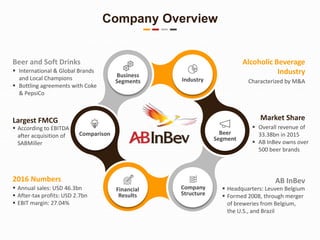
The document provides a strategic analysis of AB InBev, focusing on its competitive strategy, industry dynamics, and financial performance, emphasizing its position as the largest FMCG company post-SABMiller acquisition. It outlines the challenges and opportunities in the beer market, illustrating the company’s strengths in cost advantage and differentiation strategies. Recommendations suggest strengthening bottling agreements, pursuing M&A opportunities, and expanding into the spirits market to enhance growth and competitive advantage.