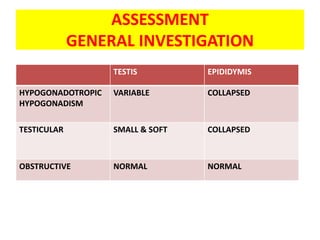
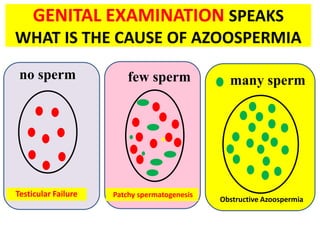
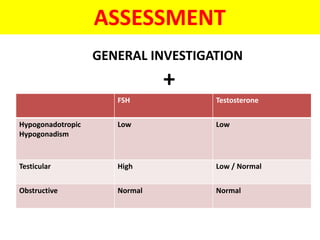
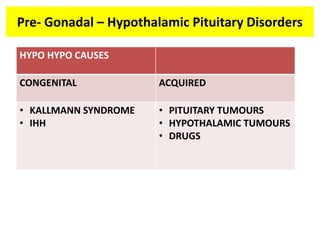
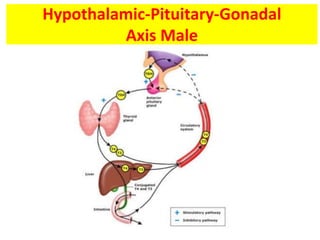
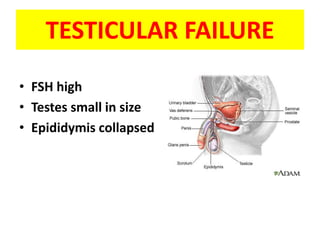
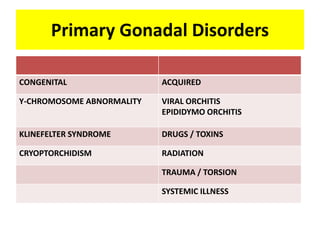
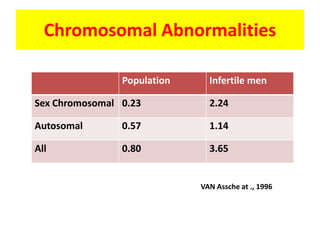
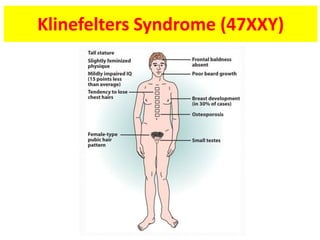
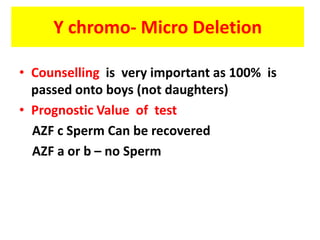
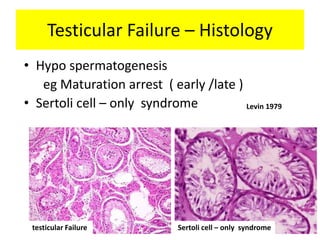
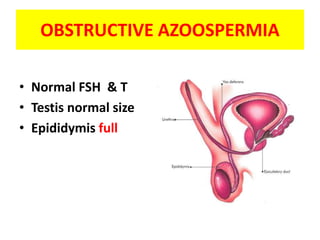
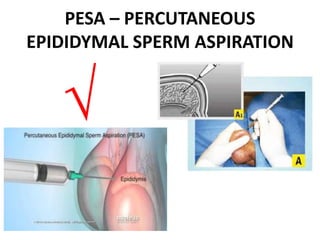
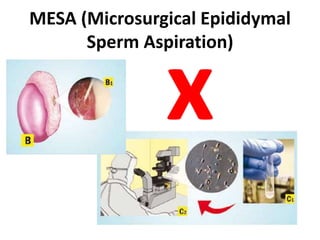
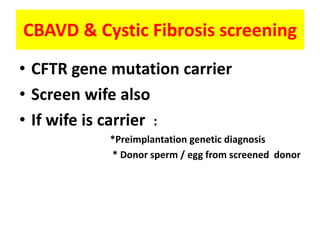
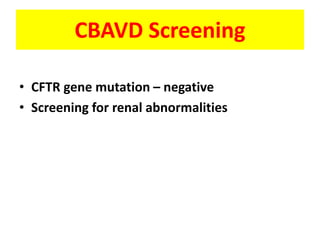
This document provides a summary of azoospermia (the absence of sperm in semen) including its causes, evaluation, and management. It discusses the three main types of azoospermia - pre-testicular, testicular failure, and obstructive. For evaluation, it recommends a three step process of history, physical exam, and basic investigations like FSH and testosterone levels. For management of obstructive azoospermia, it recommends attempting PESA first before moving to TESE/TESA extraction if needed. For testicular failure, it discusses treatments like TESE, microTESE to potentially find sperm, with a minimum 6 month gap between attempts. The document emphasizes a collaborative approach