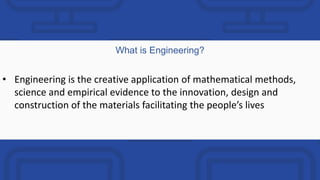
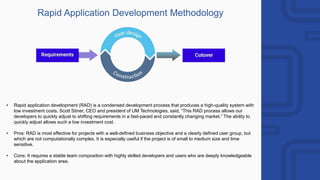
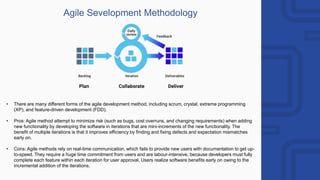
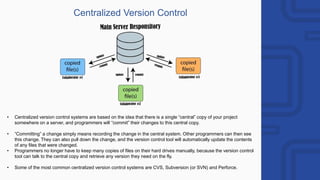
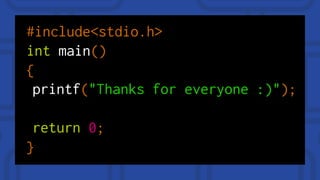
The document provides a comprehensive overview of engineering and software engineering, defining the roles and responsibilities of engineers, particularly software engineers. It discusses the importance of software engineering principles, methodologies, and the differences between computer science and software engineering, alongside the pros and cons of being a software engineer. Additionally, it covers career opportunities, educational requirements, and the concept of version control in software development.