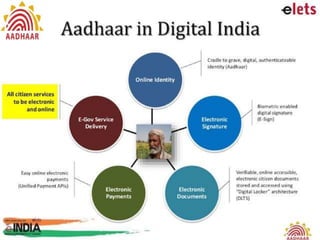
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) was established in 2009 to provide a unique identity number to all Indian residents called Aadhaar. The UIDAI is an agency of the central government led by Nandan Nilekani. The vision of UIDAI is to empower residents with a unique identity and digital authentication platform. Aadhaar is a 12-digit random number associated with minimal resident data and biometrics. It is designed to increase efficiency, transparency and delivery of services. Aadhaar can help reduce leakage in welfare services, enable direct benefit transfers and financial inclusion through linking to bank accounts. However, some issues around data privacy and protection remain.