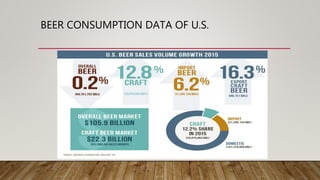
Mountain Man Brewing Co. is a market leader in West Virginia that produces one beer called Mountain Man Lager. To remain profitable amid a 2% revenue decline, the company is considering launching a light beer called Mountain Man Light to tap into the growing light beer segment. This would involve new product development, marketing, and costs of $1.65 million. The strategy could increase revenue but faces risks of high costs, competition, and difficulty building a new brand.