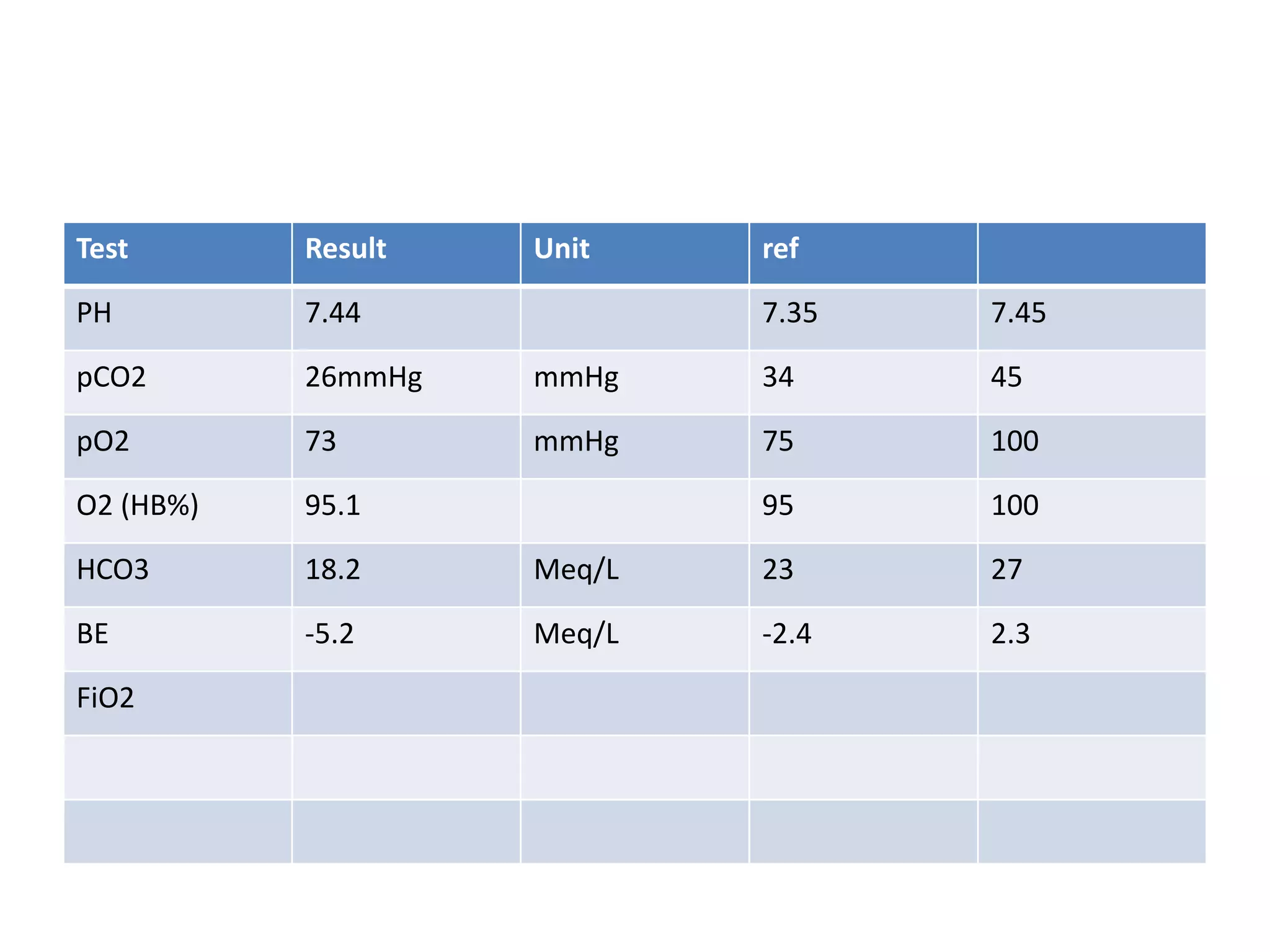
This document provides information on interpreting arterial blood gas (ABG) results, including:
1. It evaluates oxygenation by examining pO2 and SaO2 levels, ventilation by looking at pCO2 levels and production vs elimination of CO2, and acid-base balance by analyzing pH, HCO3, and BE levels.
2. Normal ranges are provided for interpreting pH, pCO2, HCO3, and BE levels to determine if the patient has respiratory or metabolic acidosis or alkalosis.
3. The document describes how to assess for compensation by seeing if other parameters have changed to correct acid-base imbalances and restore the pH to a normal range.