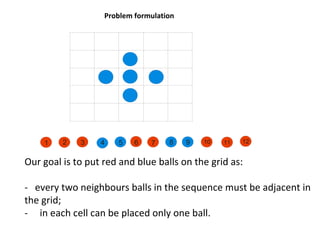
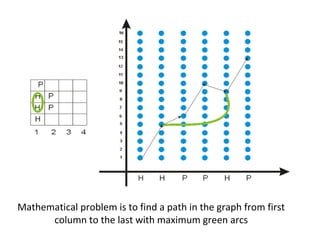
This document proposes a new integer programming model for the HP protein folding problem. [1] It formulates the HP lattice model as a graph problem to maximize the number of contacts between hydrophobic (H) amino acids. [2] The model defines binary variables to represent amino acid placement and contact edges between nodes in the lattice. [3] Computational experiments apply the model to fold two protein sequences on a 3D cubic lattice and present the results graphically.