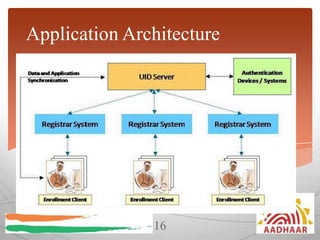
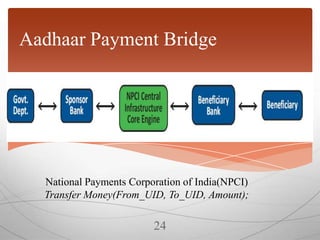
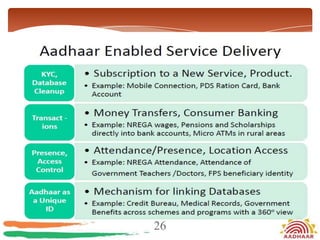
The document discusses the Aadhaar system in India, which issues a 12-digit unique identity number to all residents based on their demographic and biometric data. It describes how Aadhaar aims to provide universal identification and enable efficient delivery of services by eliminating duplicate verification. The process of obtaining an Aadhaar card and the required documents are outlined. The numbering system, privacy measures, technology architecture and various services that use Aadhaar authentication like banking, pensions and welfare schemes are also summarized.