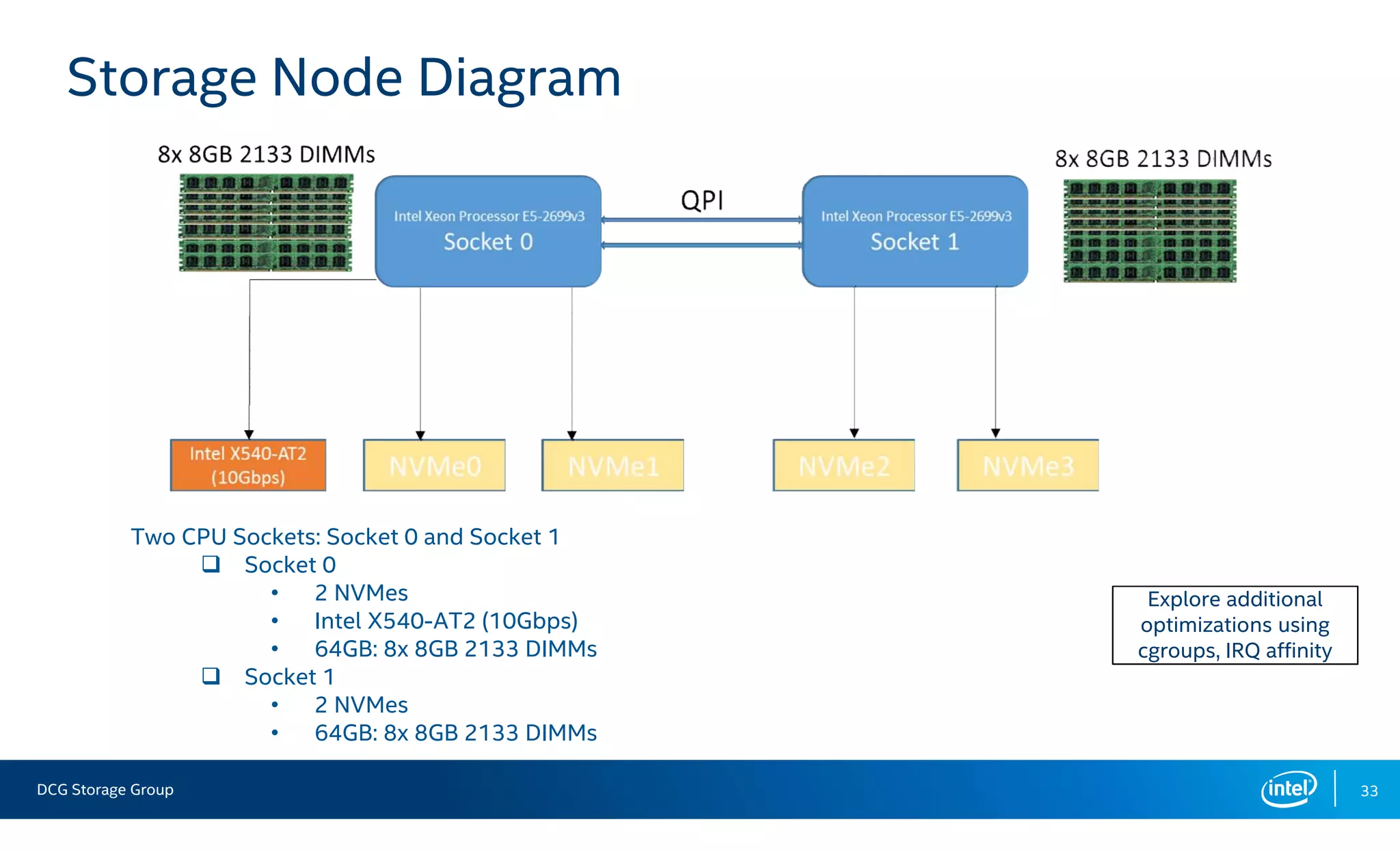
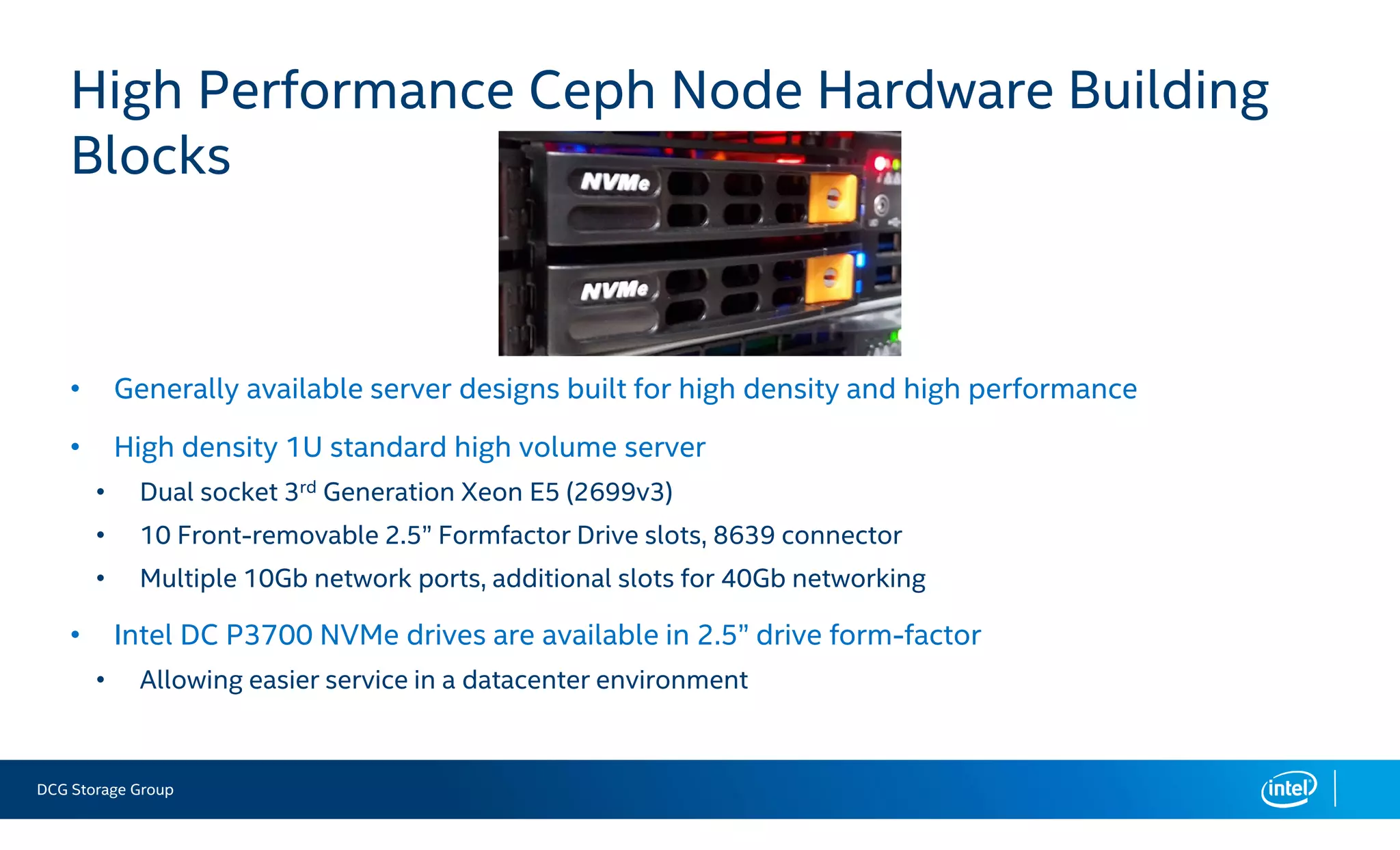
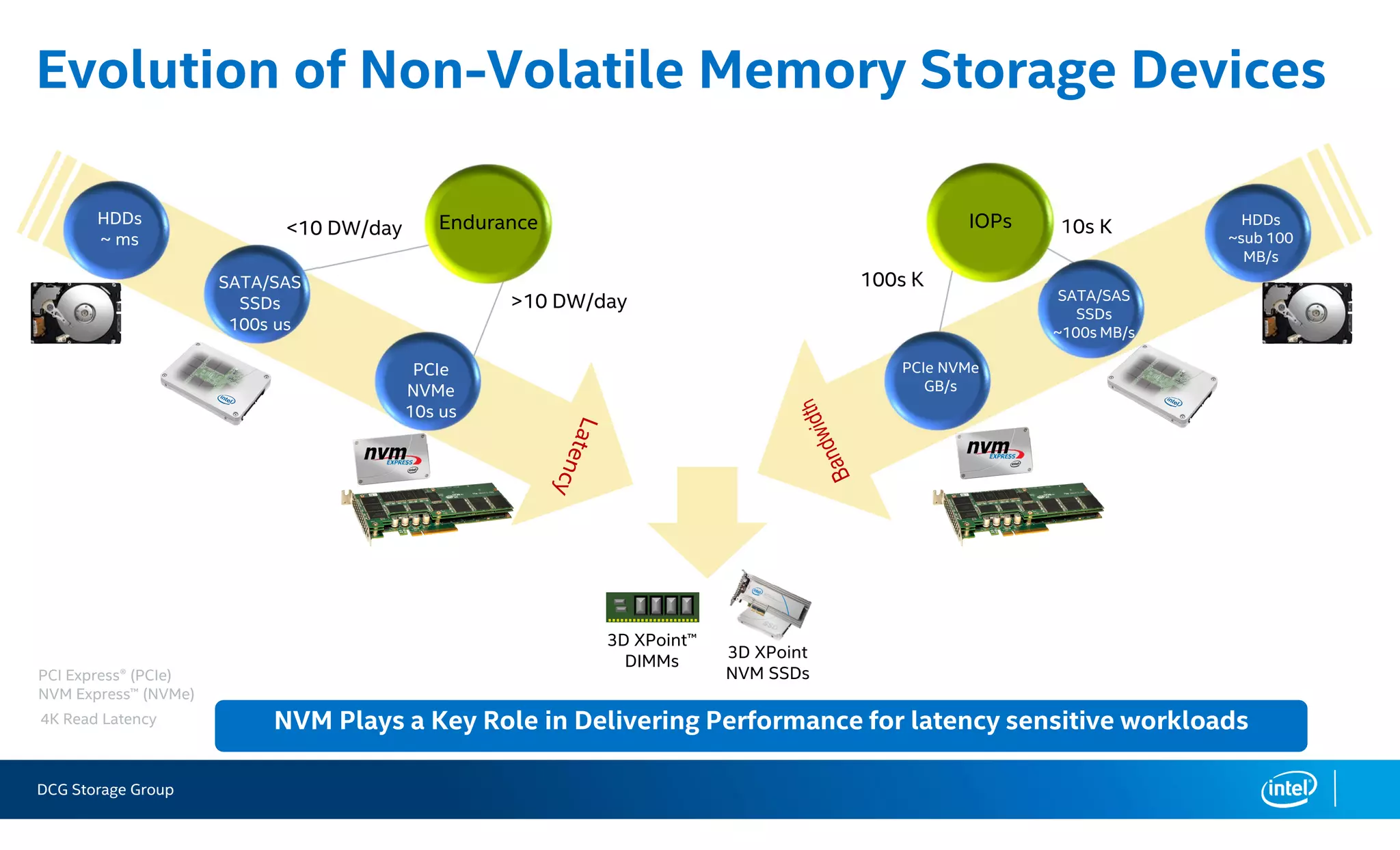
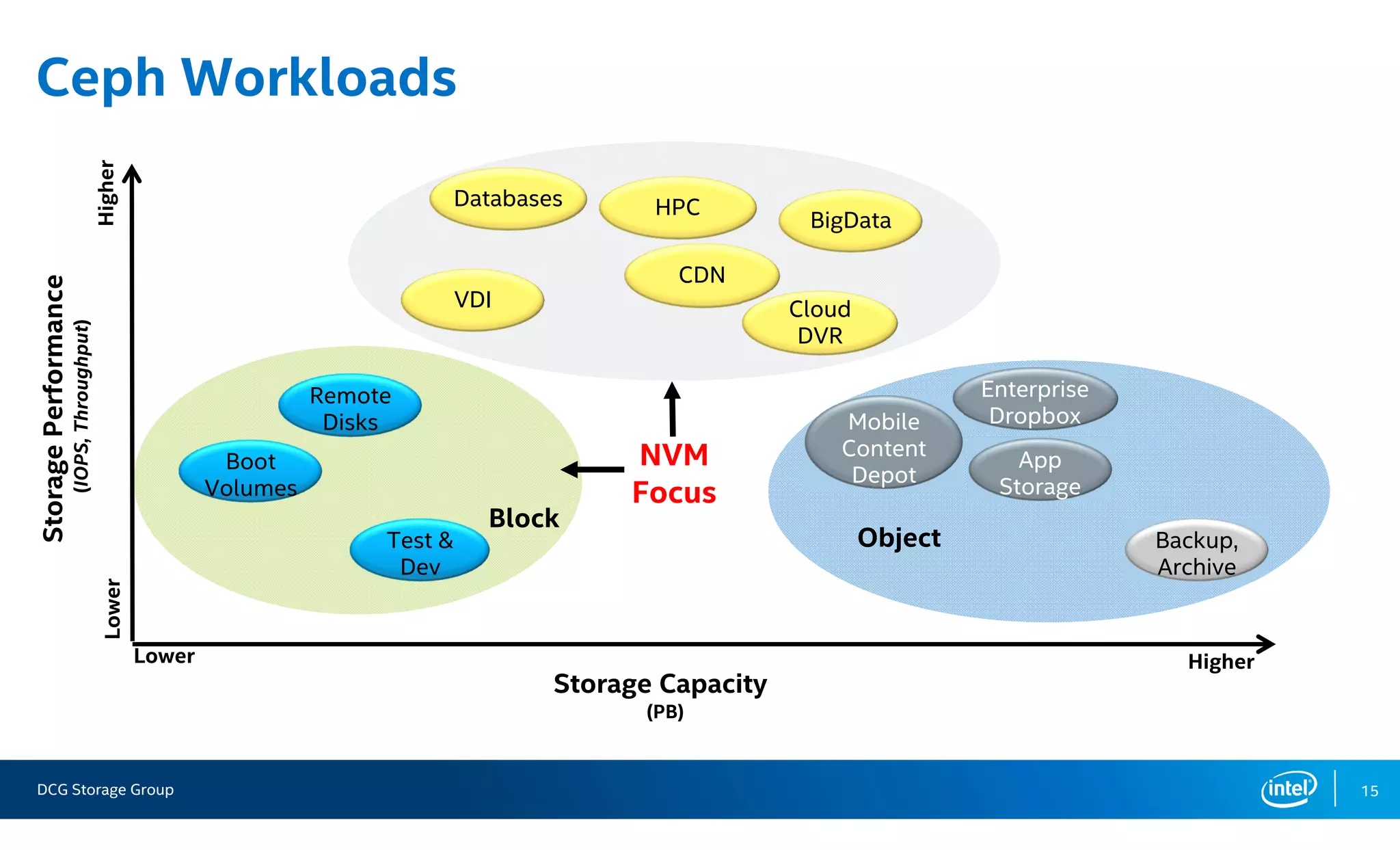
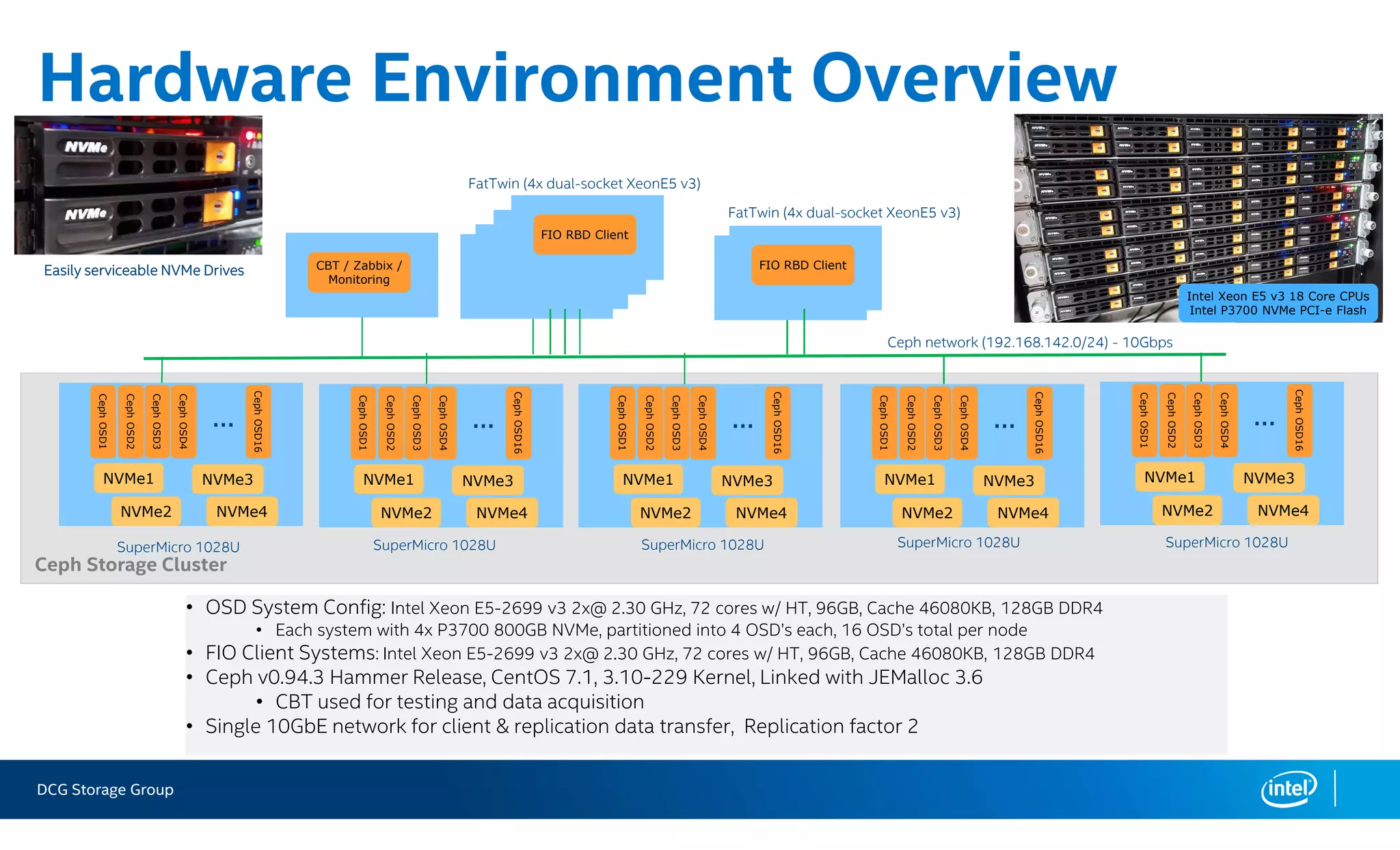
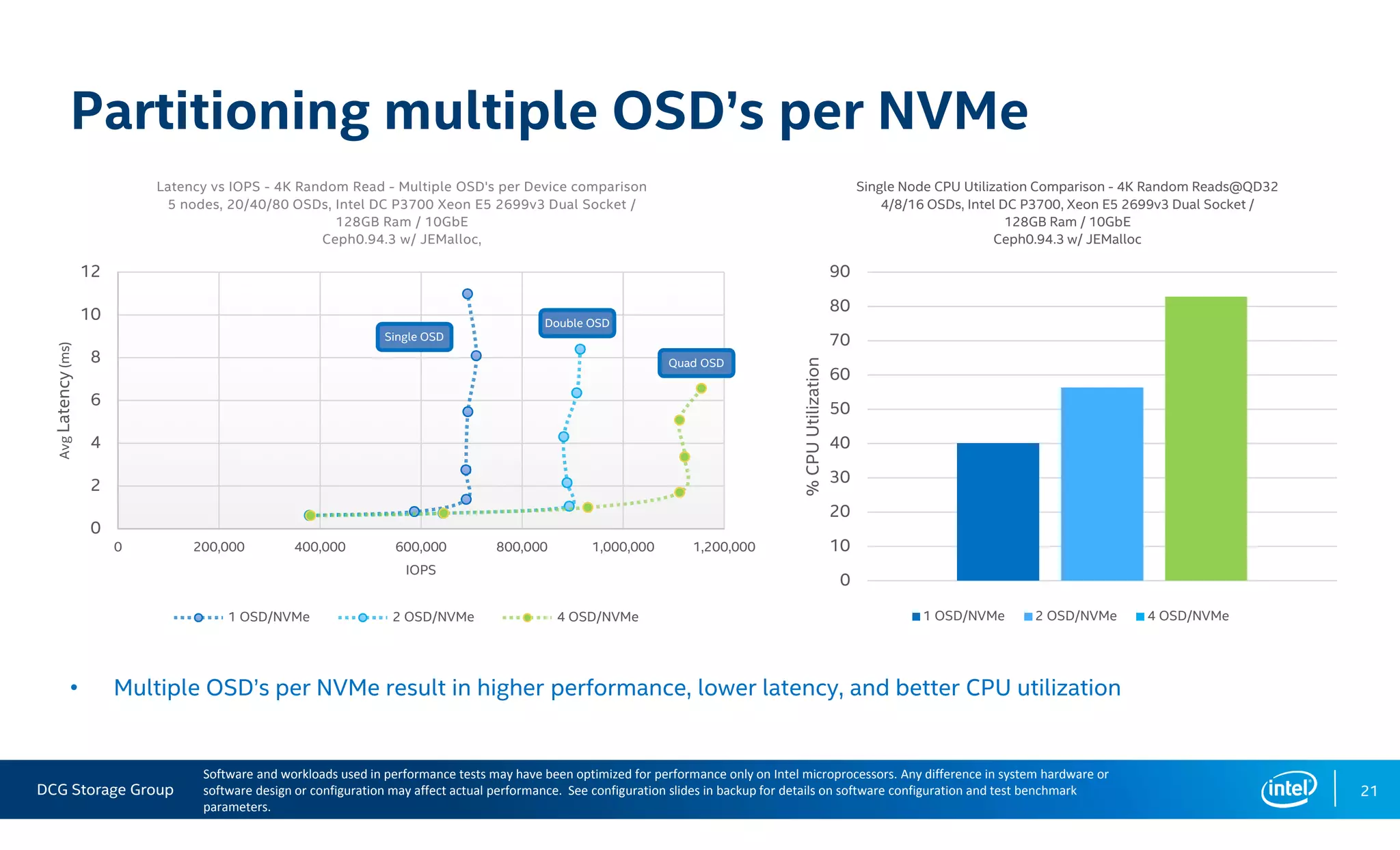
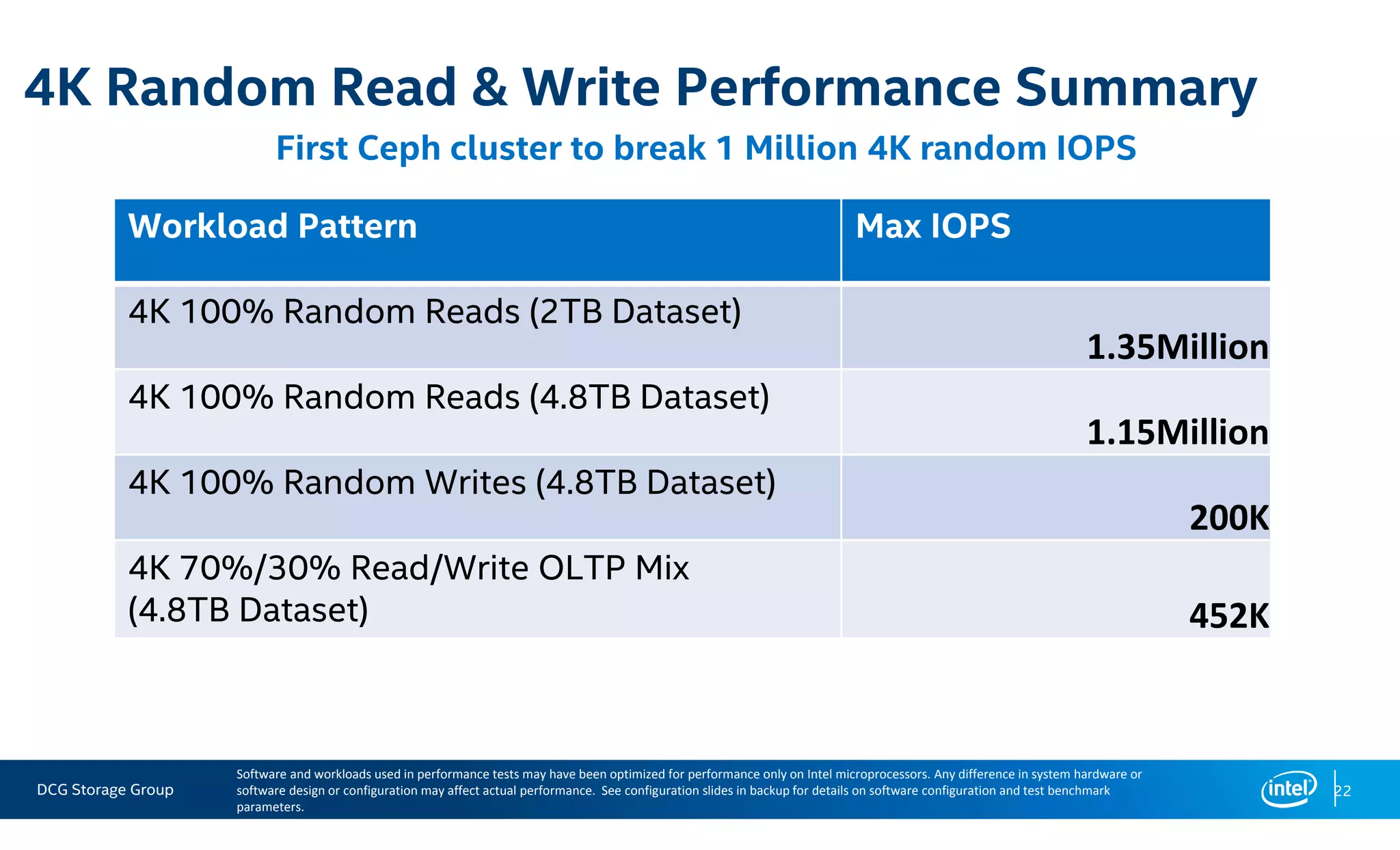
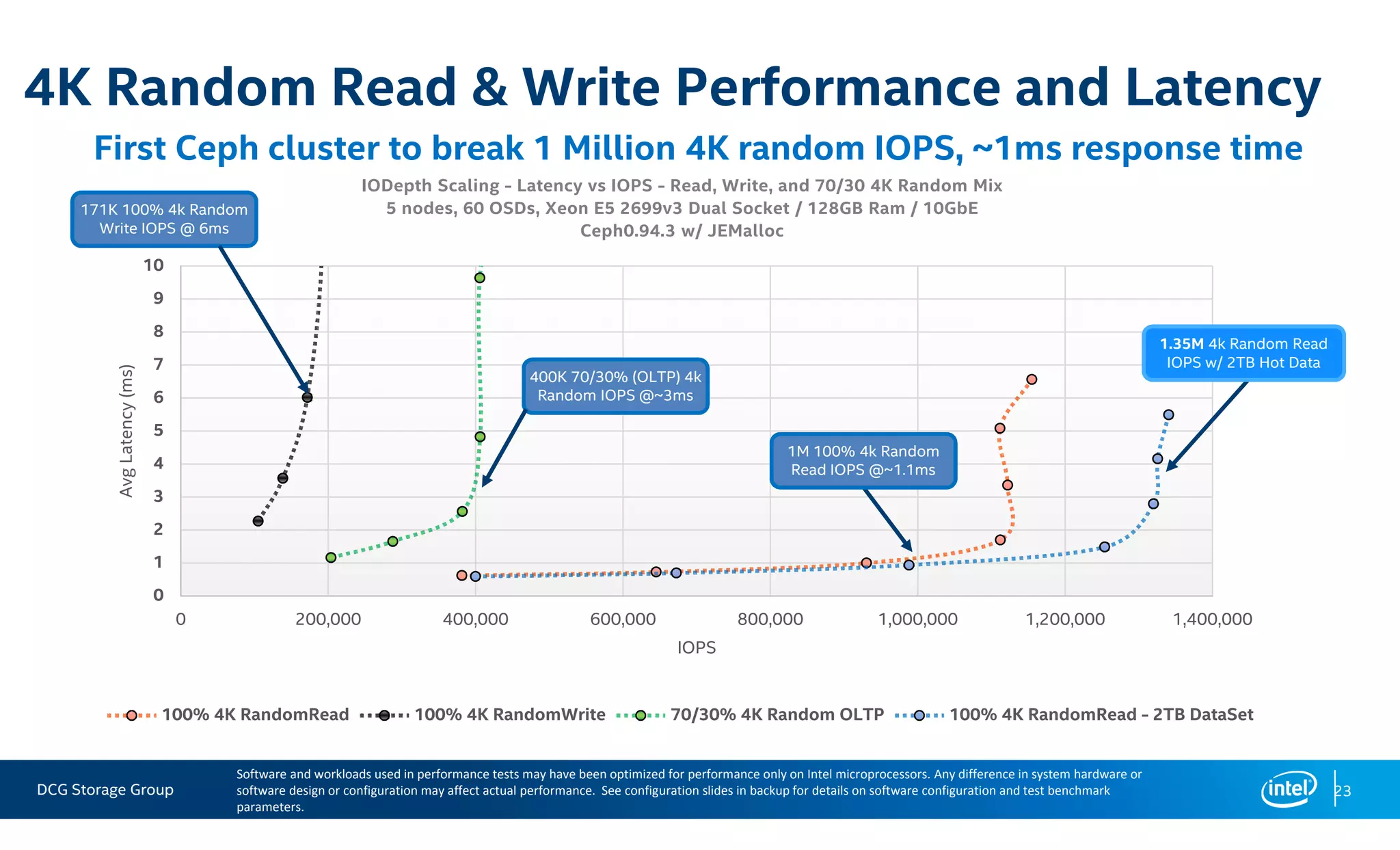
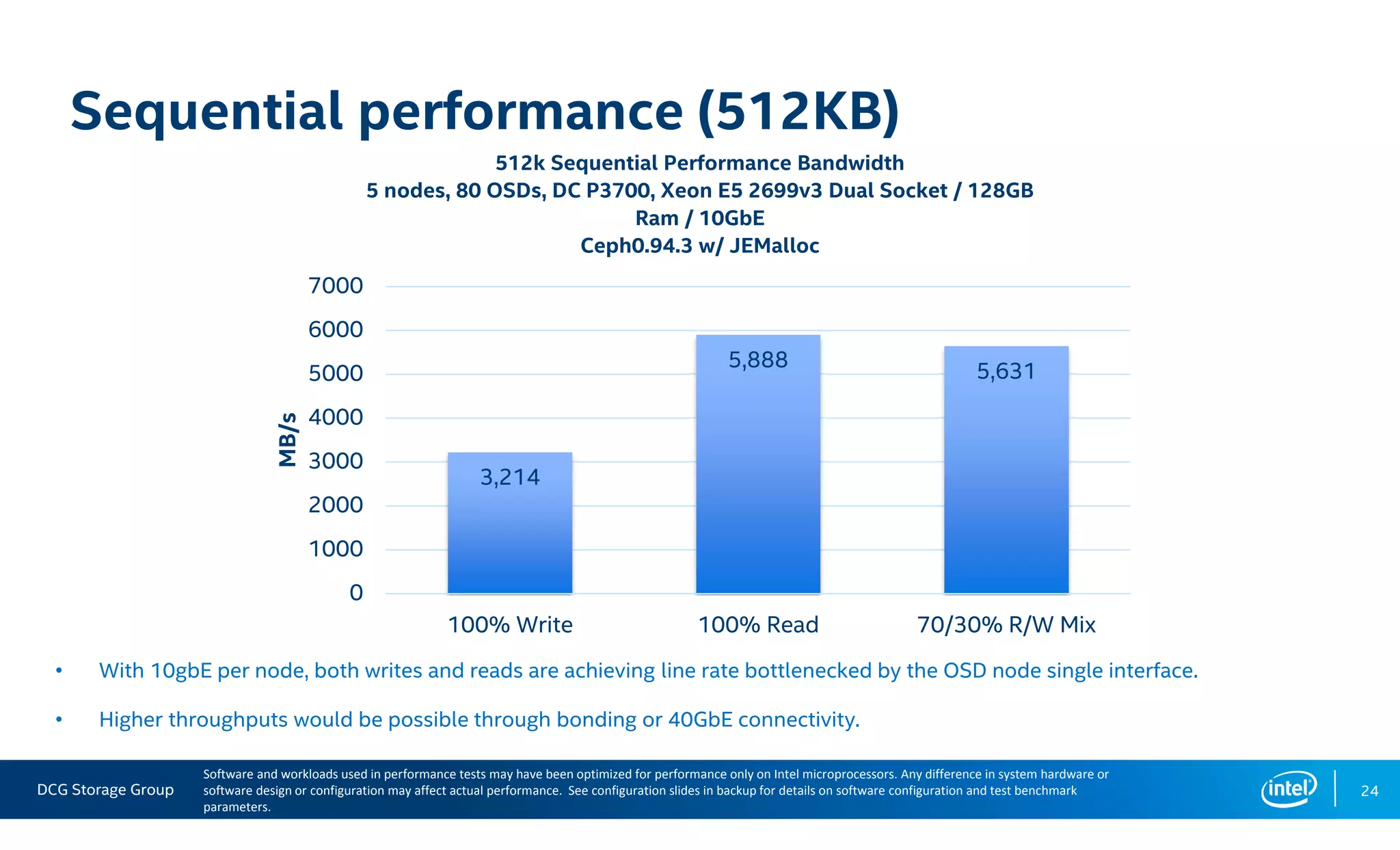
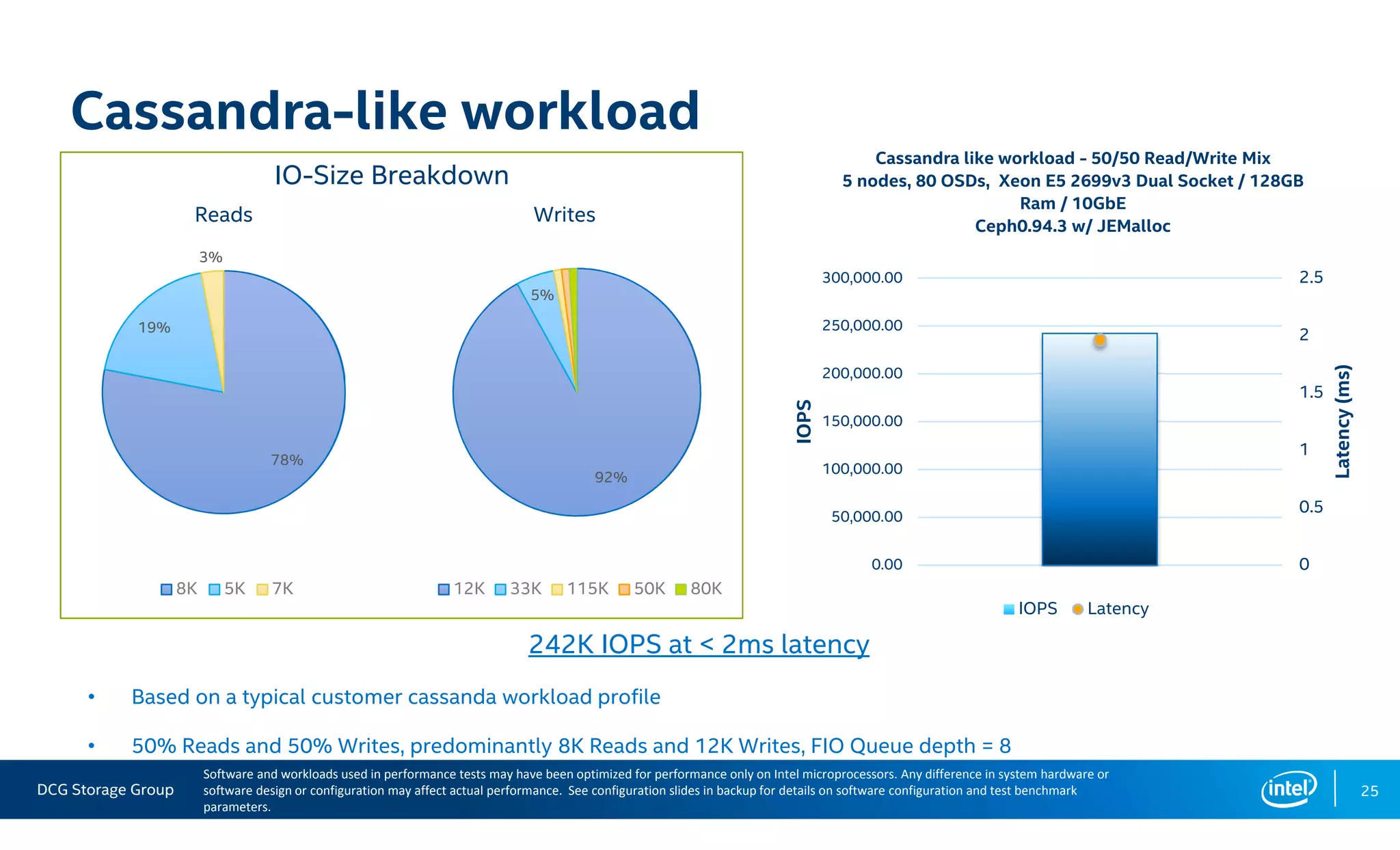
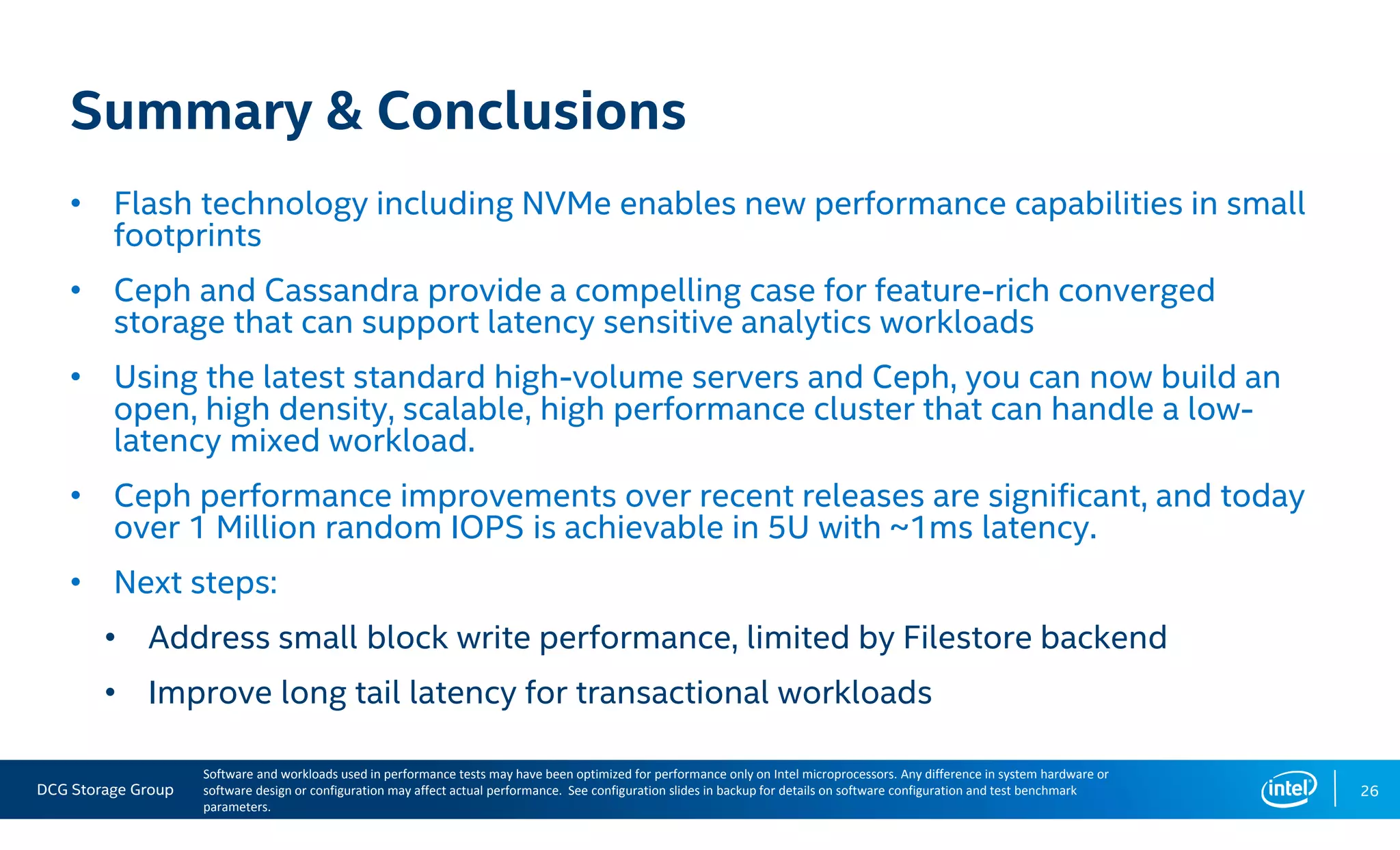
This document summarizes the performance of an all-NVMe Ceph cluster using Intel P3700 NVMe SSDs. Key results include achieving over 1.35 million 4K random read IOPS and 171K 4K random write IOPS with sub-millisecond latency. Partitioning the NVMe drives into multiple OSDs improved performance and CPU utilization compared to a single OSD per drive. The cluster also demonstrated over 5GB/s of sequential bandwidth.





![DCG Storage Group 29
Configuration Detail – ceph.conf
Section Perf. Tuning Parameter Default Tuned
[global]
Authentication
auth_client_required cephx none
auth_cluster_required cephx none
auth_service_required cephx none
Debug logging
debug_lockdep 0/1 0/0
debug_context 0/1 0/0
debug_crush 1/1 0/0
debug_buffer 0/1 0/0
debug_timer 0/1 0/0
debug_filer 0/1 0/0
debug_objector 0/1 0/0
debug_rados 0/5 0/0
debug_rbd 0/5 0/0
debug_ms 0/5 0/0
debug_monc 0/5 0/0
debug_tp 0/5 0/0
debug_auth 1/5 0/0
debug_finisher 1/5 0/0
debug_heartbeatmap 1/5 0/0
debug_perfcounter 1/5 0/0
debug_rgw 1/5 0/0
debug_asok 1/5 0/0
debug_throttle 1/1 0/0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-151103190157-lva1-app6892/75/Accelerating-Cassandra-Workloads-on-Ceph-with-All-Flash-PCIE-SSDS-19-2048.jpg)
![DCG Storage Group 30
Configuration Detail – ceph.conf (continued)Section Perf. Tuning Parameter Default Tuned
[global]
CBT specific
mon_pg_warn_max_object_skew 10 10000
mon_pg_warn_min_per_osd 0 0
mon_pg_warn_max_per_osd 32768 32768
osd_pg_bits 8 8
osd_pgp_bits 8 8
RBD cache rbd_cache true true
Other
mon_compact_on_trim true false
log_to_syslog false false
log_file /var/log/ceph/$name.log /var/log/ceph/$name.log
perf true true
mutex_perf_counter false true
throttler_perf_counter true false
[mon] CBT specific
mon_data /var/lib/ceph/mon/ceph-0 /home/bmpa/tmp_cbt/ceph/mon.$id
mon_max_pool_pg_num 65536 166496
mon_osd_max_split_count 32 10000
[osd]
Filestore parameters
filestore_wbthrottle_enable true false
filestore_queue_max_bytes 104857600 1048576000
filestore_queue_committing_max_bytes 104857600 1048576000
filestore_queue_max_ops 50 5000
filestore_queue_committing_max_ops 500 5000
filestore_max_sync_interval 5 10
filestore_fd_cache_size 128 64
filestore_fd_cache_shards 16 32
filestore_op_threads 2 6
Mount parameters
osd_mount_options_xfs rw,noatime,inode64,logbsize=256k,delaylog
osd_mkfs_options_xfs -f -i size=2048
Journal parameters
journal_max_write_entries 100 1000
journal_queue_max_ops 300 3000
journal_max_write_bytes 10485760 1048576000
journal_queue_max_bytes 33554432 1048576000
Op tracker osd_enable_op_tracker true false
OSD client
osd_client_message_size_cap 524288000 0
osd_client_message_cap 100 0
Objecter
objecter_inflight_ops 1024 102400
objecter_inflight_op_bytes 104857600 1048576000
Throttles ms_dispatch_throttle_bytes 104857600 1048576000
OSD number of threads
osd_op_threads 2 32
osd_op_num_shards 5 5
osd_op_num_threads_per_shard 2 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-151103190157-lva1-app6892/75/Accelerating-Cassandra-Workloads-on-Ceph-with-All-Flash-PCIE-SSDS-20-2048.jpg)
![DCG Storage Group 31
Configuration Detail - CBT YAML File
cluster:
user: "bmpa"
head: "ft01"
clients: ["ft01", "ft02", "ft03", "ft04", "ft05", "ft06"]
osds: ["hswNode01", "hswNode02", "hswNode03", "hswNode04", "hswNode05"]
mons:
ft02:
a: "192.168.142.202:6789"
osds_per_node: 8
fs: xfs
mkfs_opts: '-f -i size=2048 -n size=64k'
mount_opts: '-o inode64,noatime,logbsize=256k'
conf_file: '/home/bmpa/cbt/ceph_nvme_2partition_5node_hsw.conf'
use_existing: False
rebuild_every_test: False
clusterid: "ceph"
iterations: 1
tmp_dir: "/home/bmpa/tmp_cbt"
pool_profiles:
2rep:
pg_size: 4096
pgp_size: 4096
replication: 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-151103190157-lva1-app6892/75/Accelerating-Cassandra-Workloads-on-Ceph-with-All-Flash-PCIE-SSDS-21-2048.jpg)
![DCG Storage Group 32
Configuration Detail - CBT YAML File (Continued)
benchmarks:
librbdfio:
time: 300
ramp: 600
vol_size: 81920
mode: ['randrw‘]
rwmixread: [0, 70, 100]
op_size: [4096]
procs_per_volume: [1]
volumes_per_client: [10]
use_existing_volumes: False
iodepth: [4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 96, 128]
osd_ra: [128]
norandommap: True
cmd_path: '/usr/bin/fio'
pool_profile: '2rep'
log_avg_msec: 250](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-151103190157-lva1-app6892/75/Accelerating-Cassandra-Workloads-on-Ceph-with-All-Flash-PCIE-SSDS-22-2048.jpg)