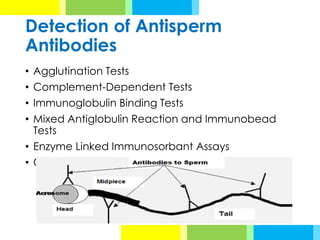
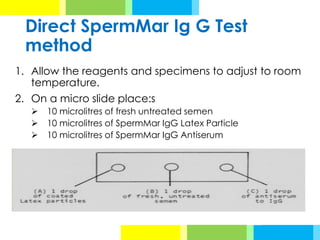
The document outlines various antisperm antibody (ASA) detection methods utilized in evaluating male infertility, emphasizing when these assays should be performed. Key testing methods include agglutination tests, complement-dependent tests, immunoglobulin binding tests, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, each with specific advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it provides detailed procedures for direct and indirect sperm antibody tests to assess immunological factors impacting fertility.