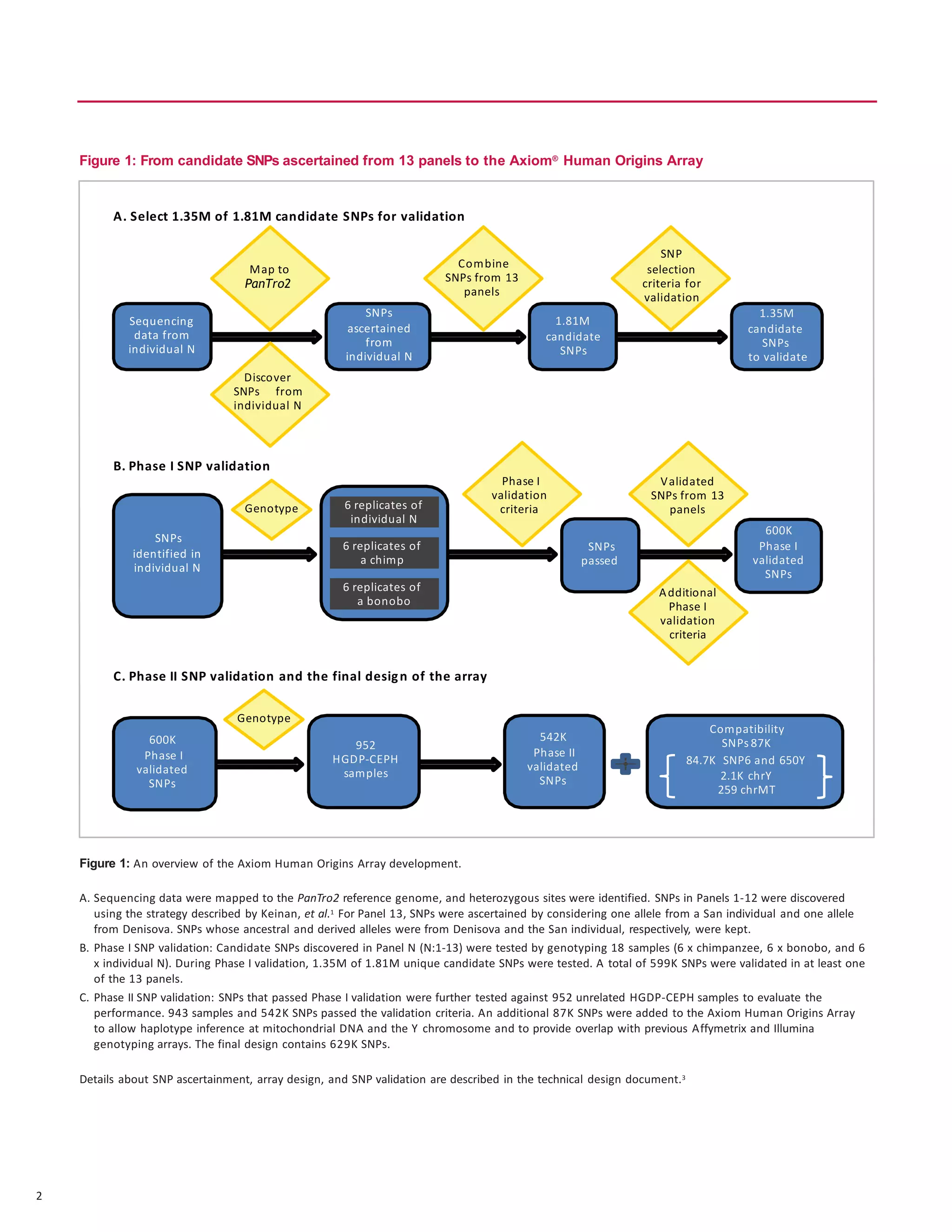
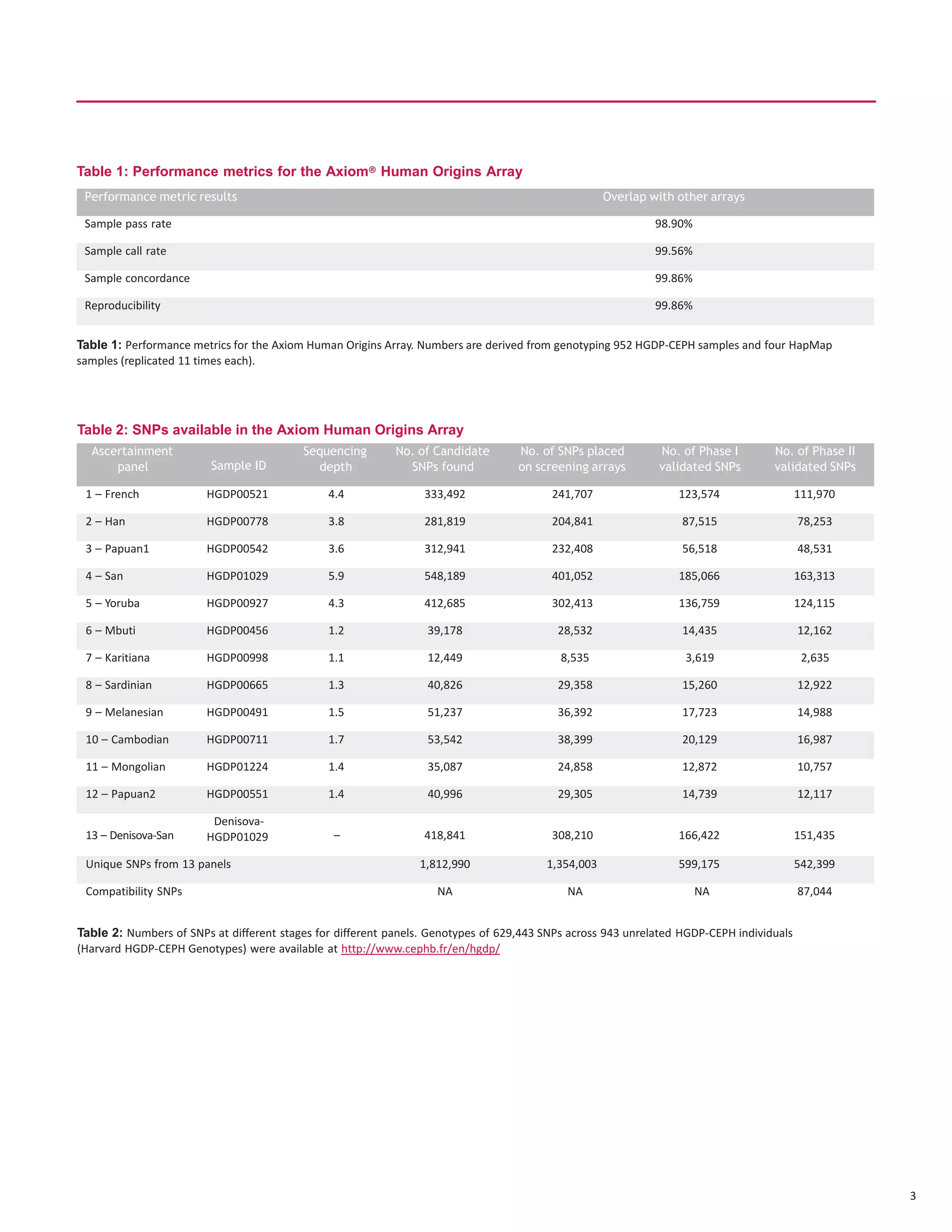
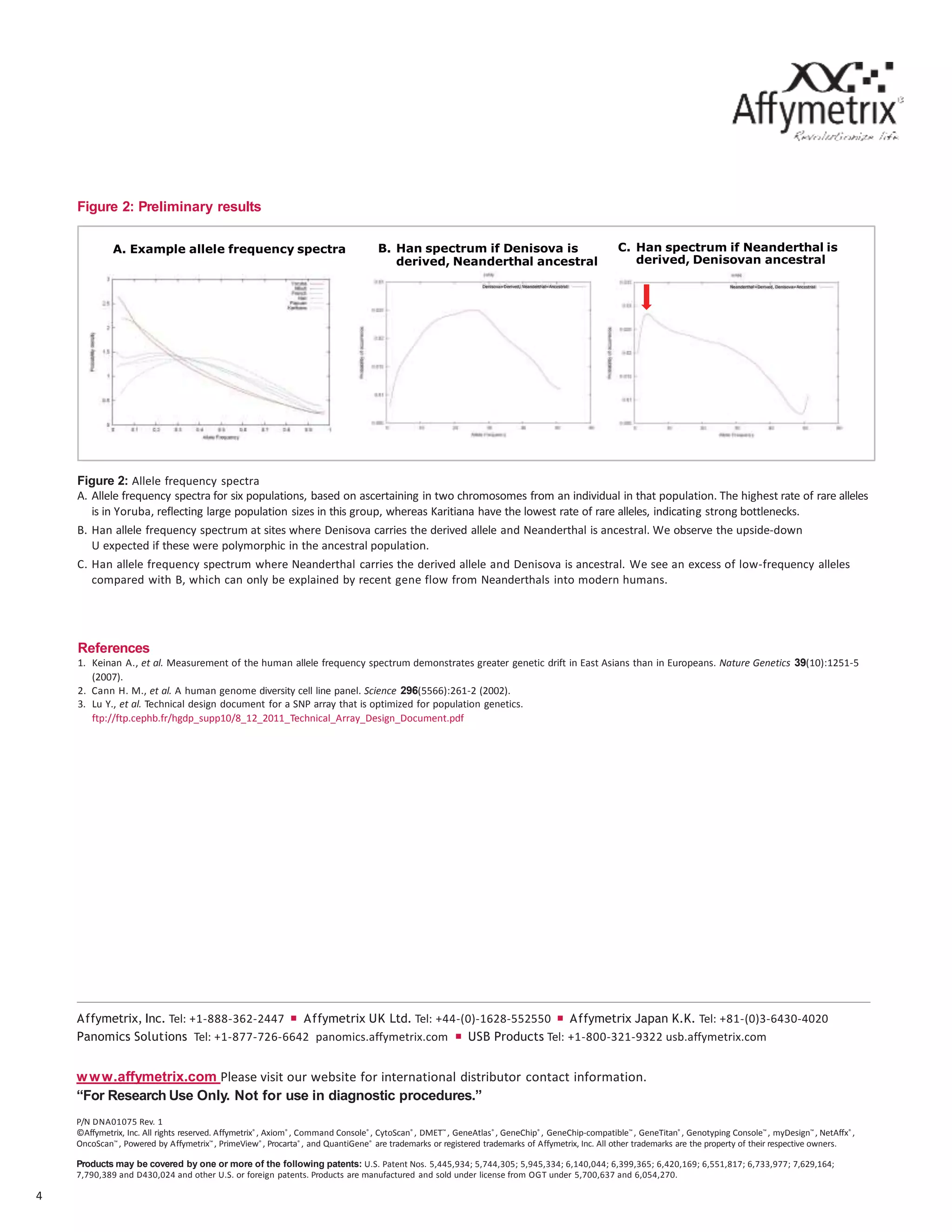
The document discusses the development of the first SNP array specifically for human population genetics studies, consisting of 1.81 million candidate SNPs derived from sequencing data of Neanderthals, Denisovans, and chimpanzees. It highlights the validation of 542,399 SNPs that passed quality criteria and the inclusion of additional SNPs for compatibility with existing datasets, enabling significant population genetic analyses. Preliminary analyses suggest the array's potential in exploring gene flow from Neanderthals to modern humans.