The document discusses different approaches to measuring software quality, including:
1. ISO 9126 which defines 6 quality factors: functionality, reliability, usability, efficiency, maintainability, and portability.
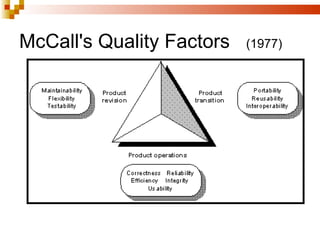
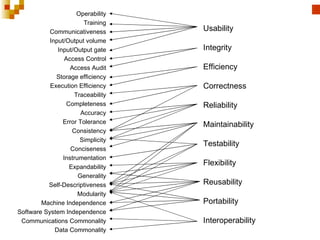
2. McCall's quality factors from 1977 which defines 11 factors and provides examples for each.
3. IEEE 982 which defines 9 classes of reliability measures including product measures like errors/faults/failures and process measures like management control.
The document emphasizes that quality factors should be defined in requirements and measuring them indicates where improvement is needed.