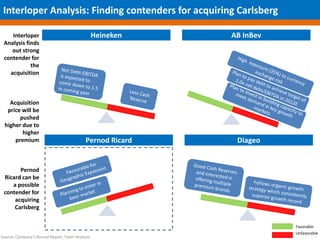
The document provides an overview of the alcoholic beverages industry with a focus on the beer market. It discusses key trends such as consolidation in the industry and growth in emerging markets. The beer market is dominated by large brewers like AB Inbev, SABMiller, and Carlsberg. The document analyzes SABMiller and Carlsberg, comparing their financials, strategies, and brand portfolios. It identifies reasons for SABMiller to acquire Carlsberg such as complementing geographical presence, segment coverage, brands, and strategies. Key risks of such an acquisition like financial risks and regulatory hurdles are also discussed.