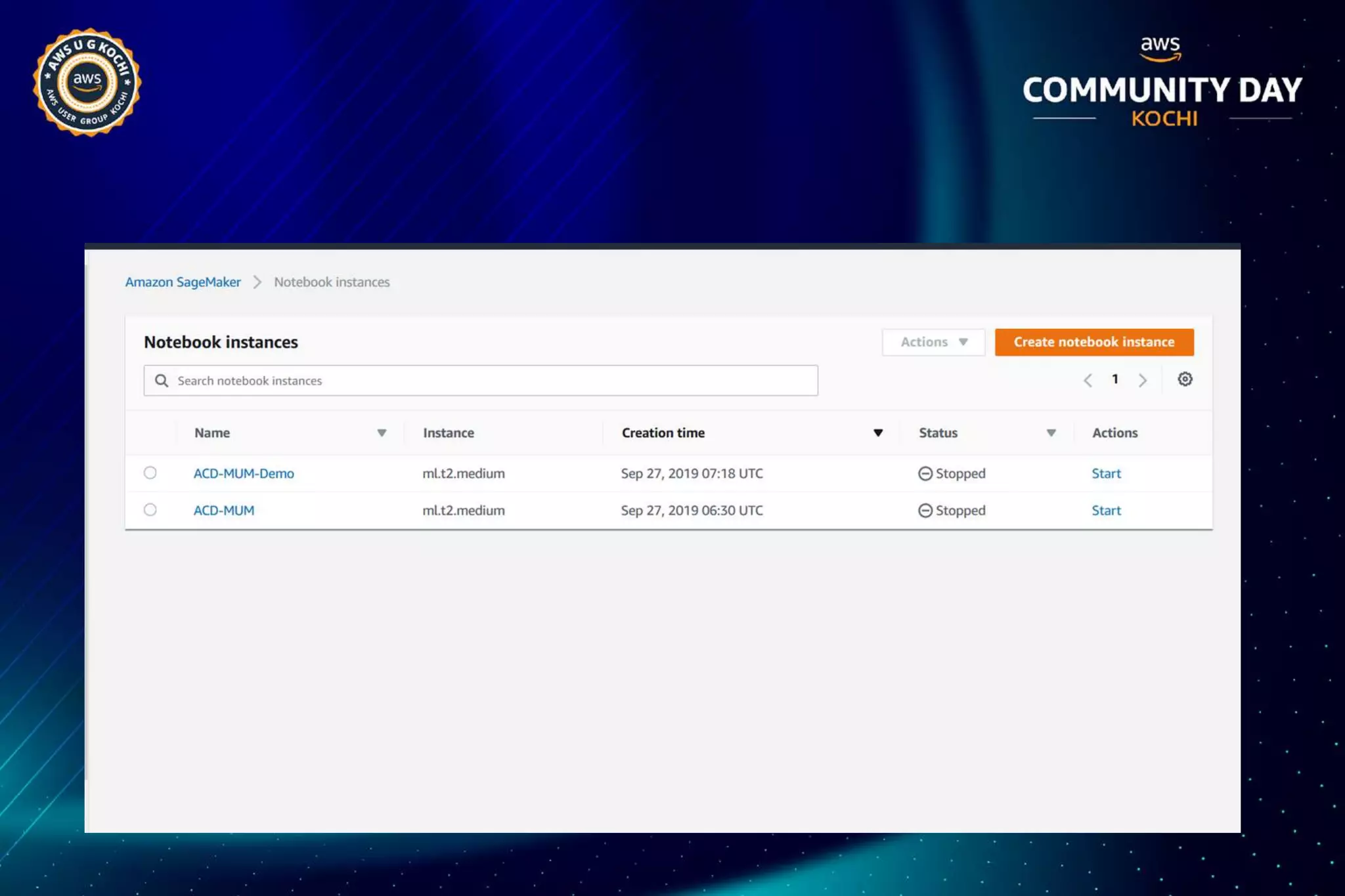
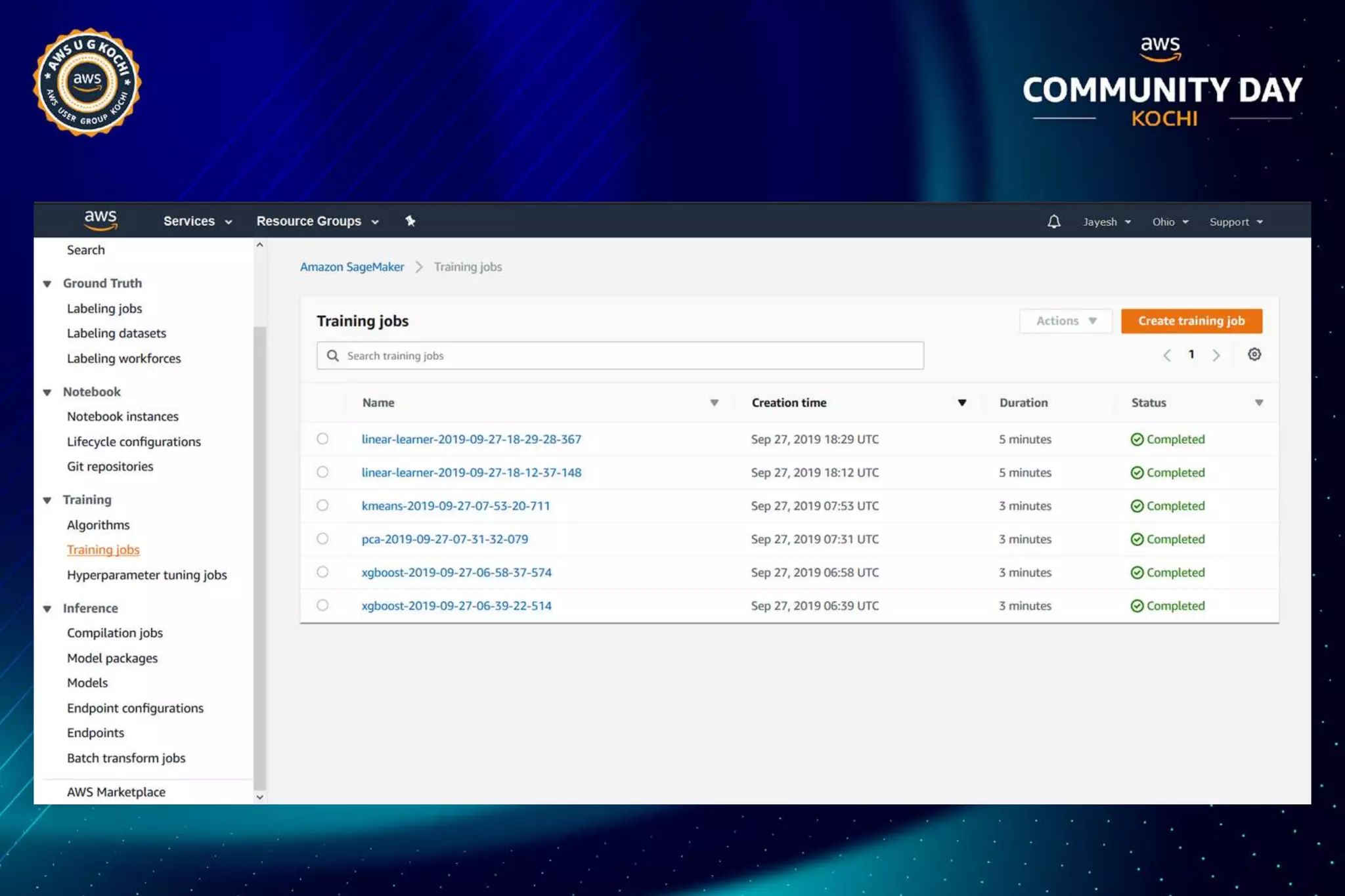
The document discusses Amazon SageMaker, a fully managed machine learning service that simplifies the machine learning process from building to deployment. It highlights features such as auto-scaling, one-click deployment, and support for custom algorithms, as well as various tools for data processing, model training, and optimization. Additionally, it addresses security measures and cost-saving options like managed spot training to enhance machine learning operations on AWS.