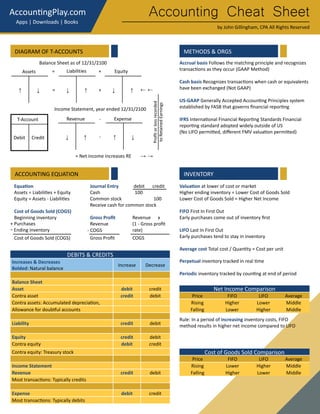
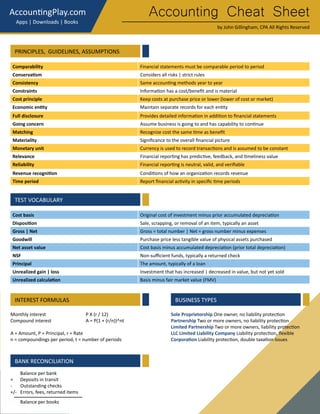
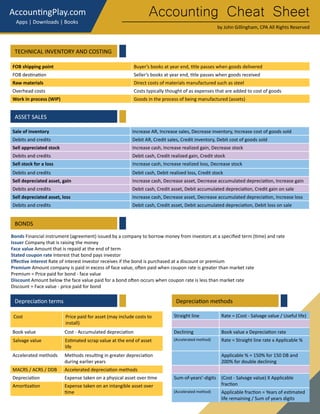
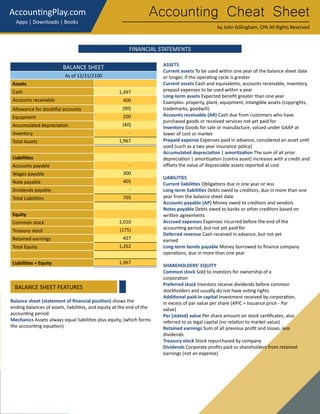
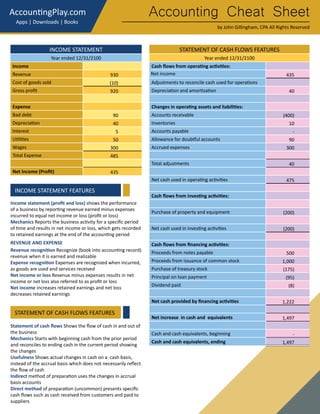
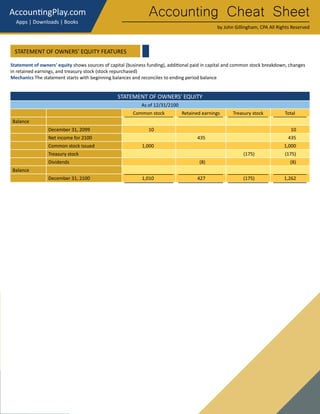
This document provides an accounting cheat sheet that summarizes key accounting concepts, principles, and methods. It covers topics like the accounting equation, debits and credits, financial statements, inventory costing methods, and more. Key terms are defined concisely with examples to help the reader learn essential accounting concepts in a simple and straightforward manner.