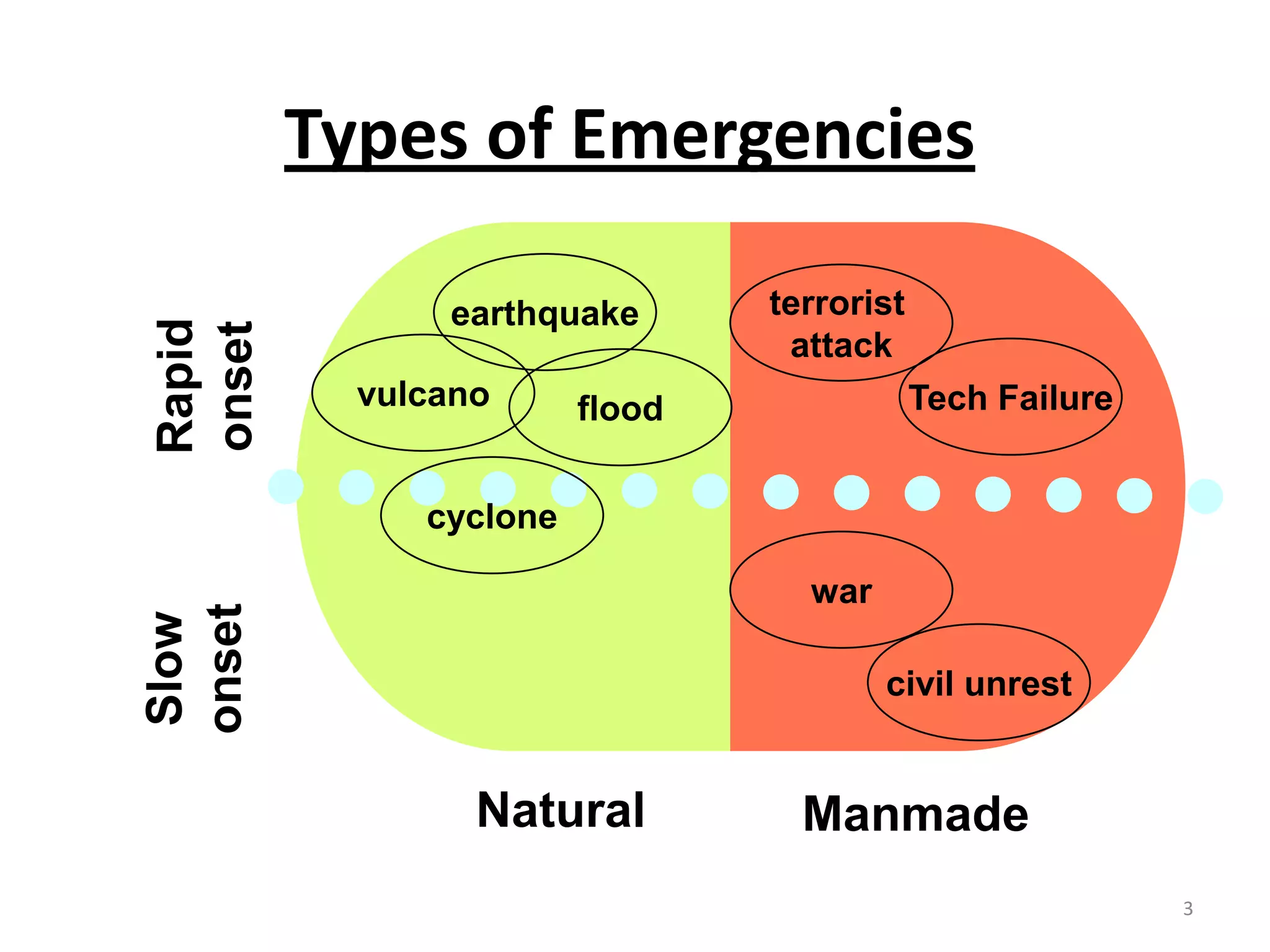
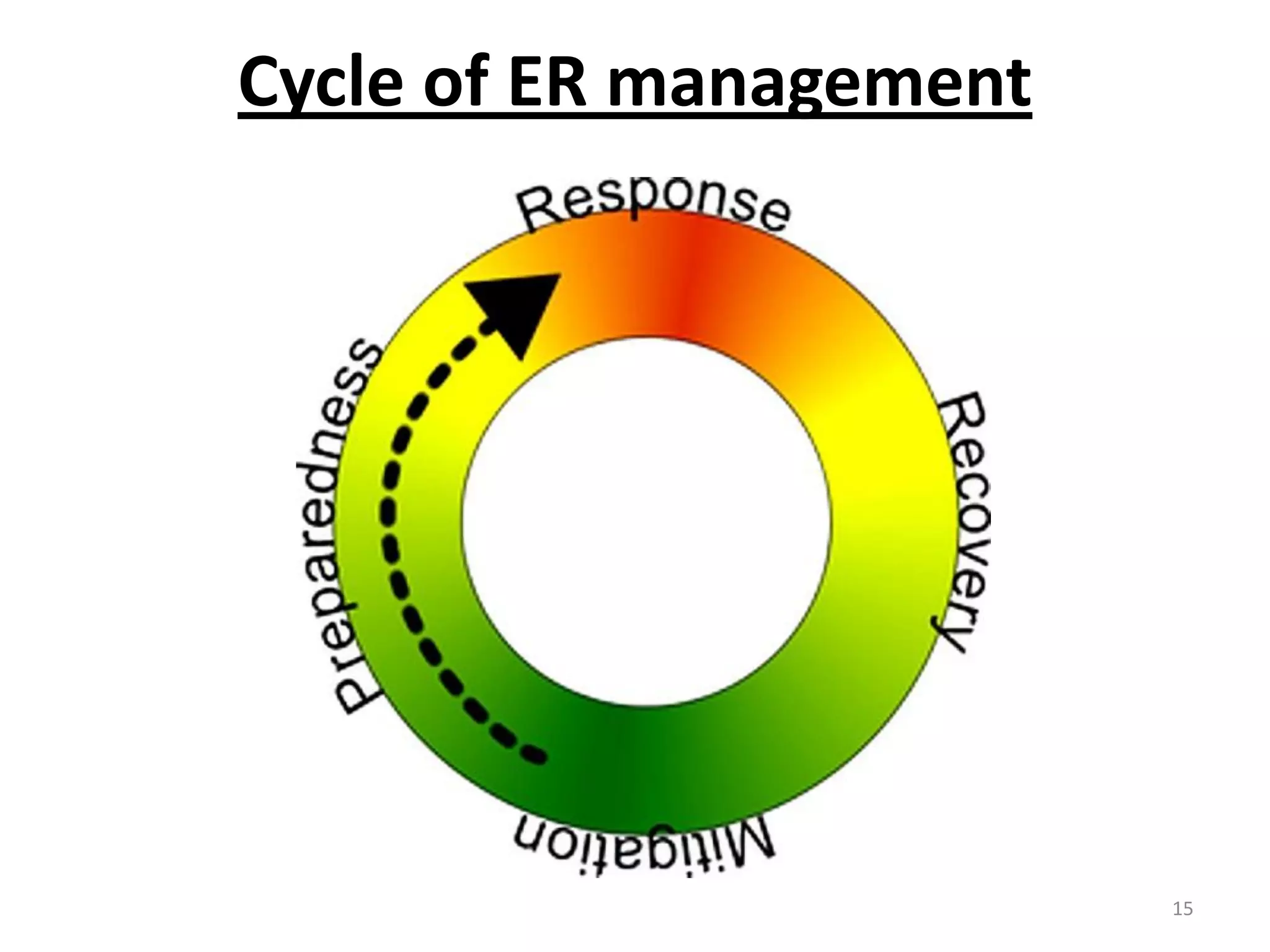
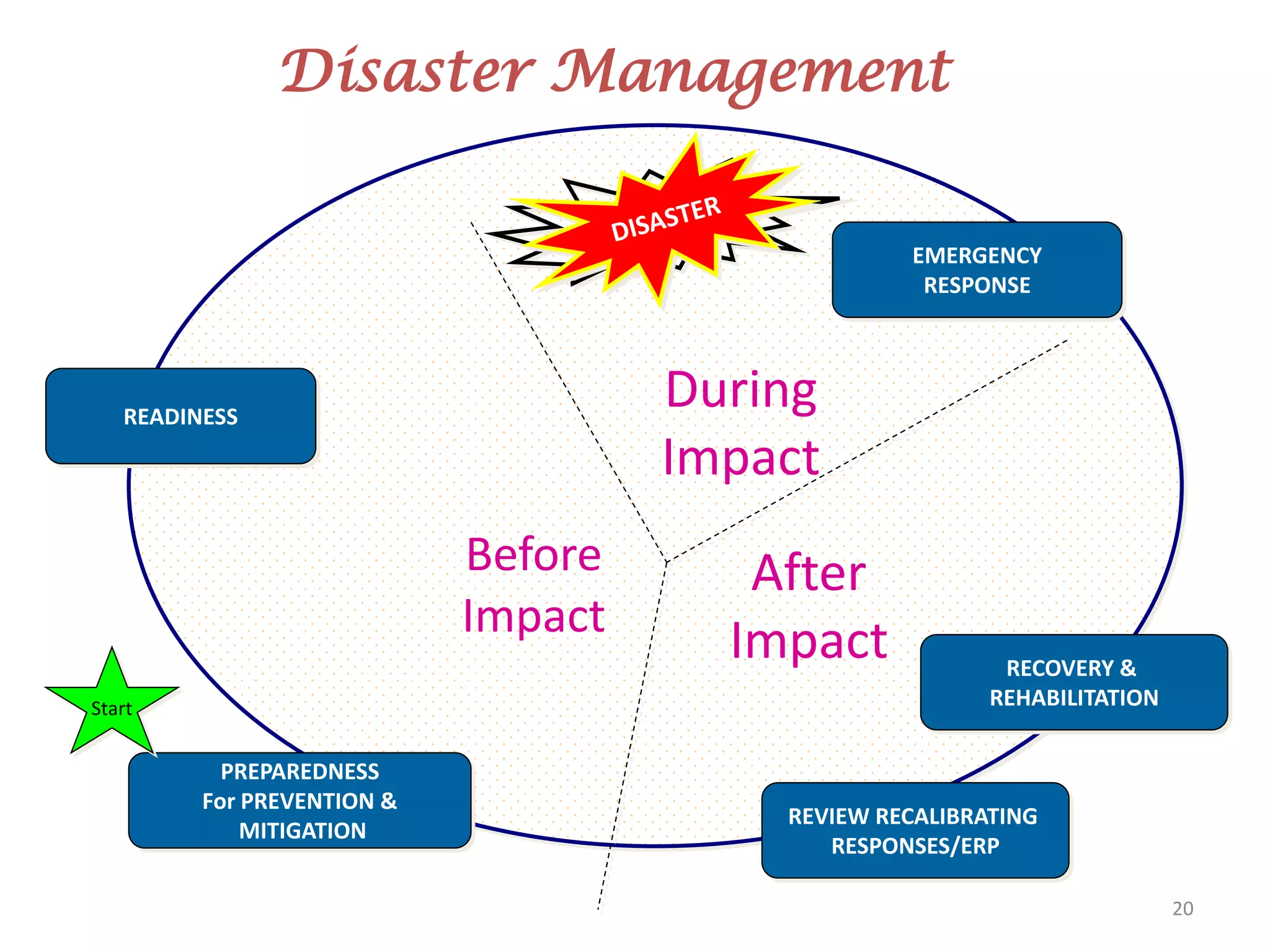
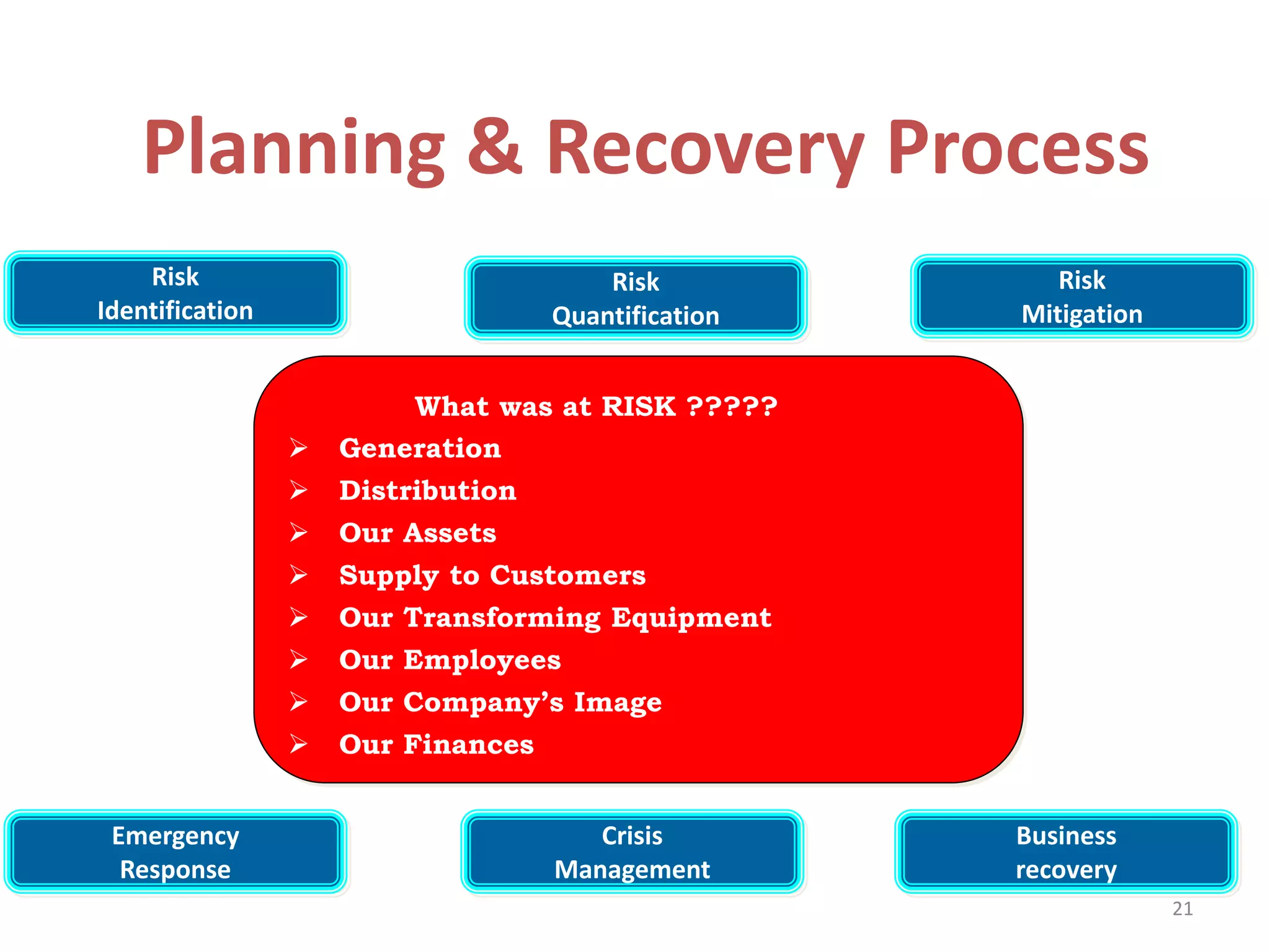
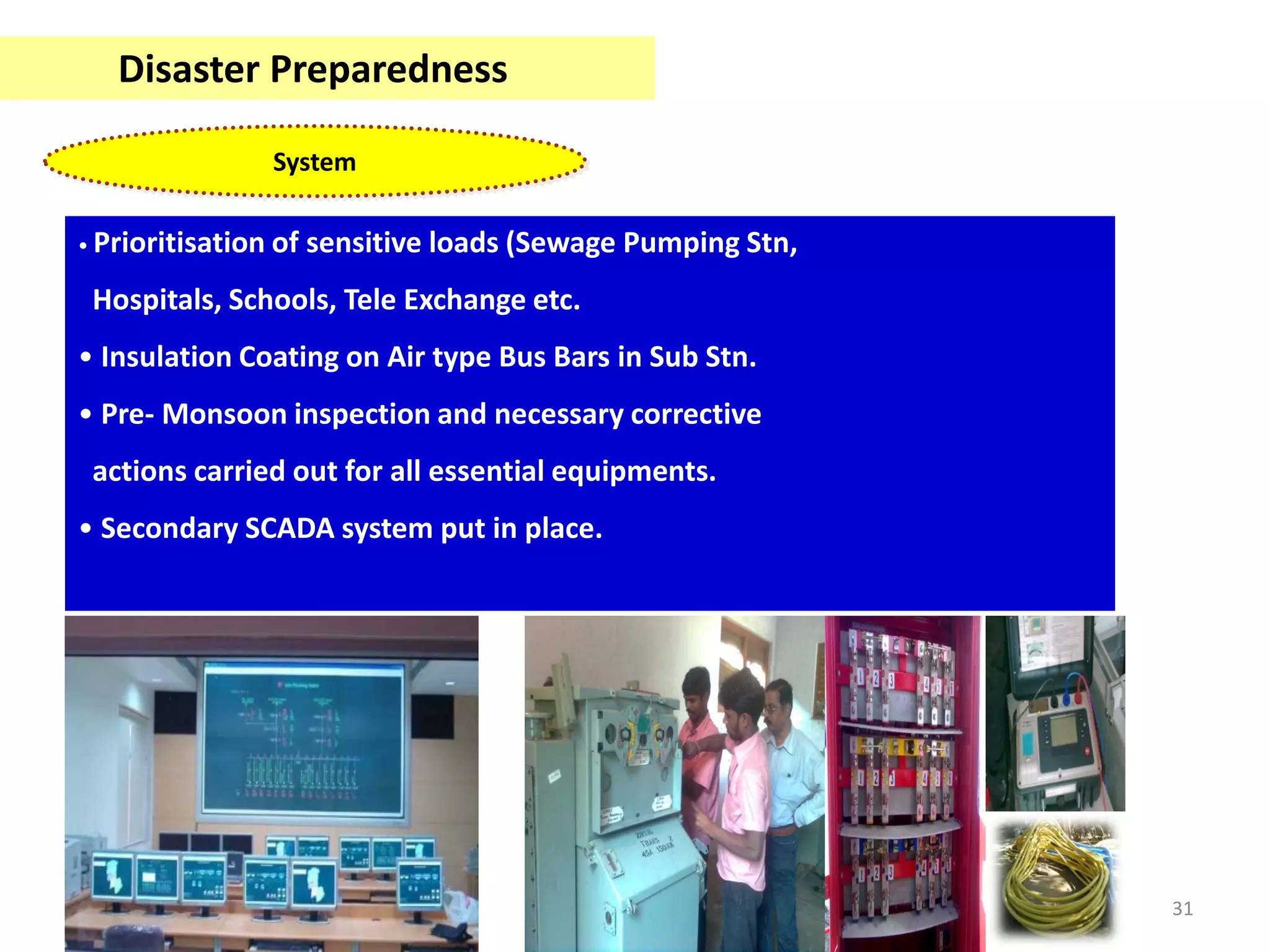
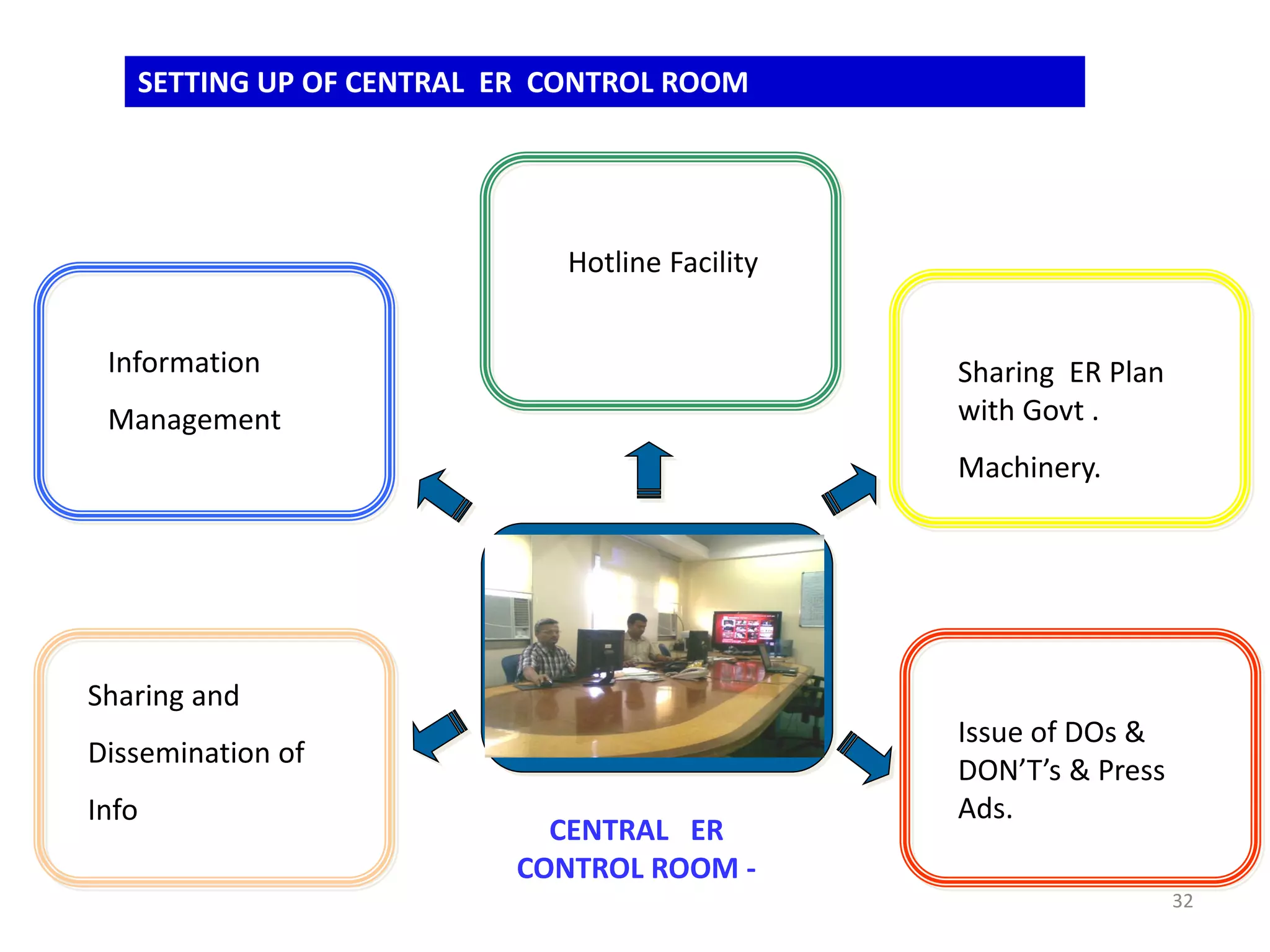
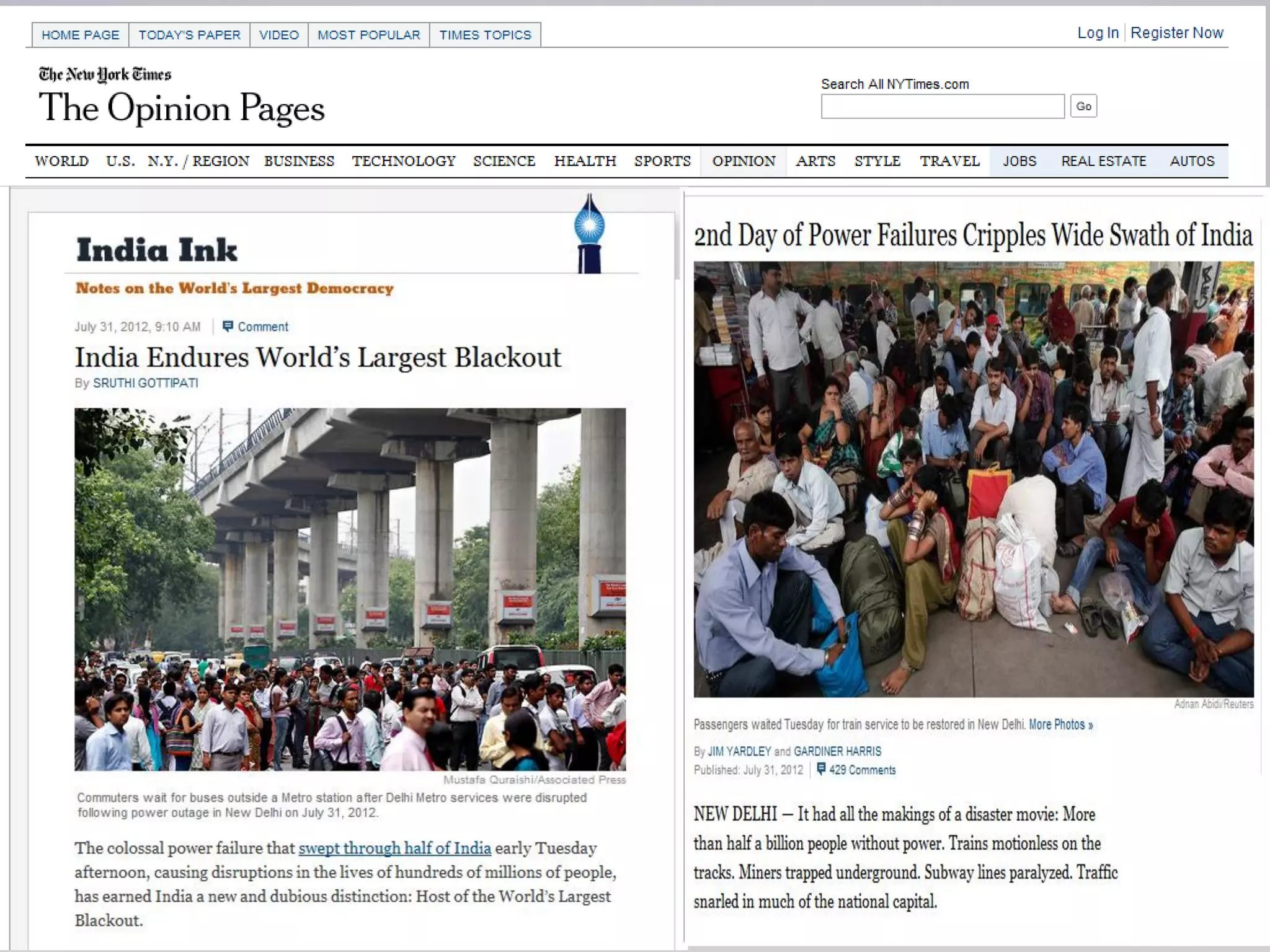
This document discusses emergency response planning for critical infrastructure. It covers various types of emergencies including natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and storms, as well as man-made disasters like terrorist attacks and technical failures. The key aspects of emergency response planning discussed are risk assessment, defining roles and responsibilities, developing response plans, training personnel, and conducting drills and rehearsals. The document emphasizes the importance of preparedness and having response plans in place before a disaster occurs to enable quick and effective action. It also outlines the various phases of emergency management including prevention, preparedness, response, recovery, and review.