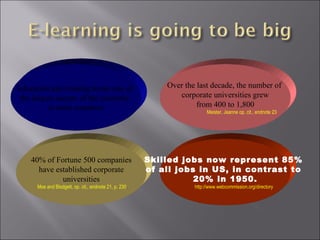
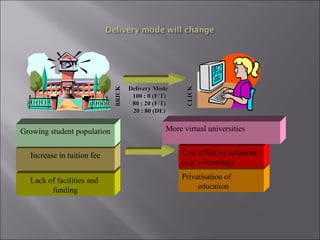
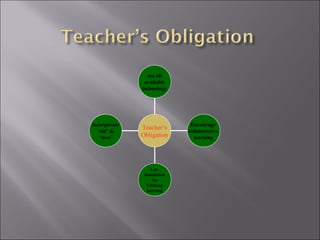
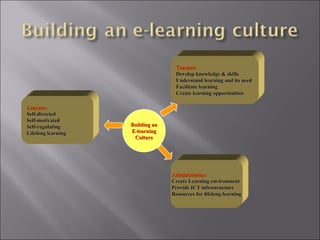
The document discusses the transformative impact of e-learning and internet technologies on education, projecting significant growth in the e-learning market from $2.2 billion to $11.4 billion by 2003. It highlights the shift from traditional classrooms to digital environments, the rise in corporate universities, and the necessity for educational institutions to adapt to new learning models. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of ICT infrastructure and collaborative learning in fostering lifelong learning and improving educational standards.