1. Liver function tests measure three categories: direct hepatocellular damage, cholestasis, and the liver's synthetic ability.
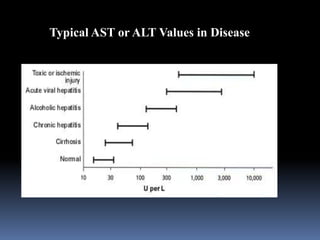
2. Transaminases like AST and ALT are elevated with hepatocyte injury from conditions like hepatitis, toxic injury, or ischemia. One-third of hepatitis C patients can have normal transaminase levels.
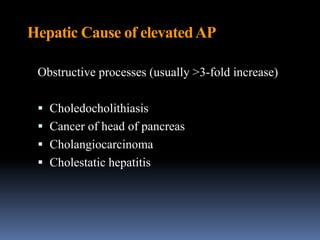
3. Cholestasis is reflected in elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels, which take longer to rise than AST/ALT in acute bile duct obstruction.