Embed presentation
Download to read offline



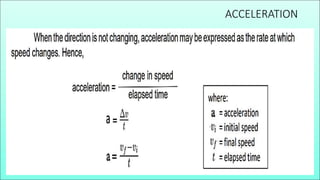





Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of an object's velocity. An object accelerates when its speed changes, its direction changes, or both change. Positive acceleration occurs when speed increases, while negative acceleration occurs when speed decreases. Even if speed stays the same, an object accelerates when its direction changes, such as when rounding a curve.








