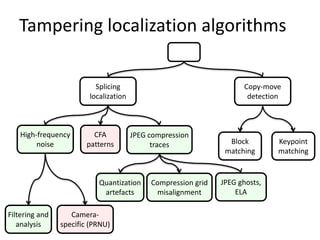
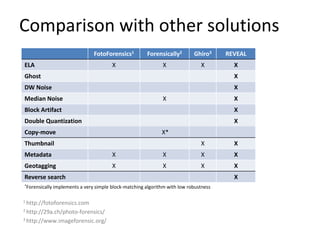
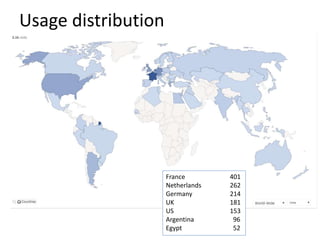
The document discusses a web-based service for detecting image tampering, detailing various types of tampering such as splicing, inpainting, and copy-move. It outlines the development of algorithms for tampering localization and evaluation through quantitative and qualitative methodologies, highlighting existing limitations and future plans for improvement. The tool is available for public testing and aims to incorporate advanced features and deep learning techniques in its future iterations.