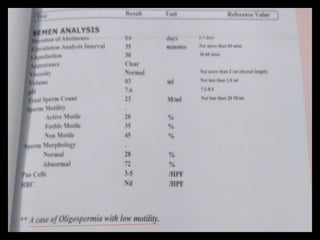
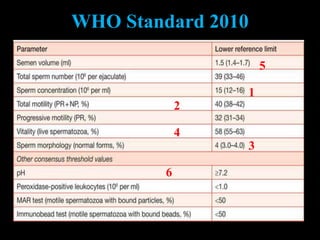
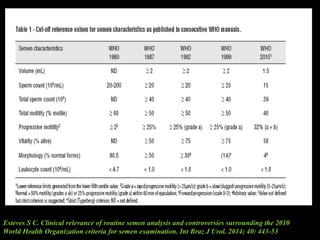
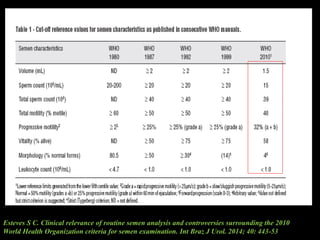
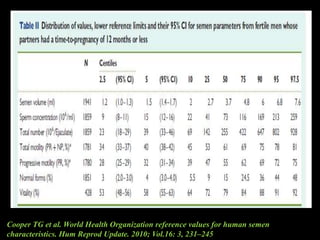
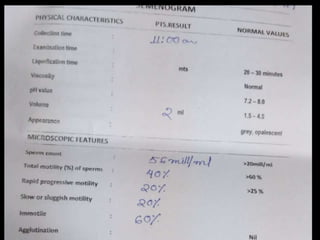
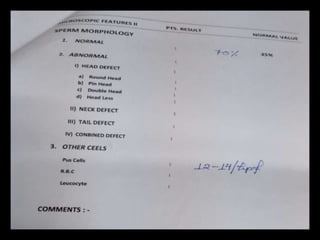
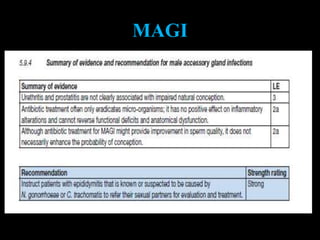
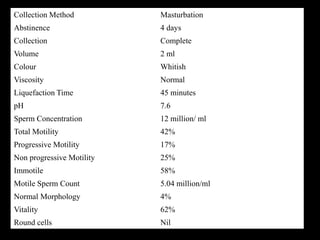
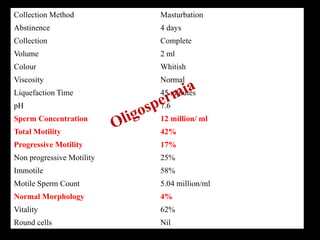
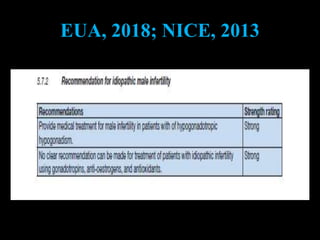
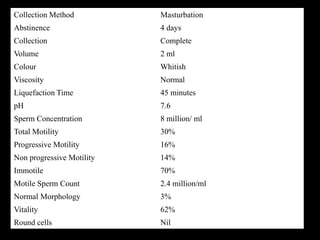
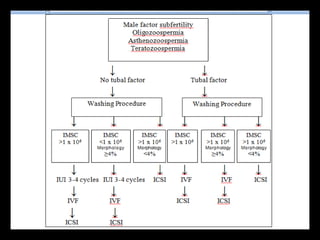
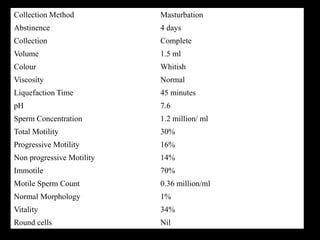
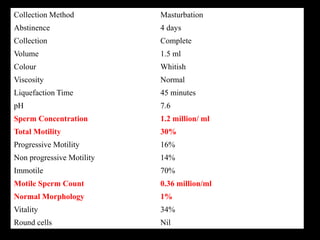
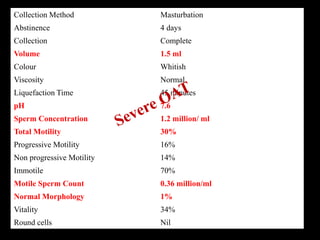
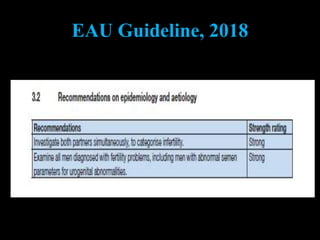
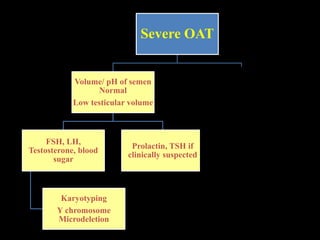
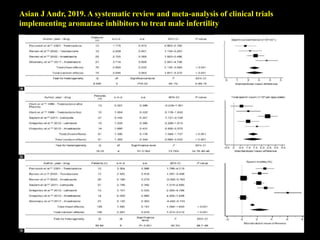
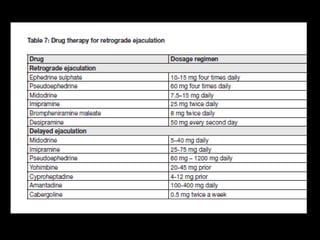
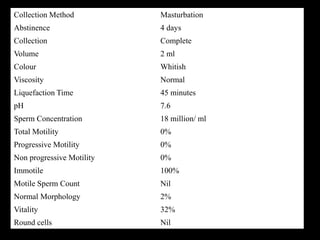
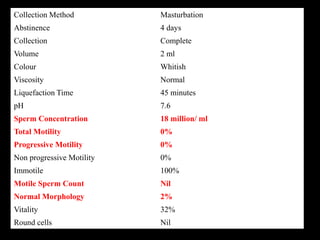
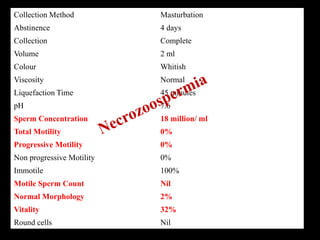
The document discusses various case scenarios regarding semen analysis results, addressing clinical significance, methods of collection, and treatment options for male fertility issues. It emphasizes the limitations of the WHO 2010 semen analysis criteria and suggests lifestyle changes, antioxidants, and medical interventions as potential aids for improving semen quality. The recommendations include thorough history taking, physical examinations, and additional tests for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.