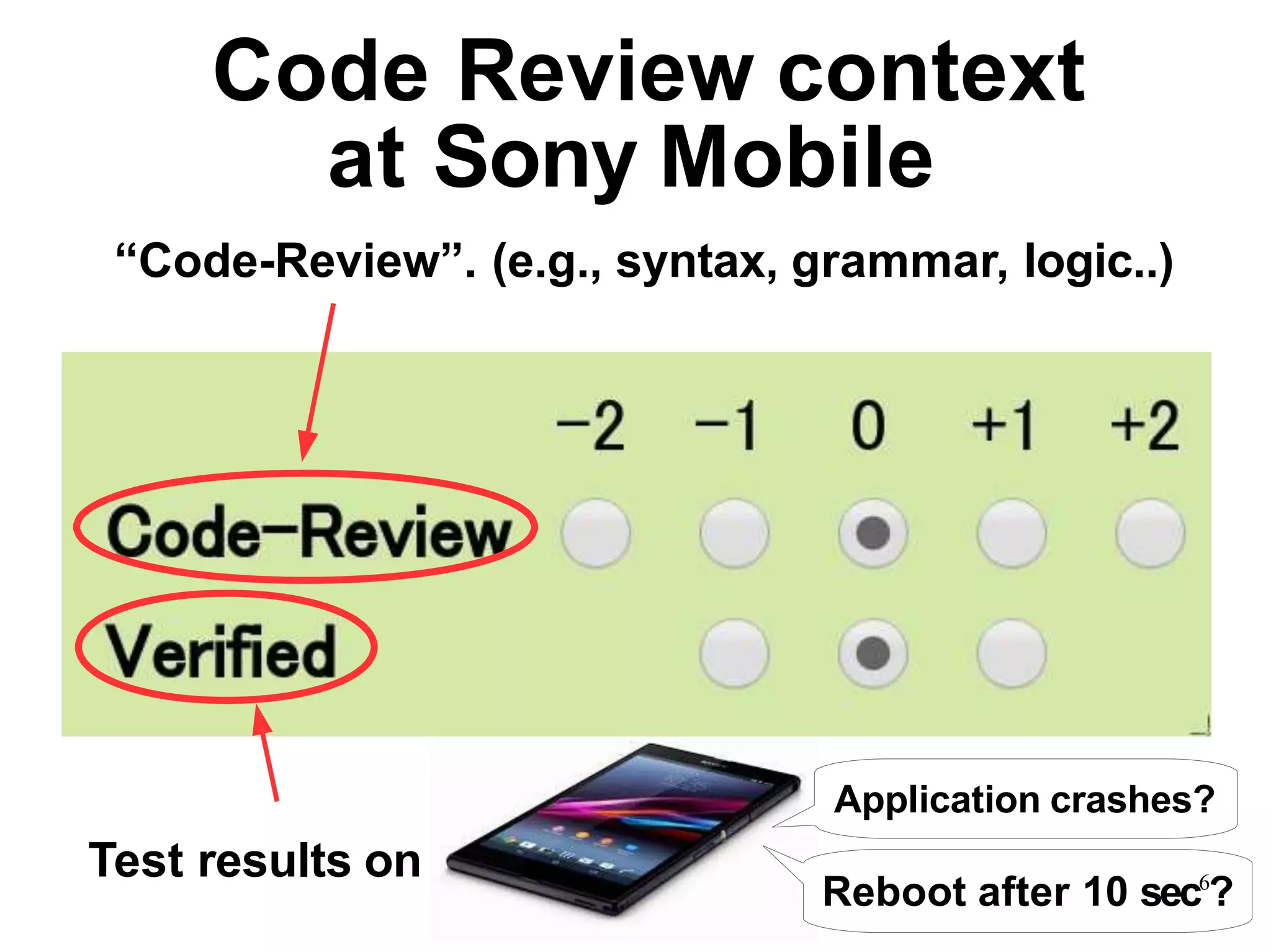
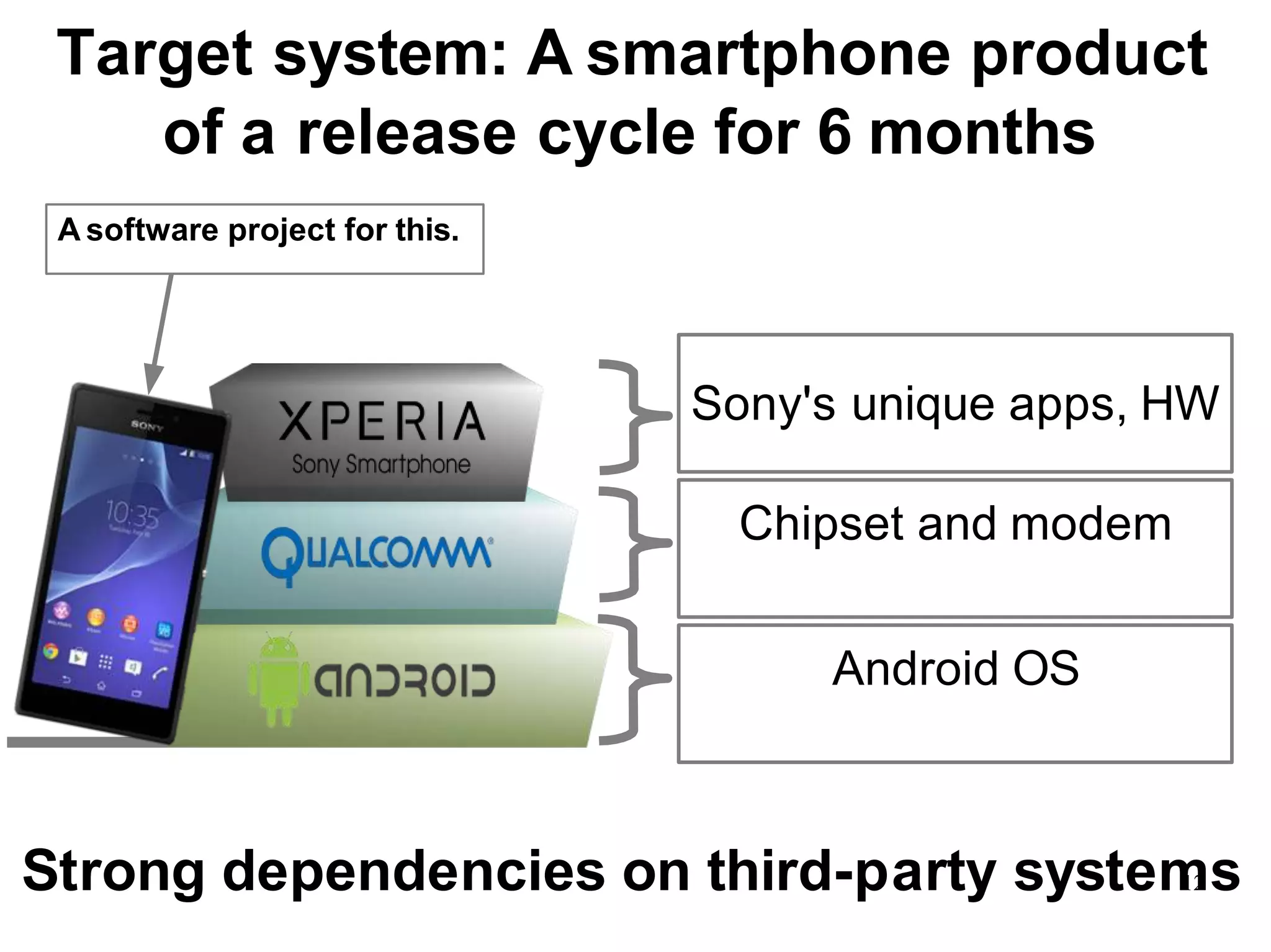
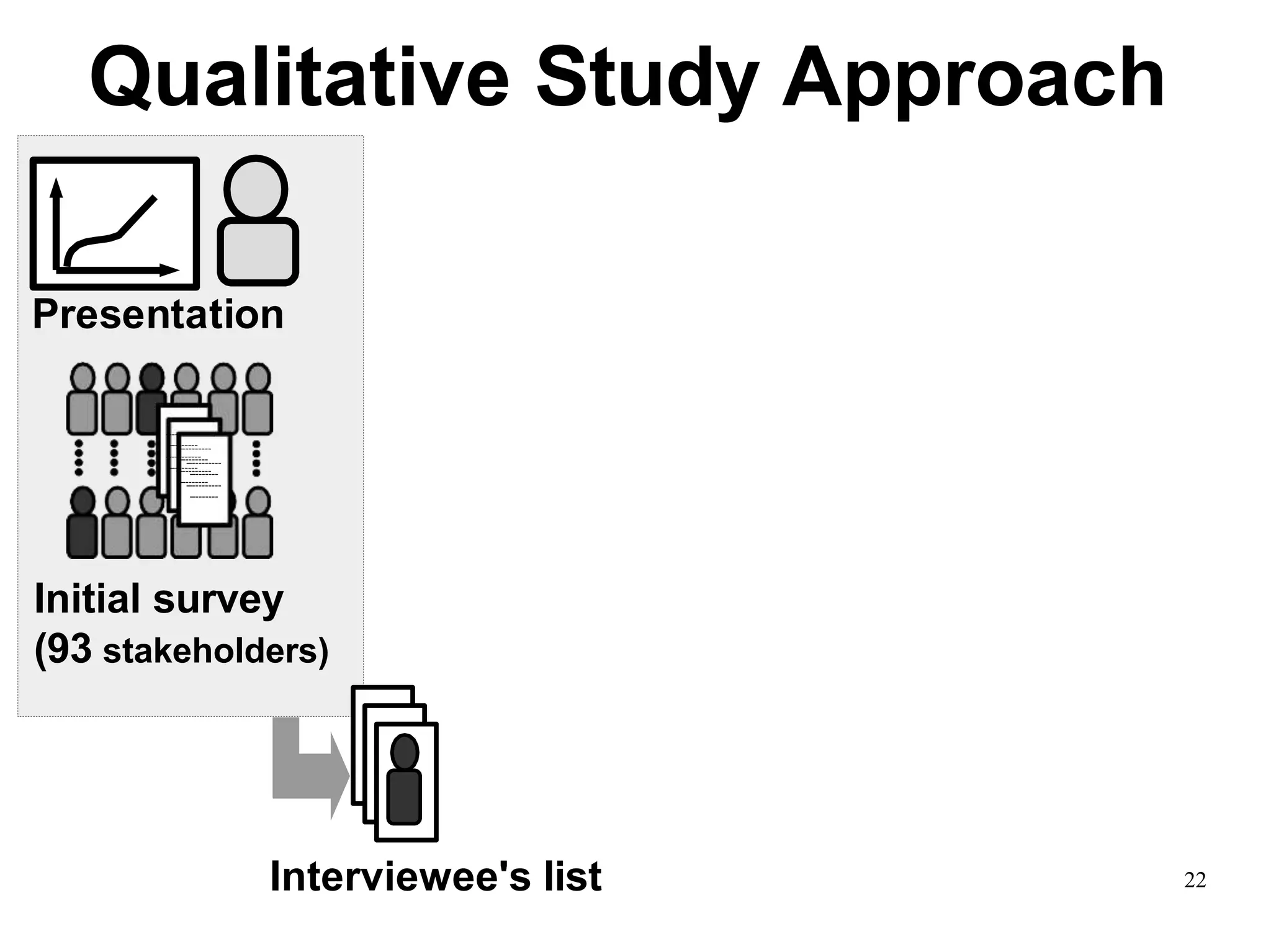
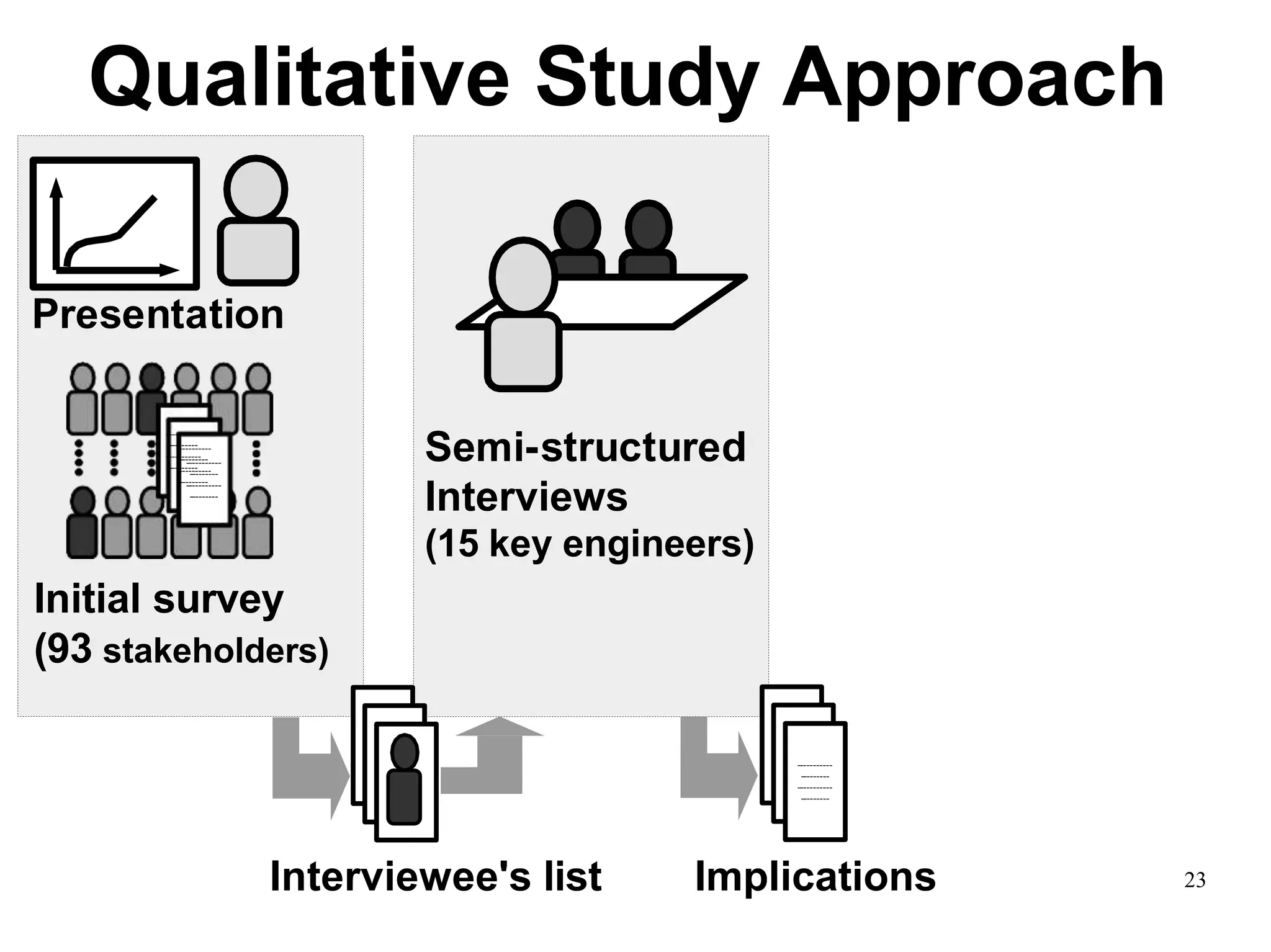
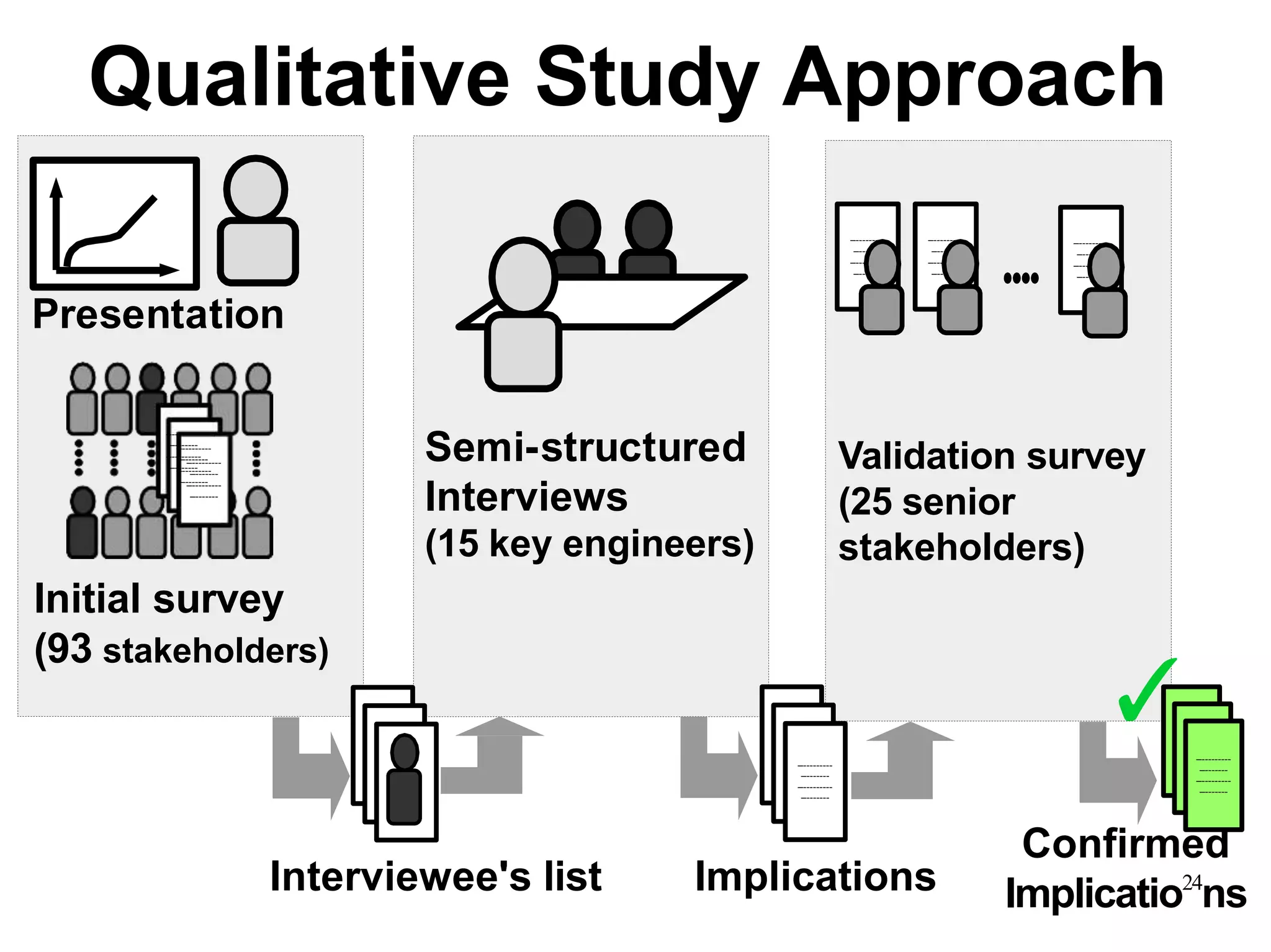
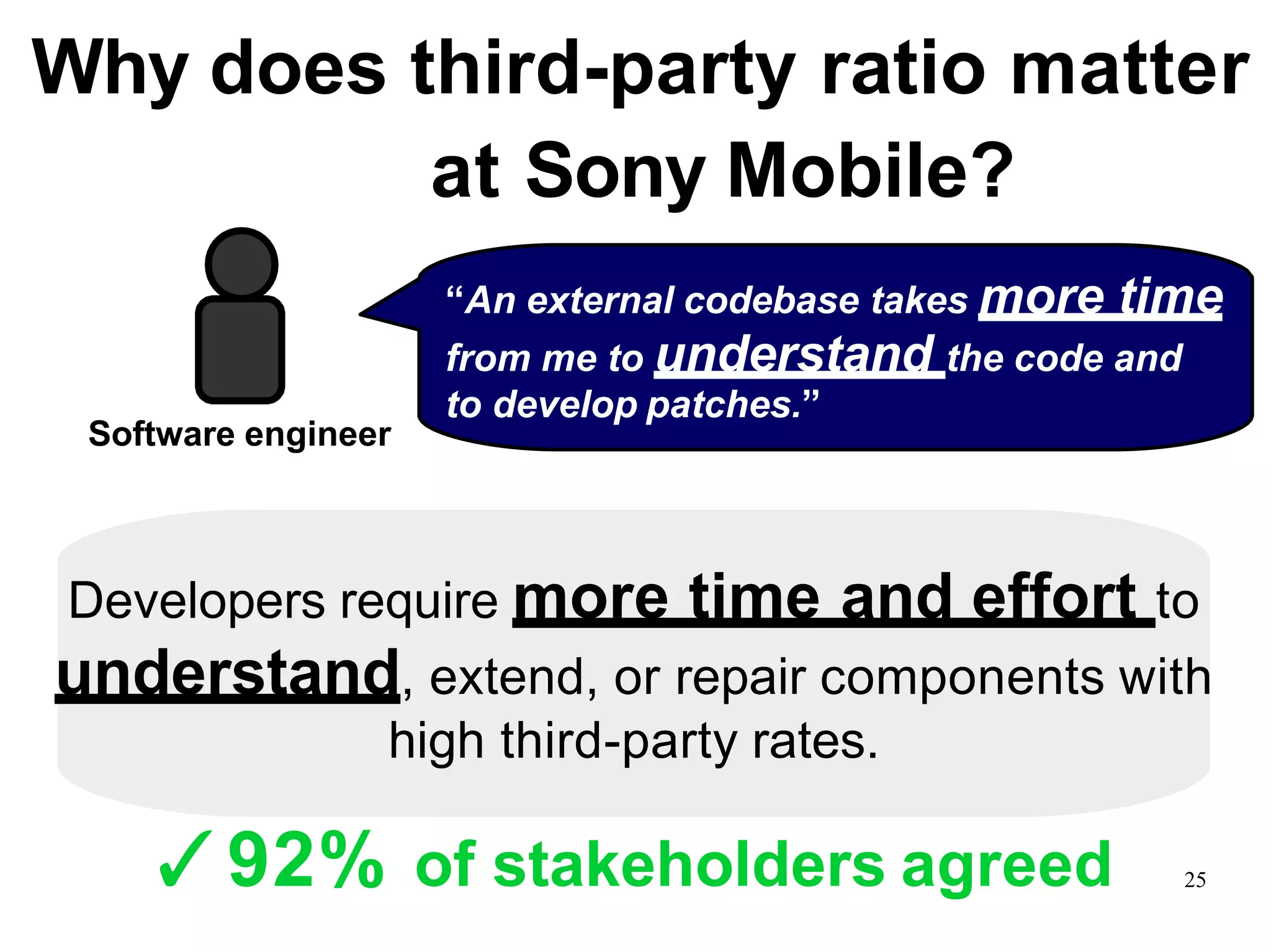
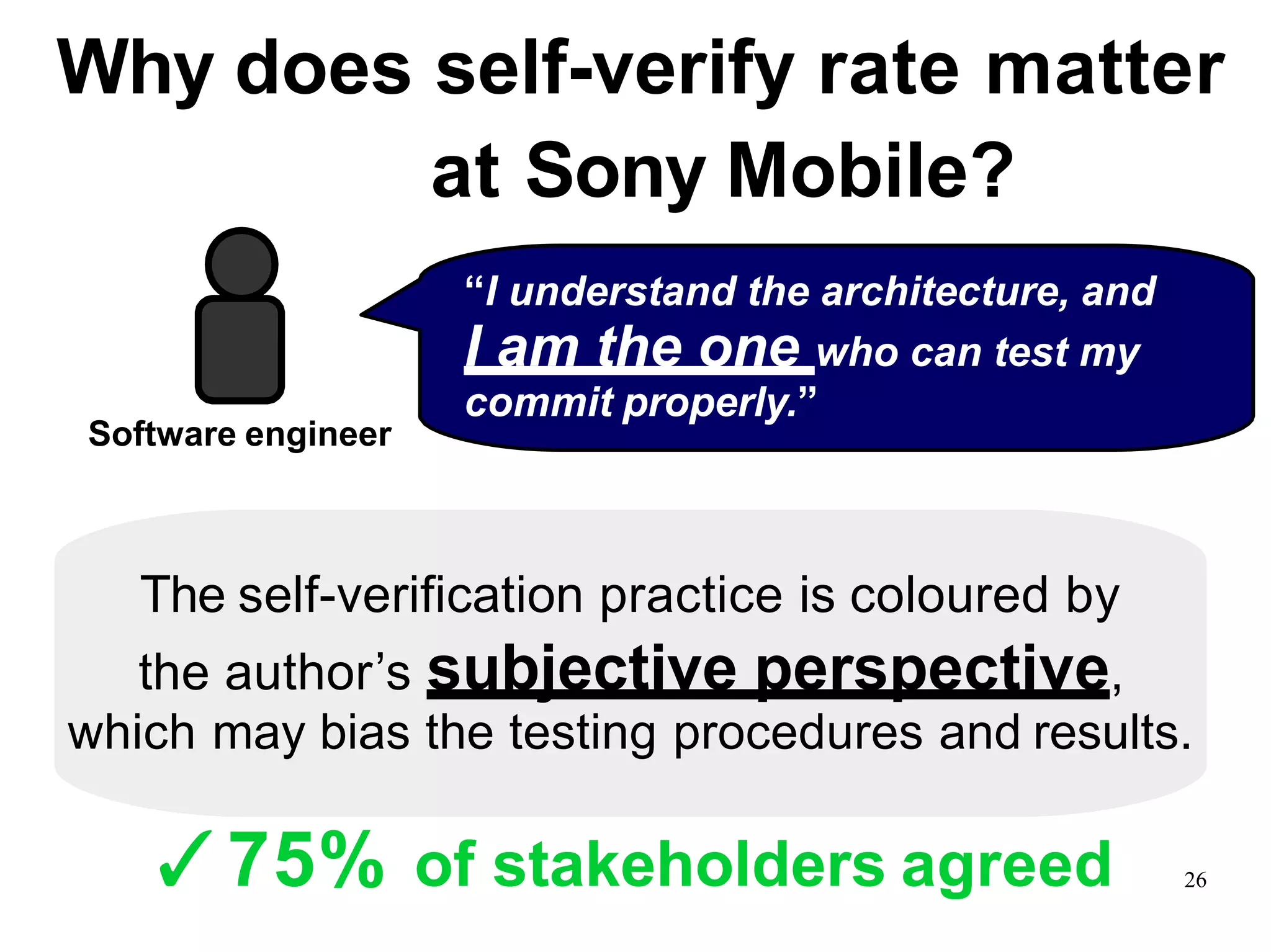
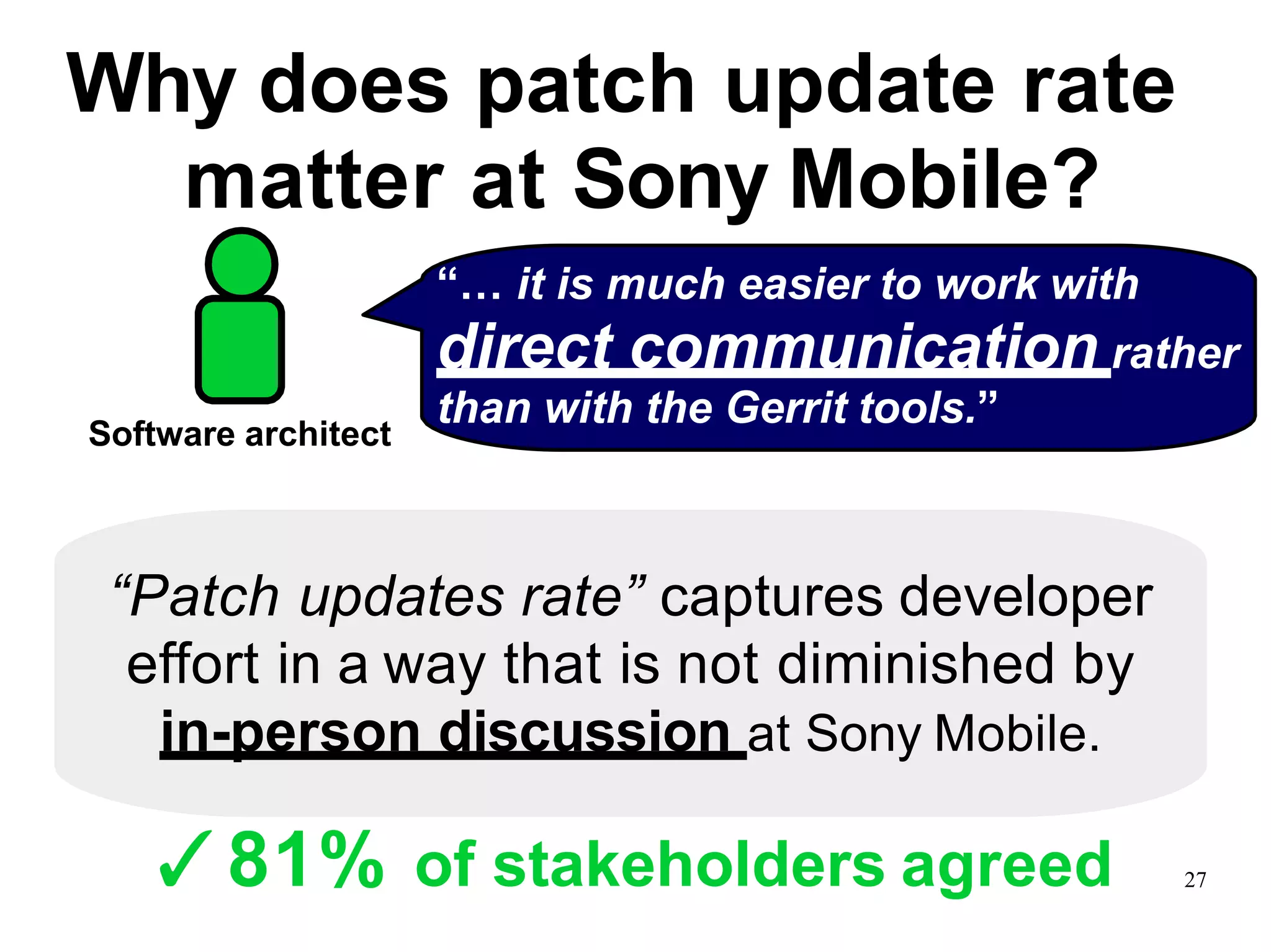
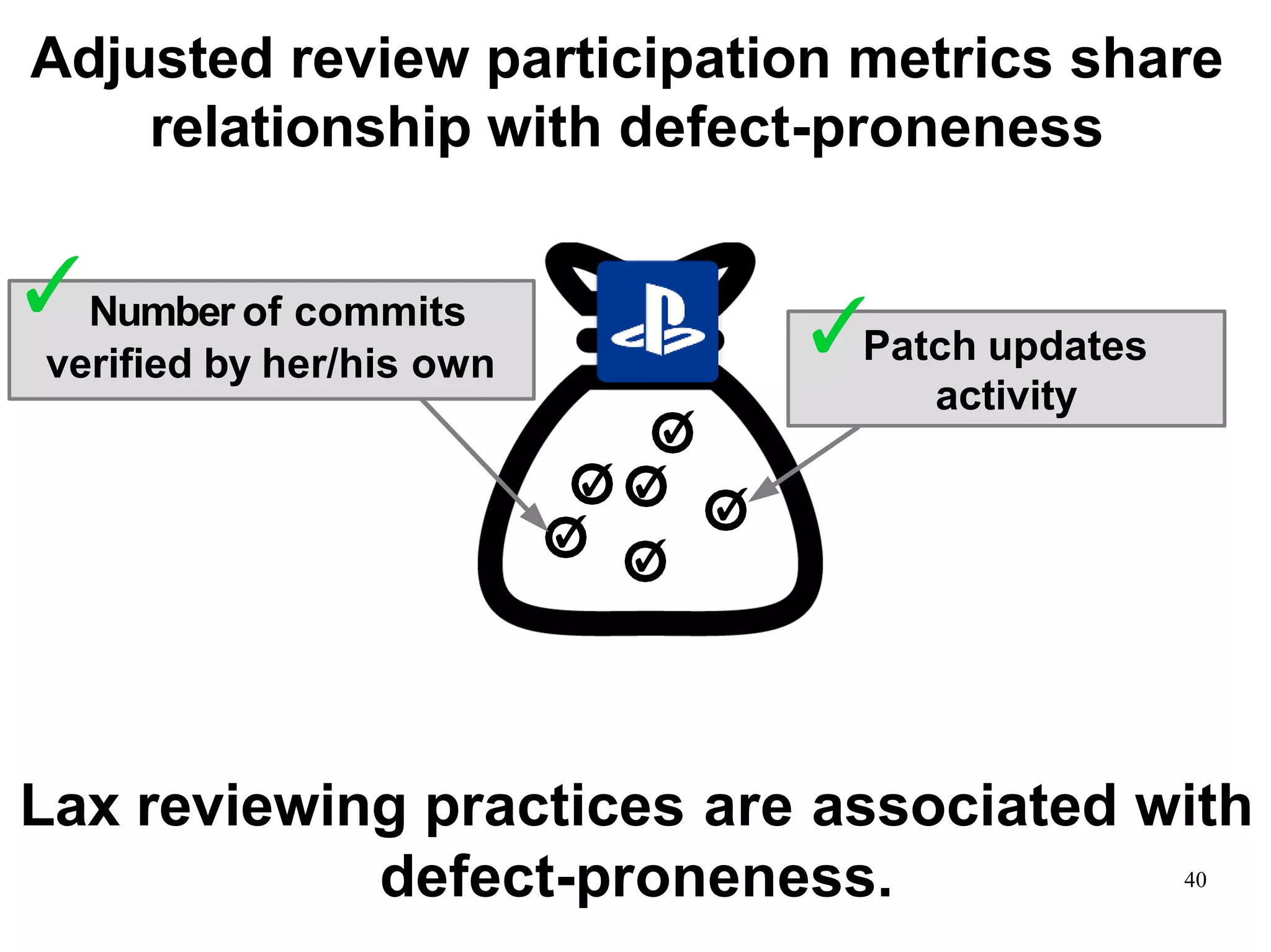
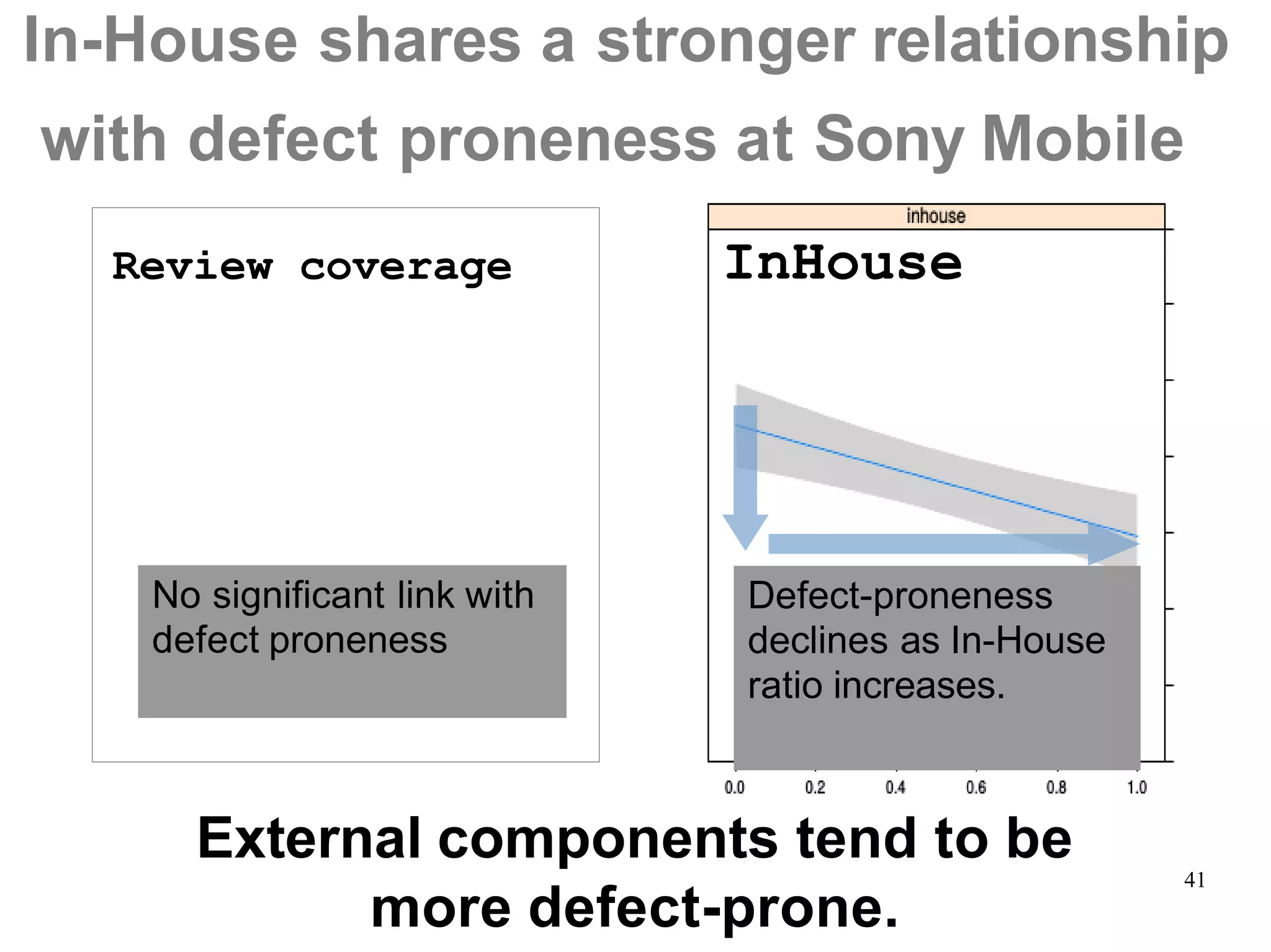
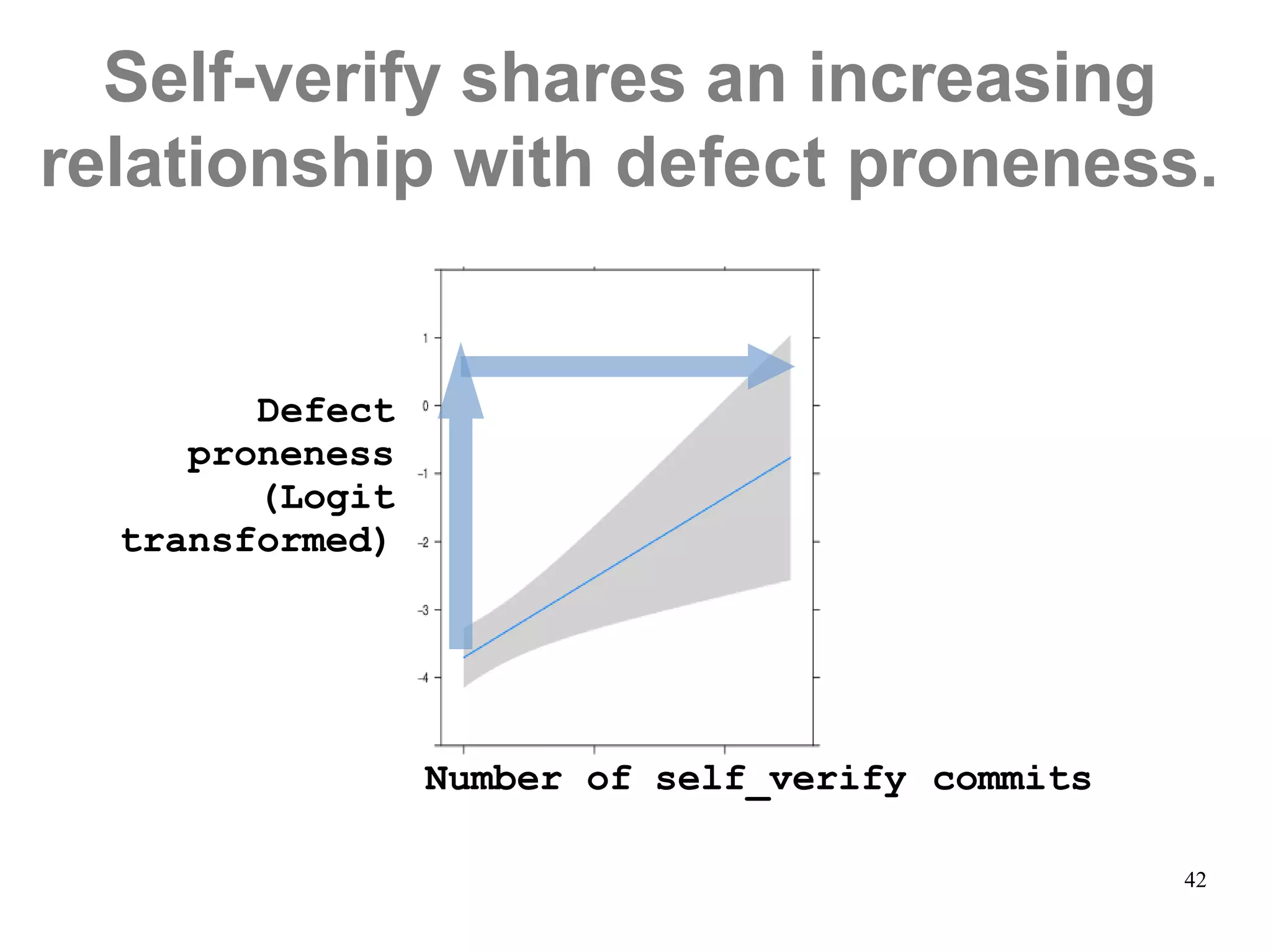
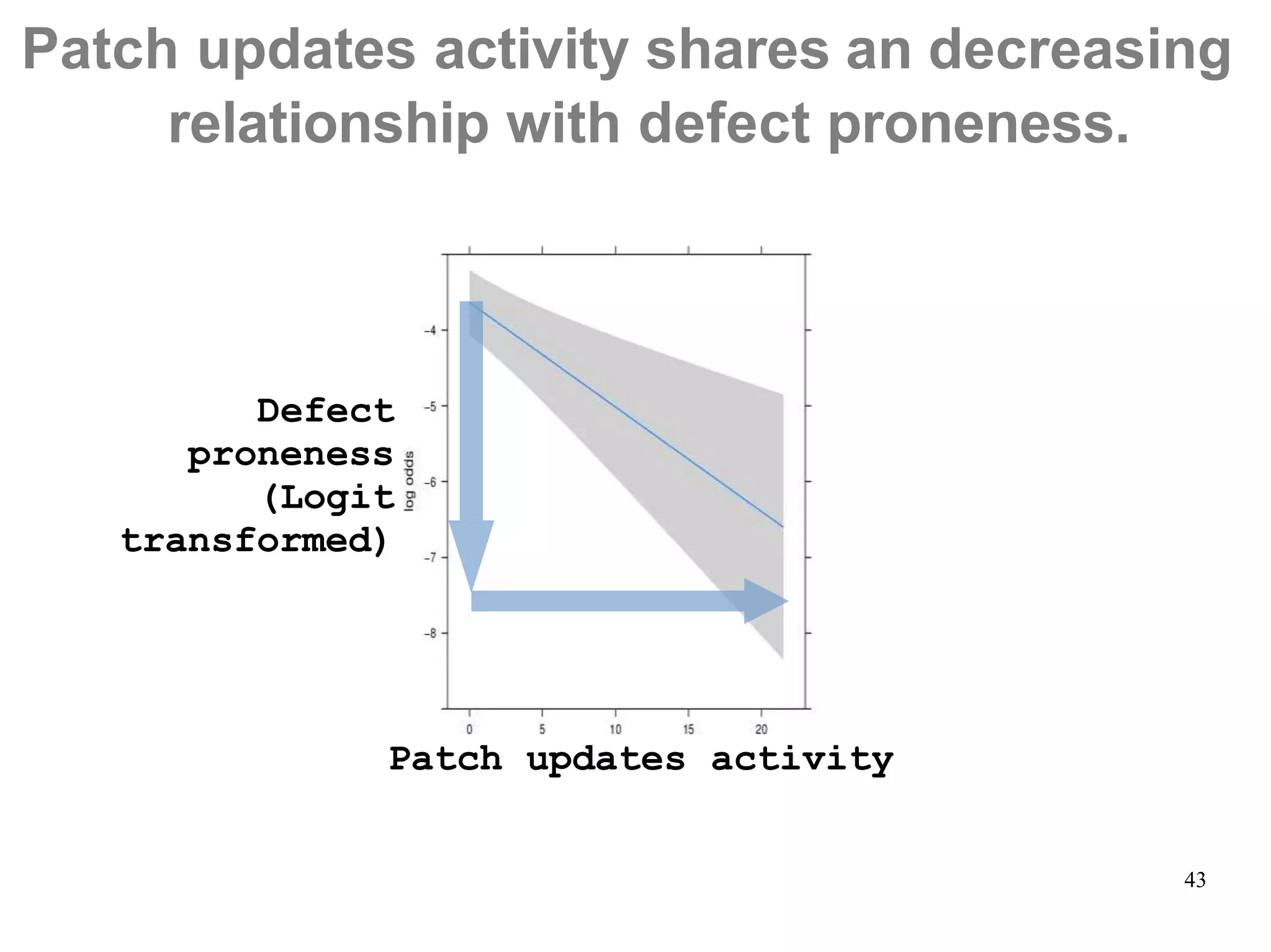
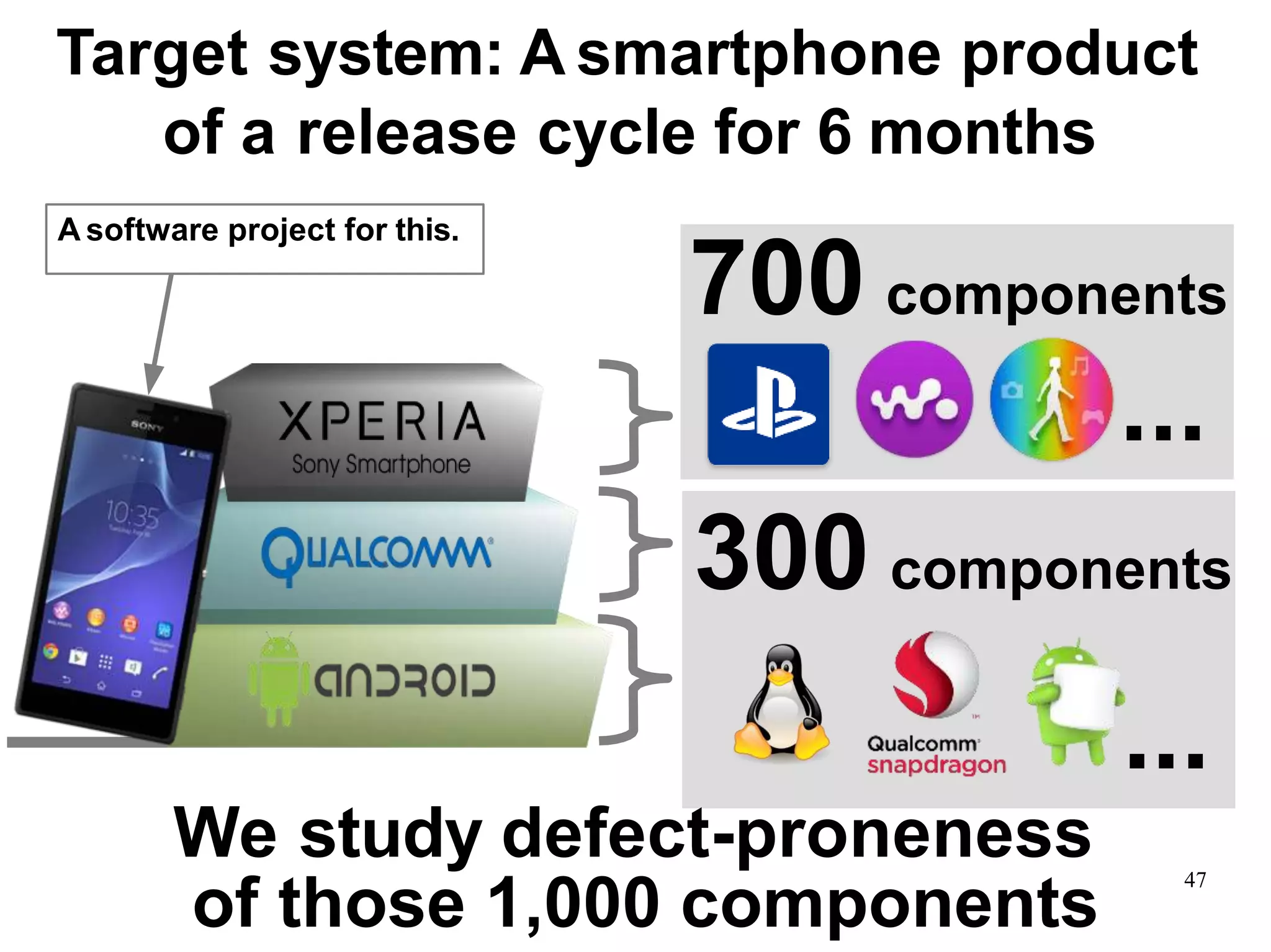
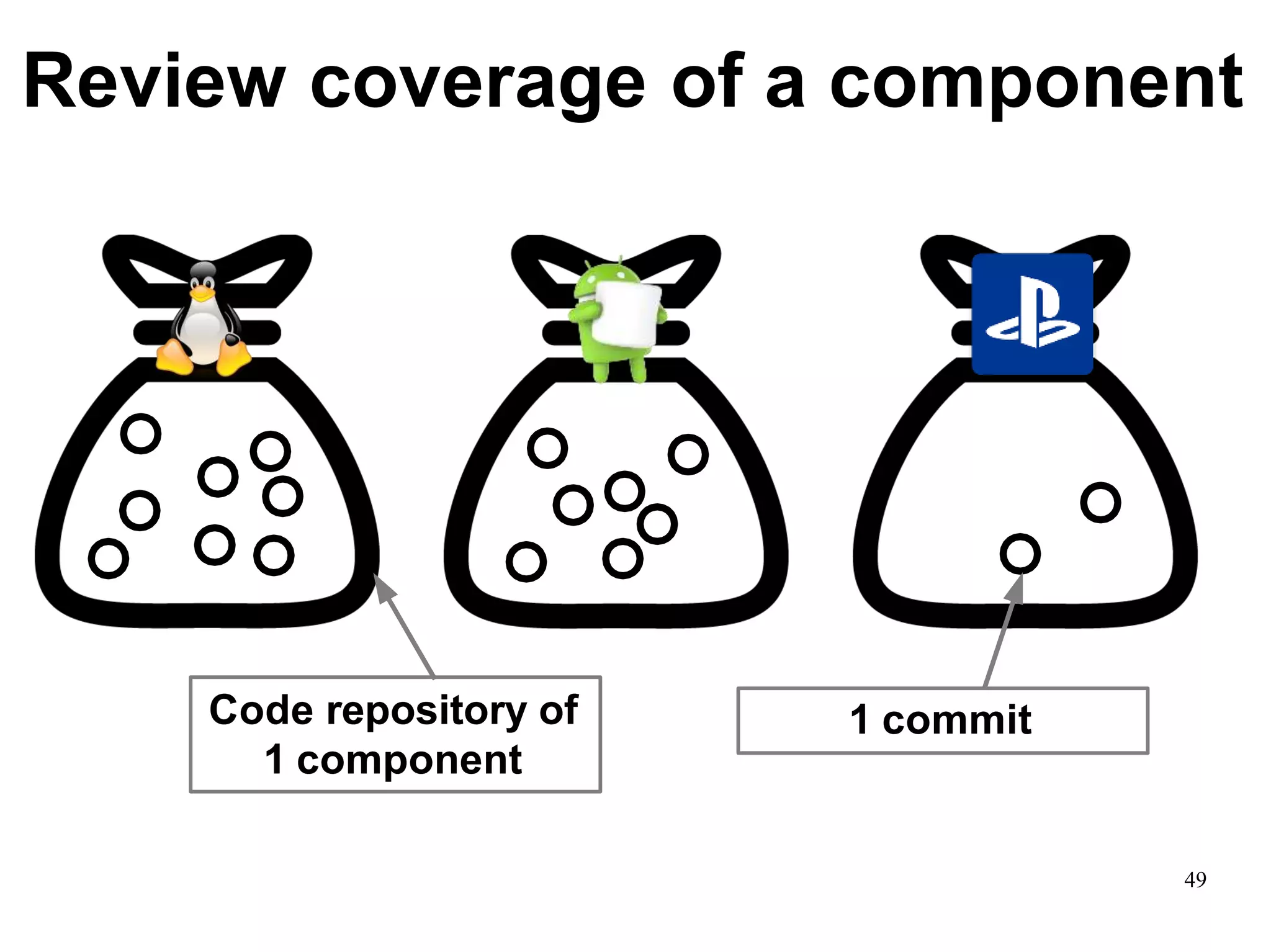
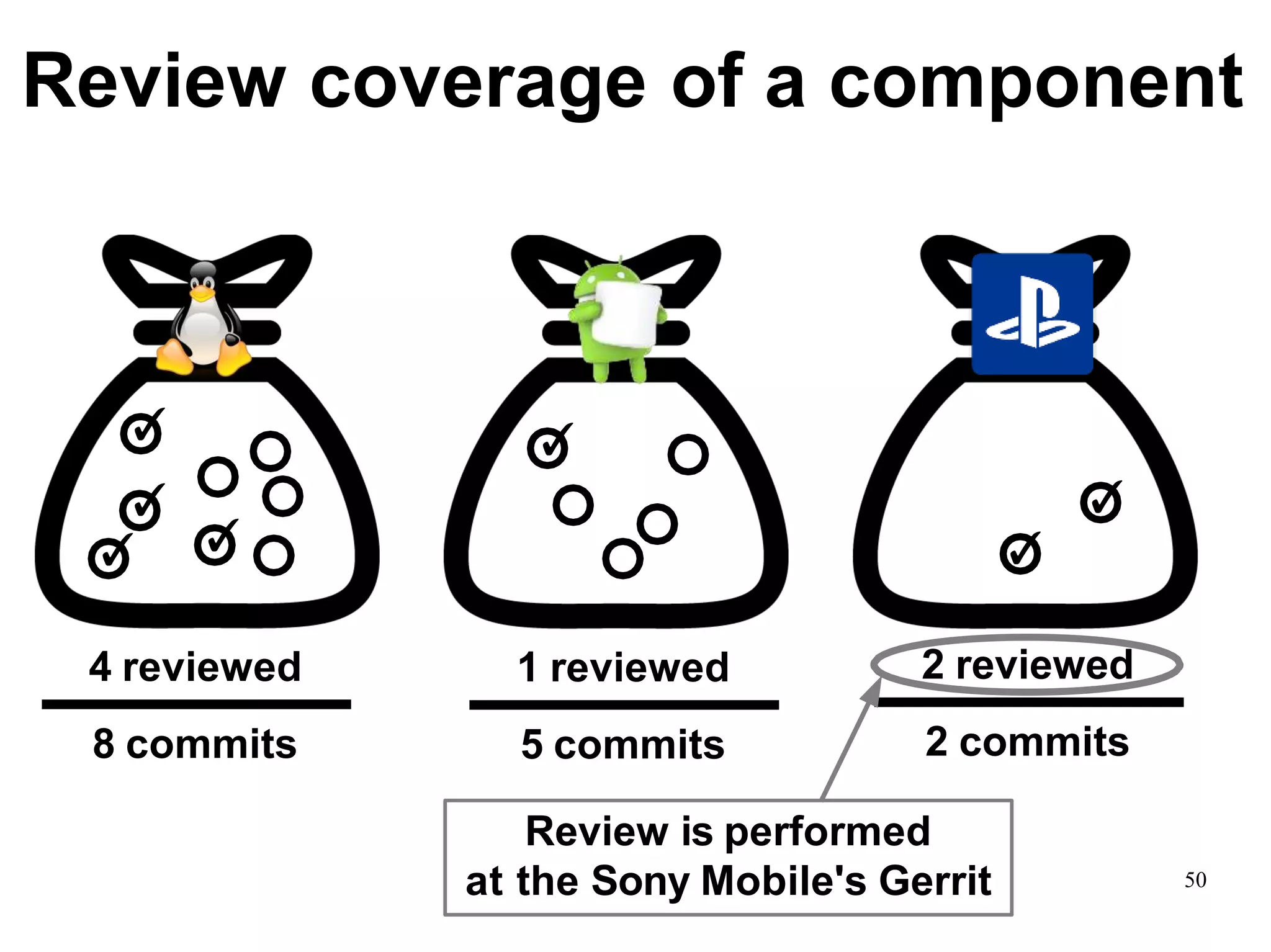
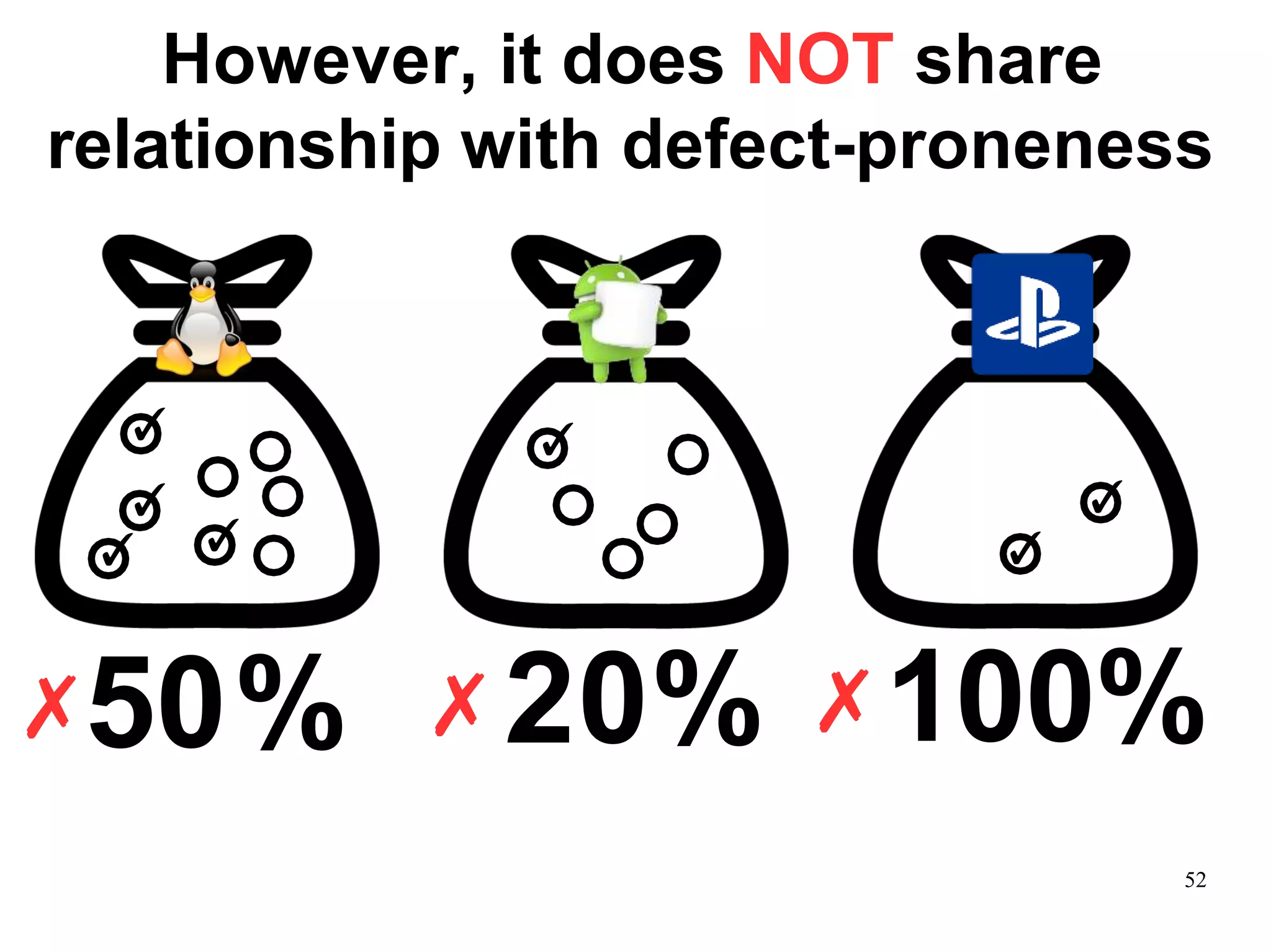
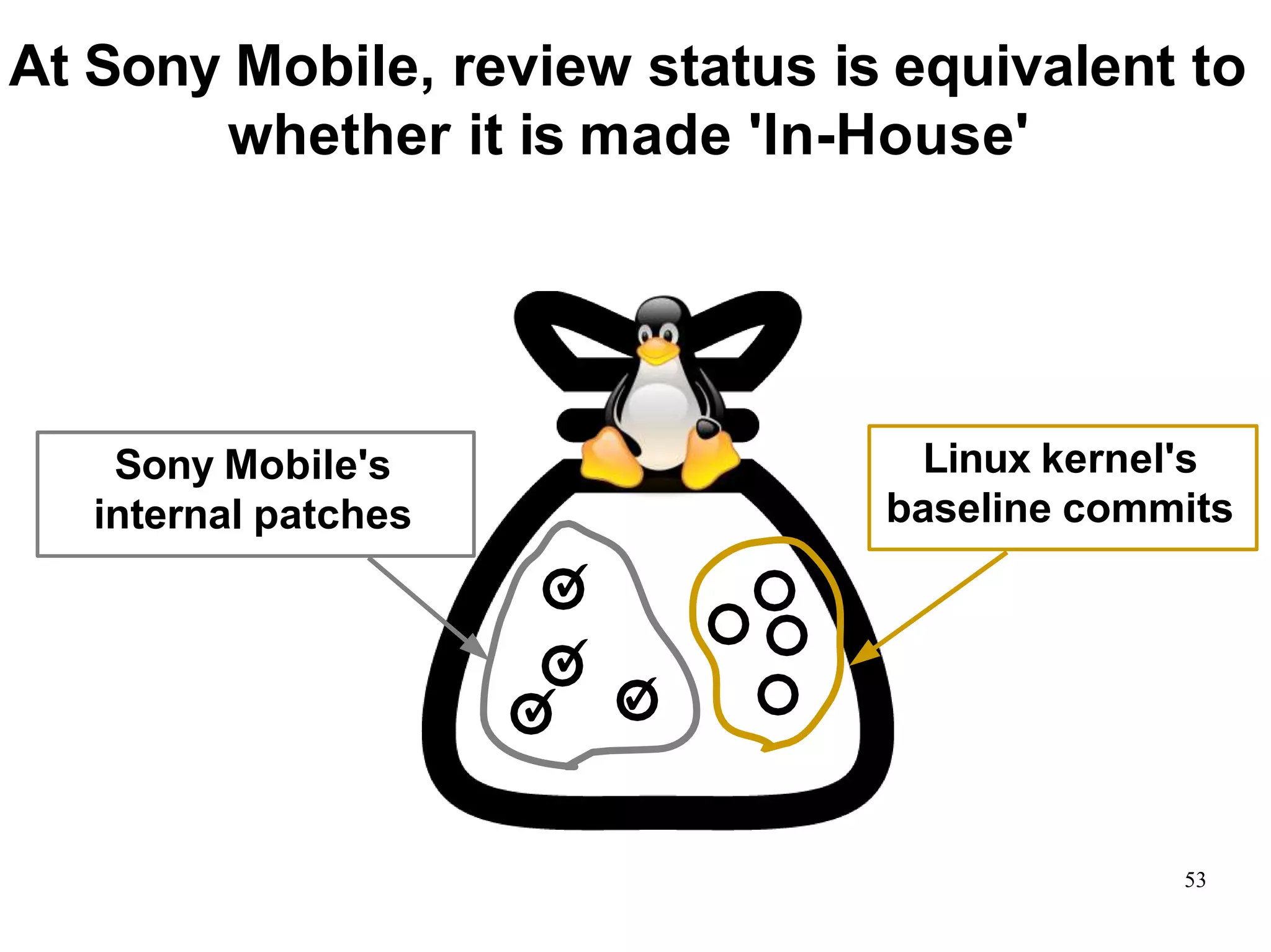
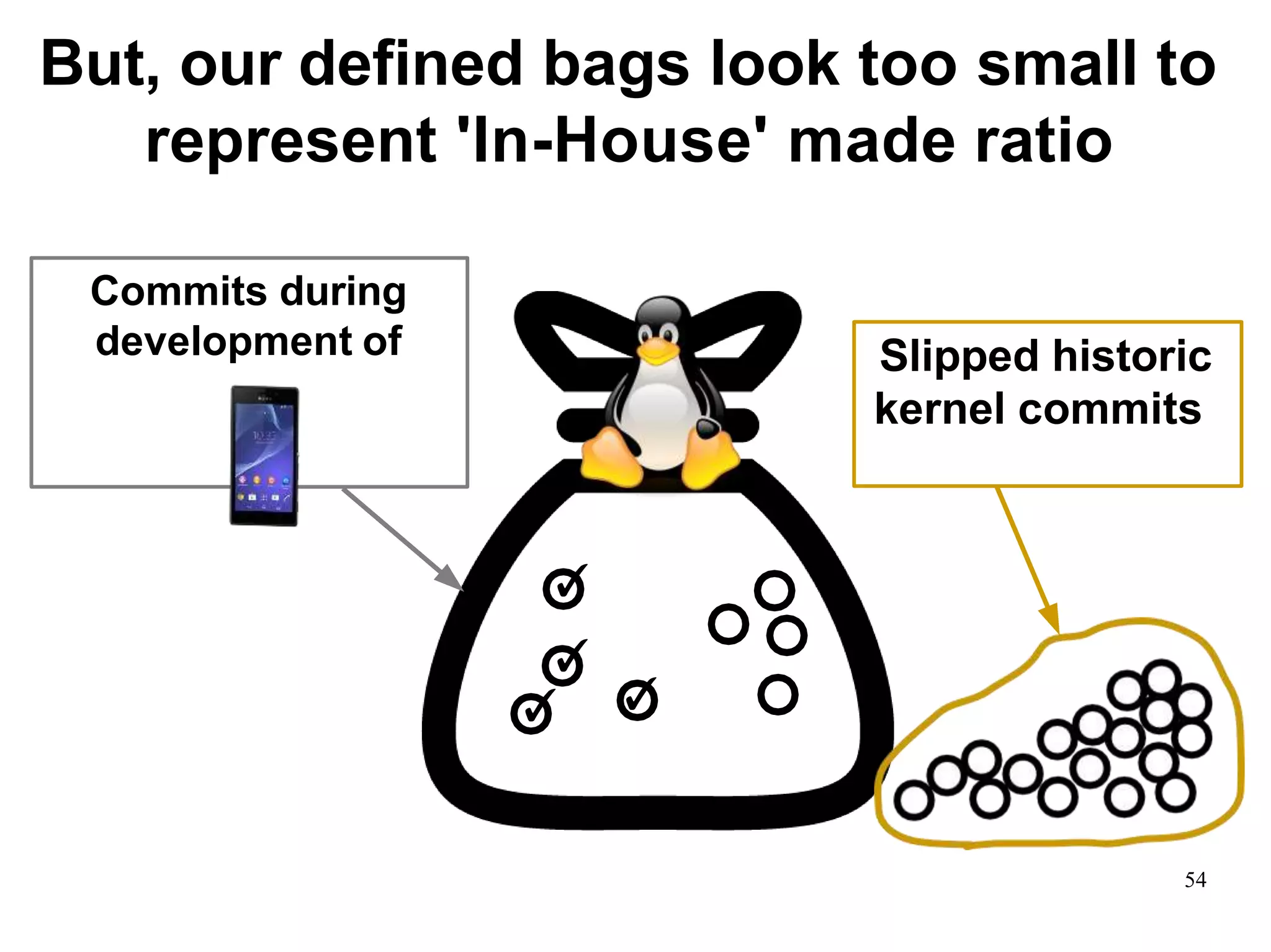
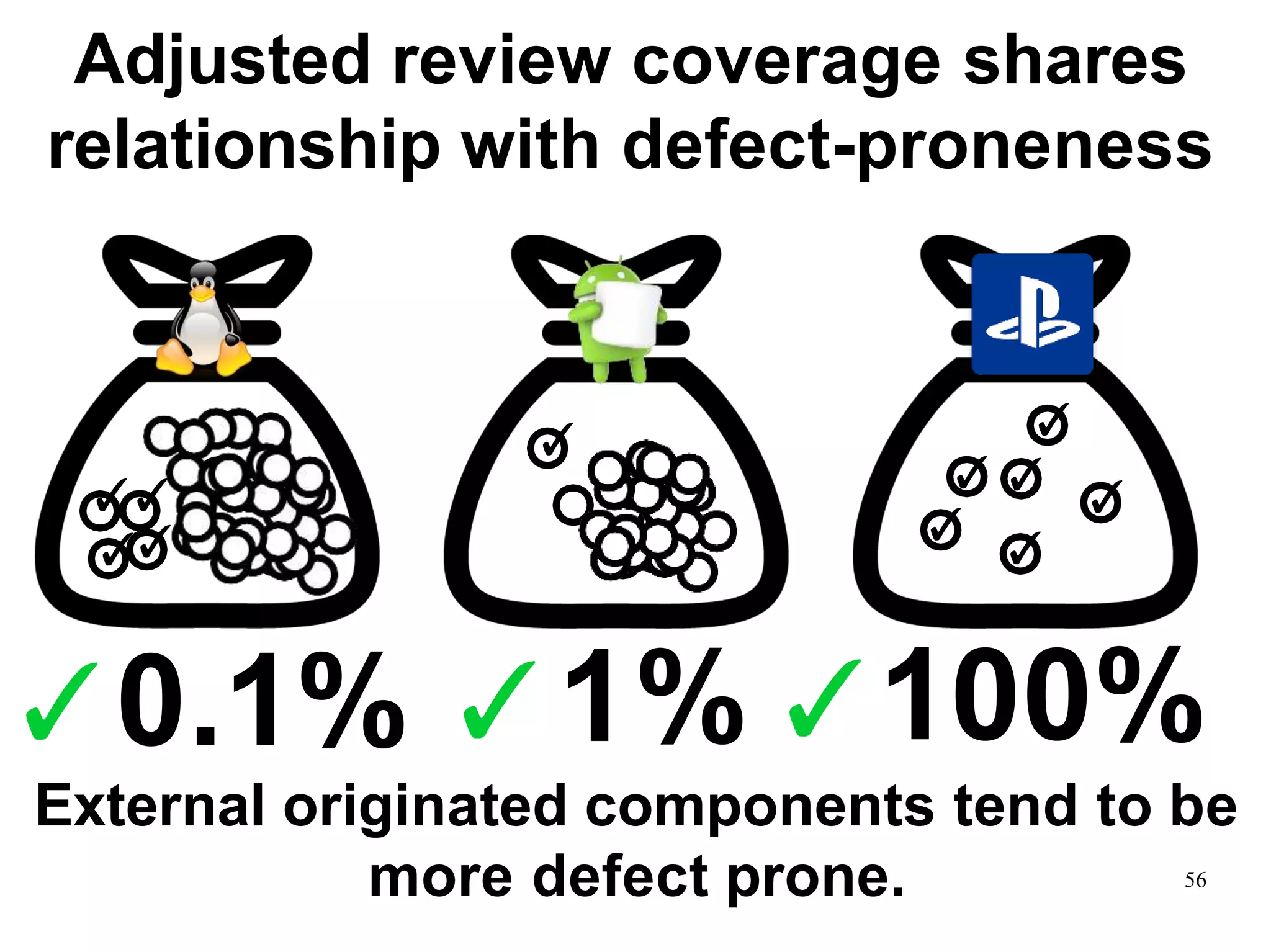
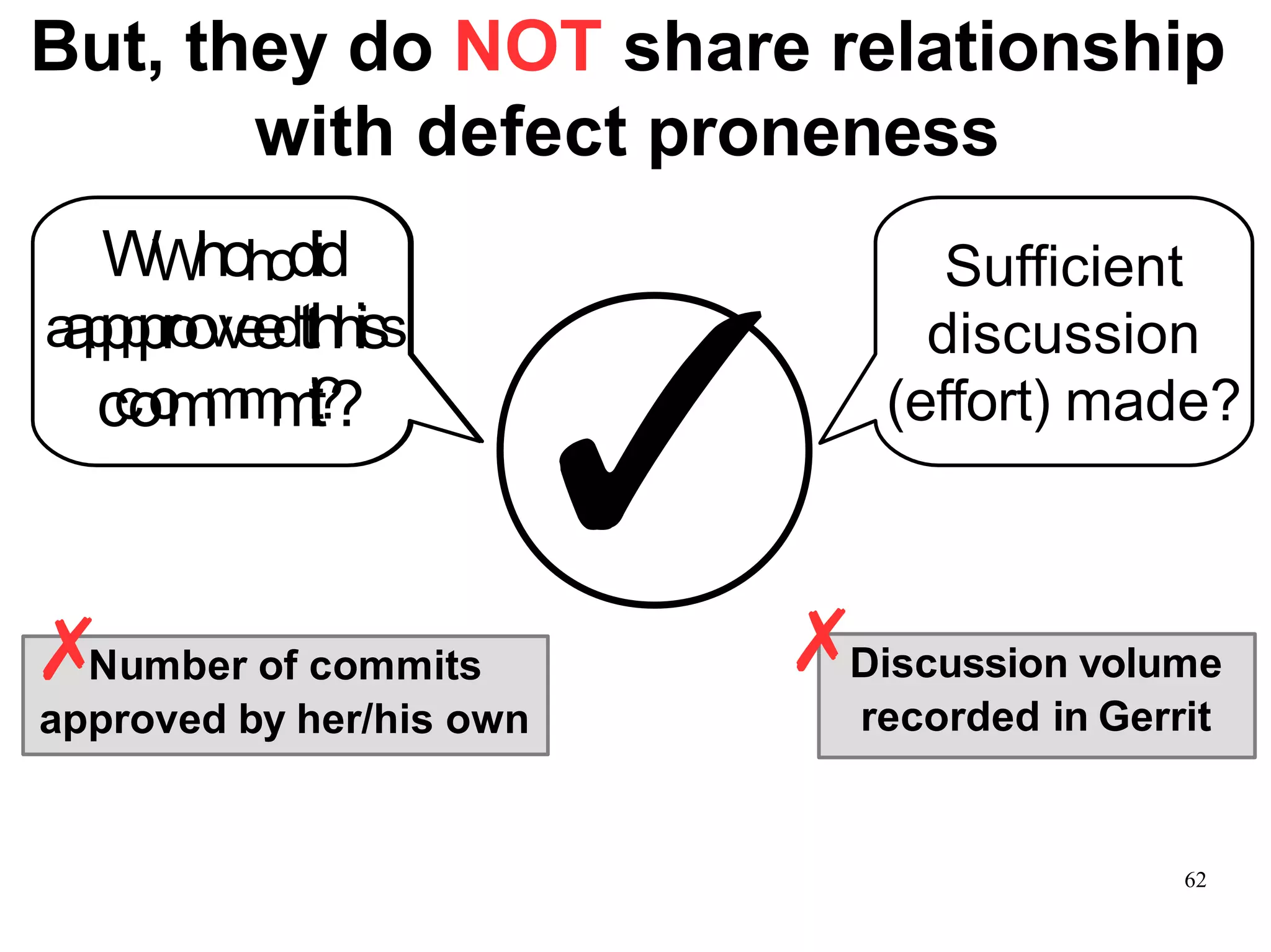
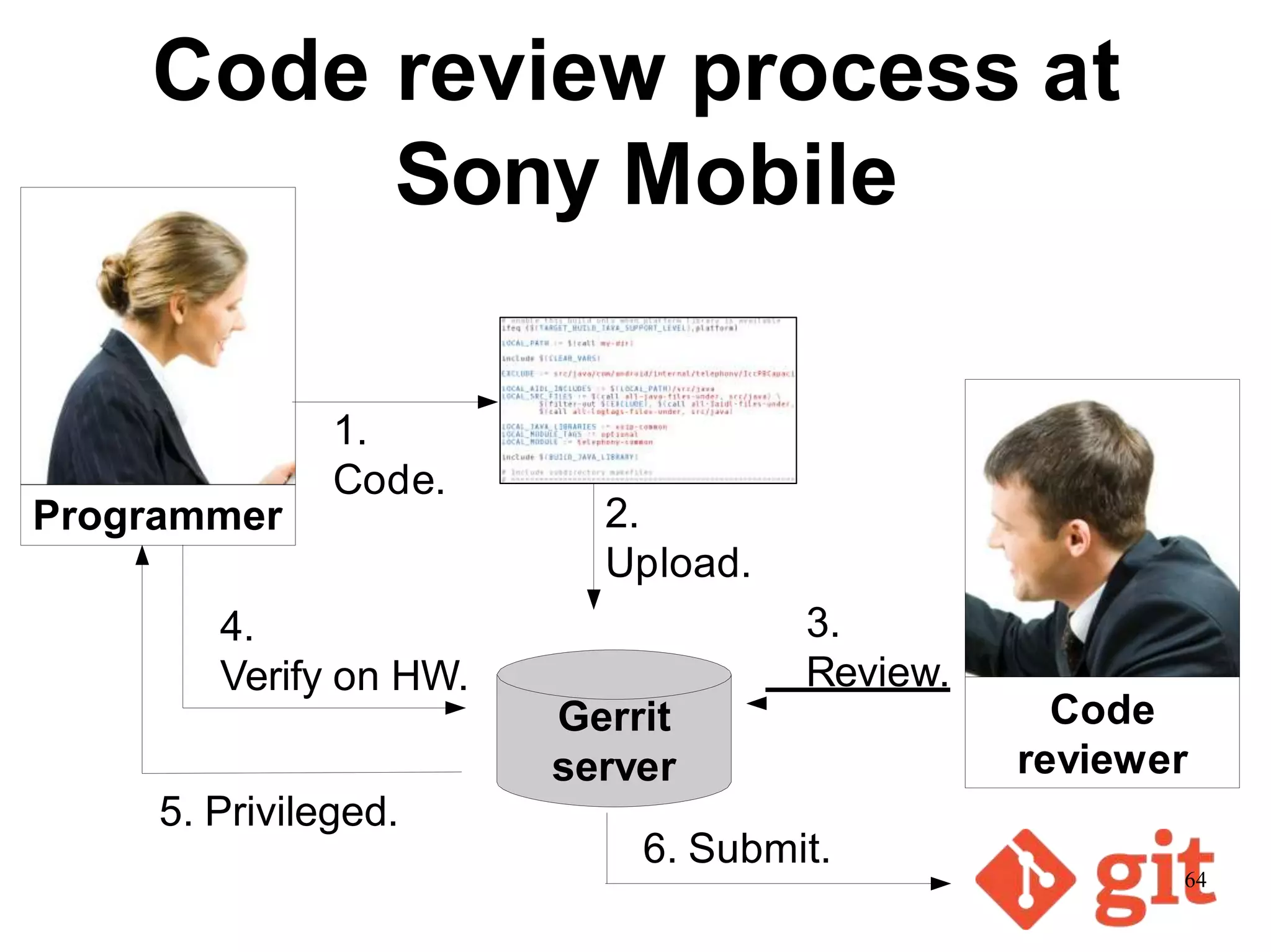
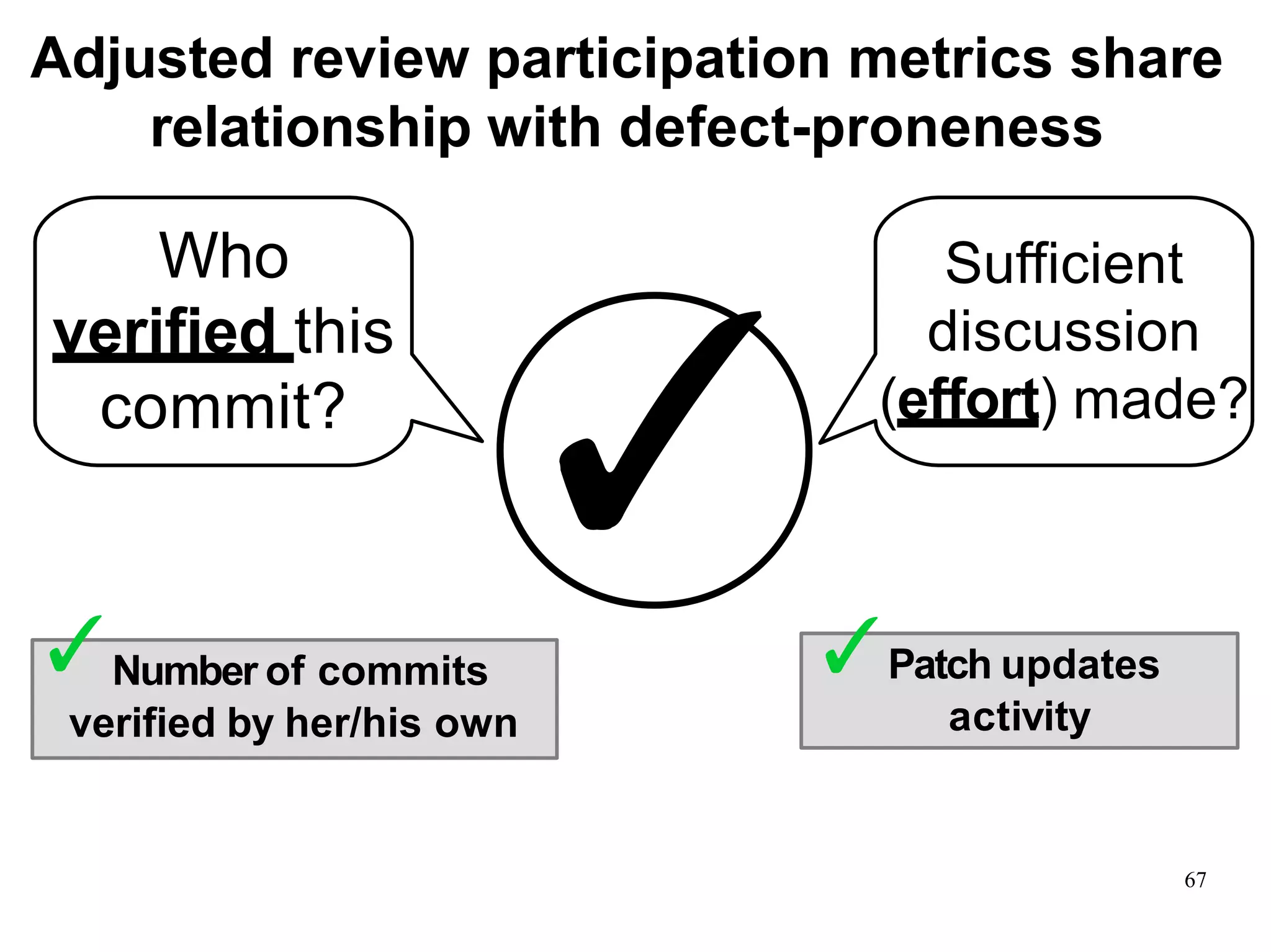
Sony Mobile uses code review tools like Gerrit to facilitate code reviews of commits. The study found that components with a higher ratio of third-party code and those where developers frequently self-approved or self-verified their own code without peer review were more defect-prone. Additionally, components with high rates of code patches after initial approval tended to be less defect-prone. Qualitative interviews with developers validated these findings and indicated that external code takes more time and effort to understand, third-party bias may impact self-reviews, and in-person communication improves code quality over tools alone. Sony Mobile is now discouraging self-verification, encouraging passive reviewers to participate more, and focusing QA testing on external code coverage.