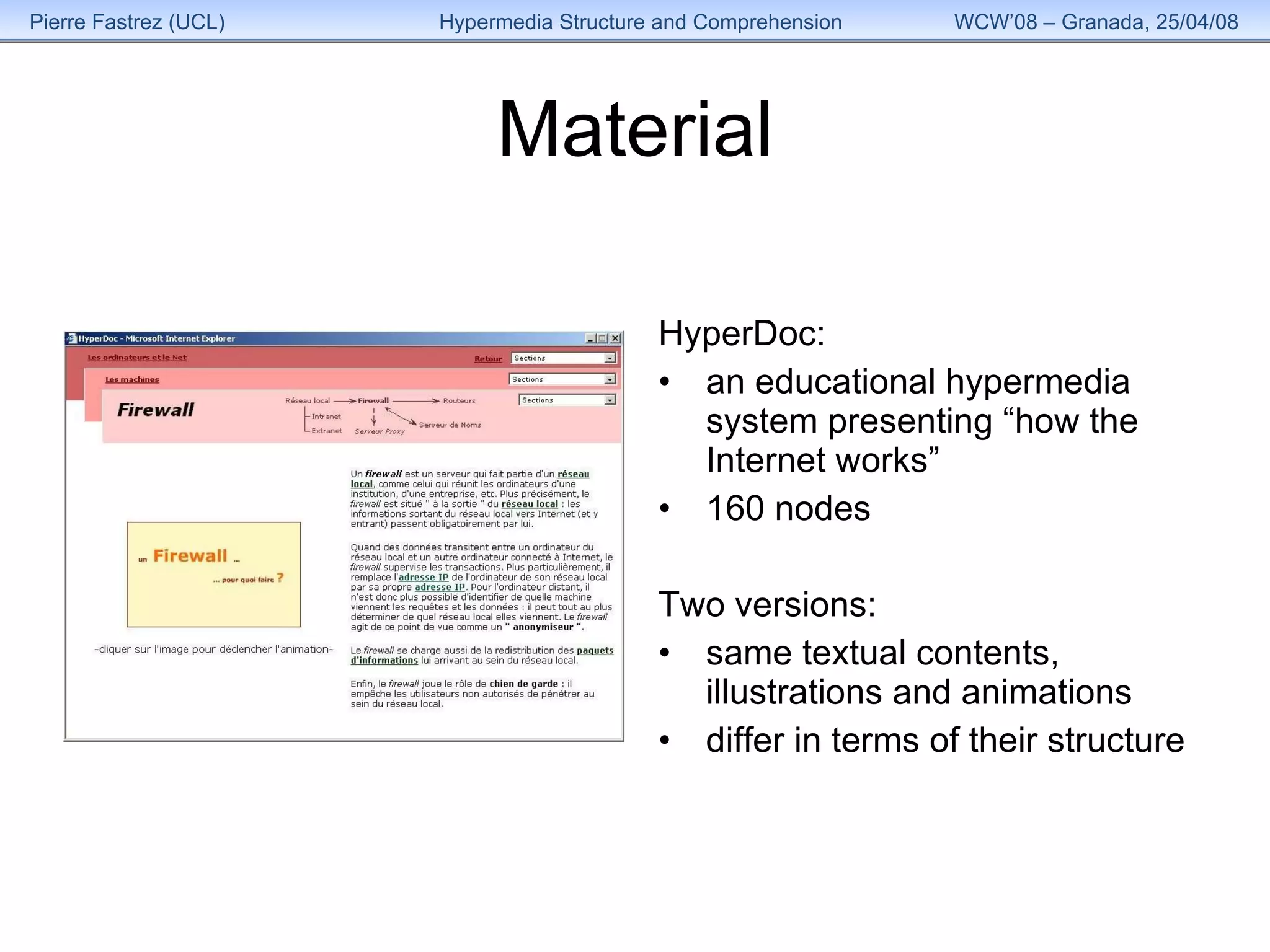
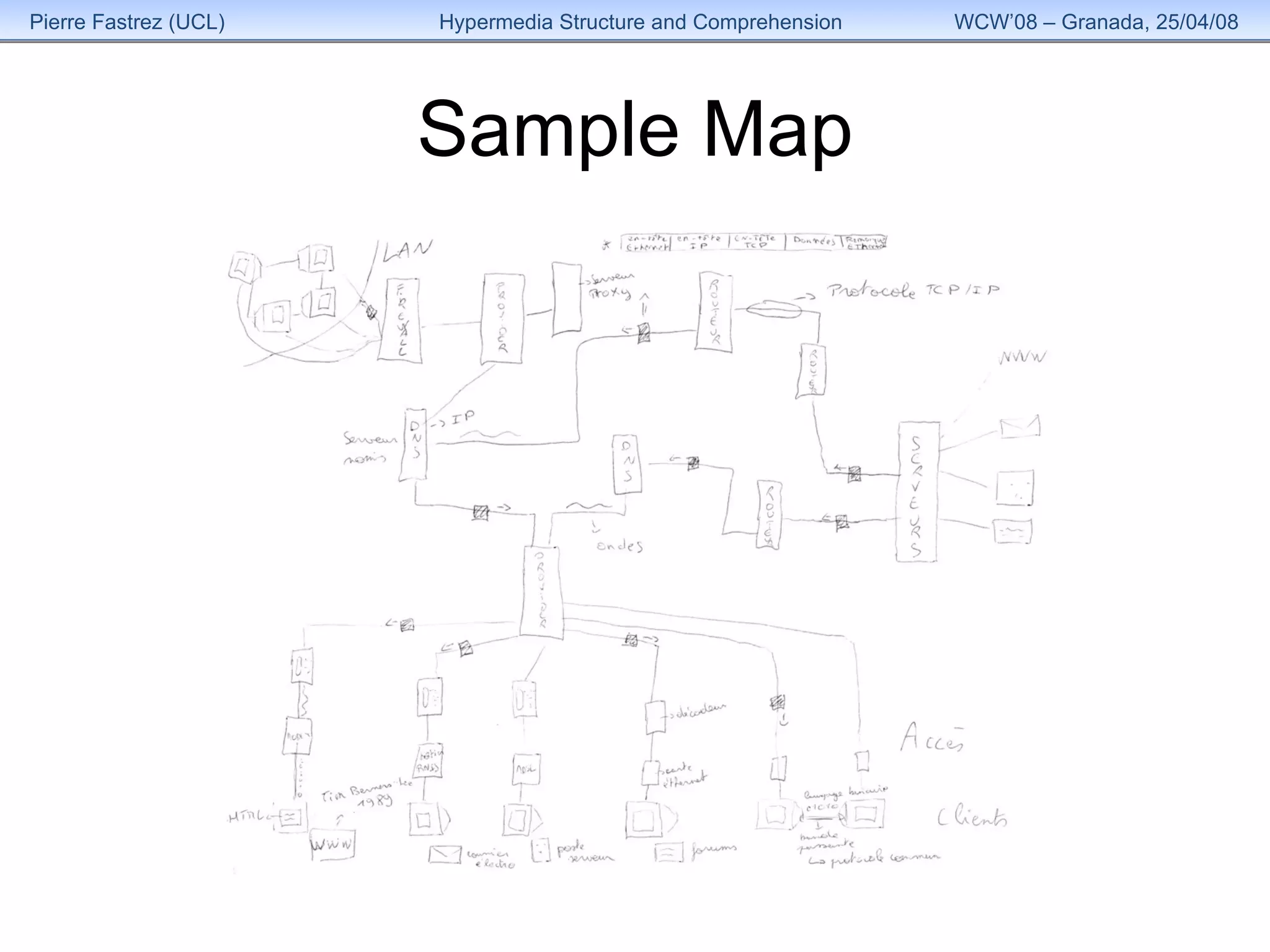
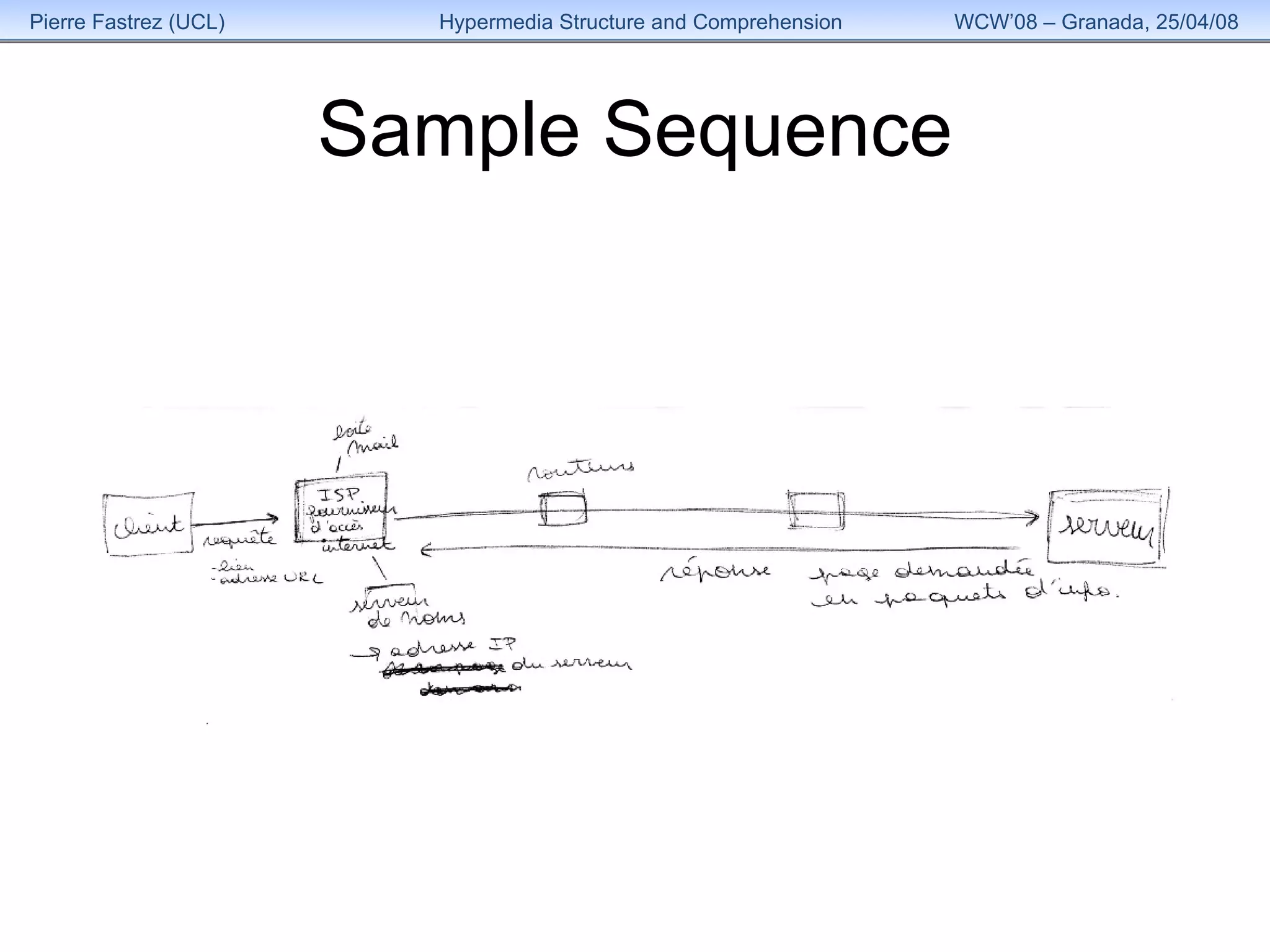
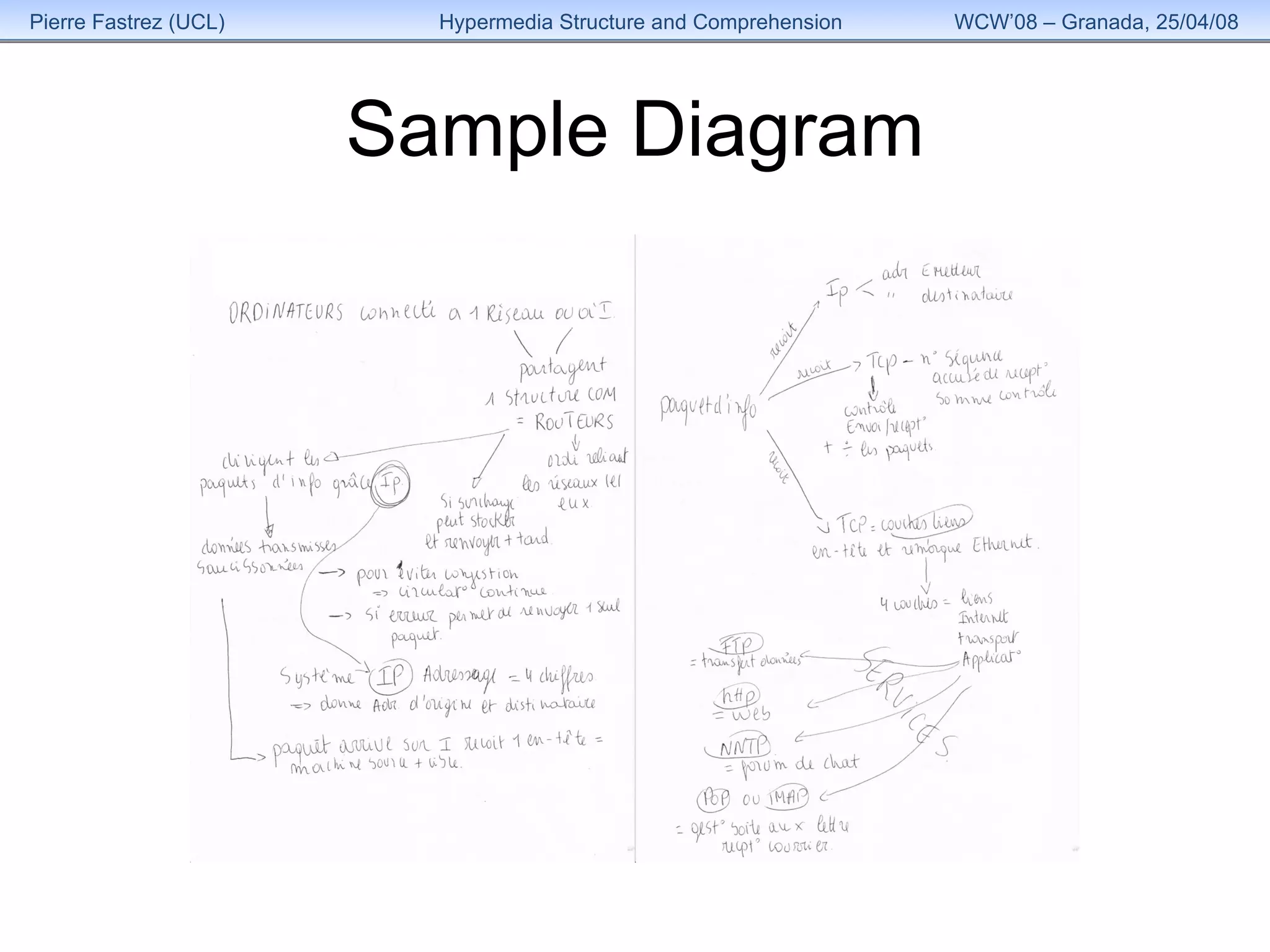
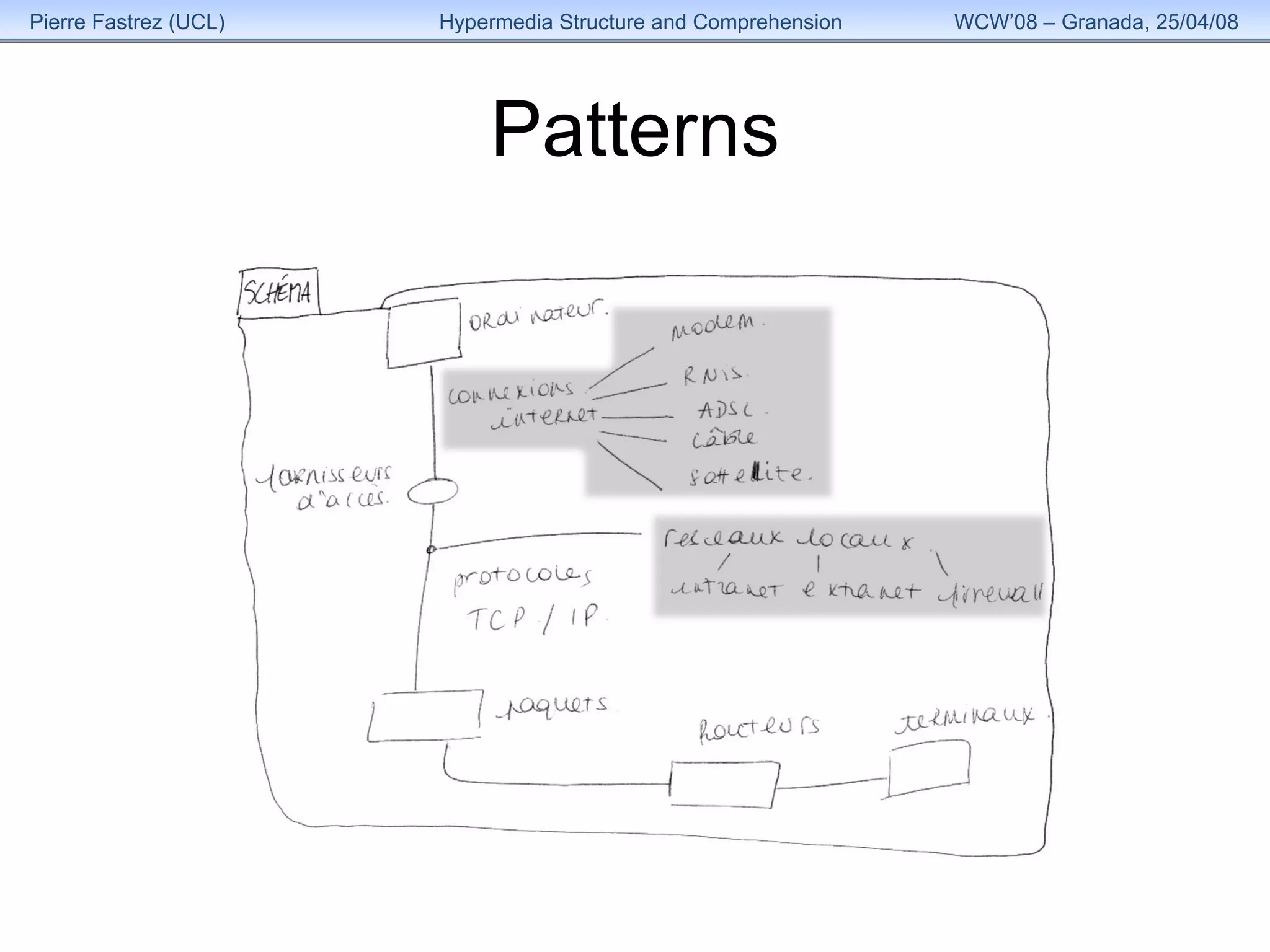
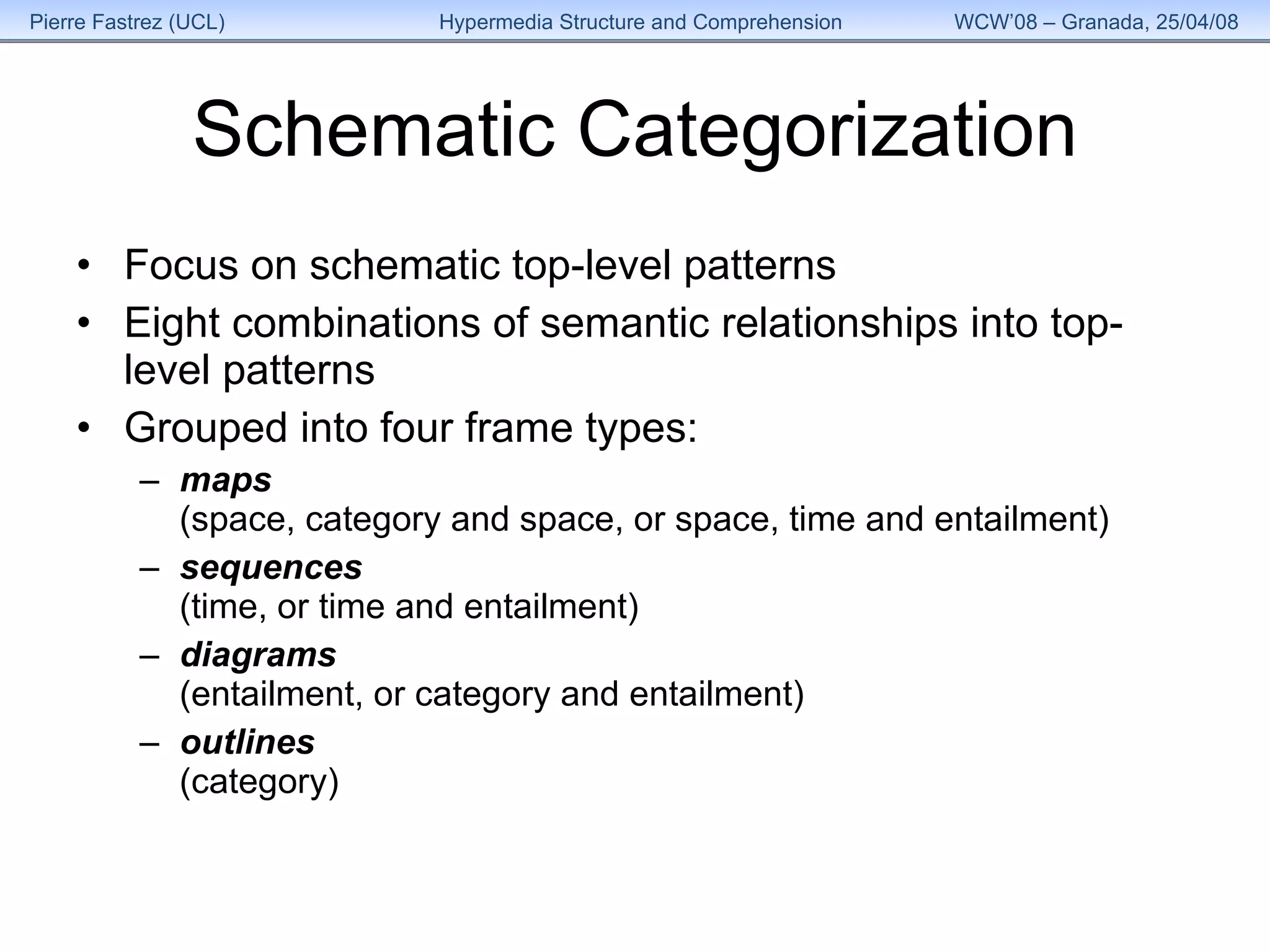
1) The study examined how the structure of an educational hypermedia system called HyperDoc influenced learners' comprehension of its content over multiple sessions.
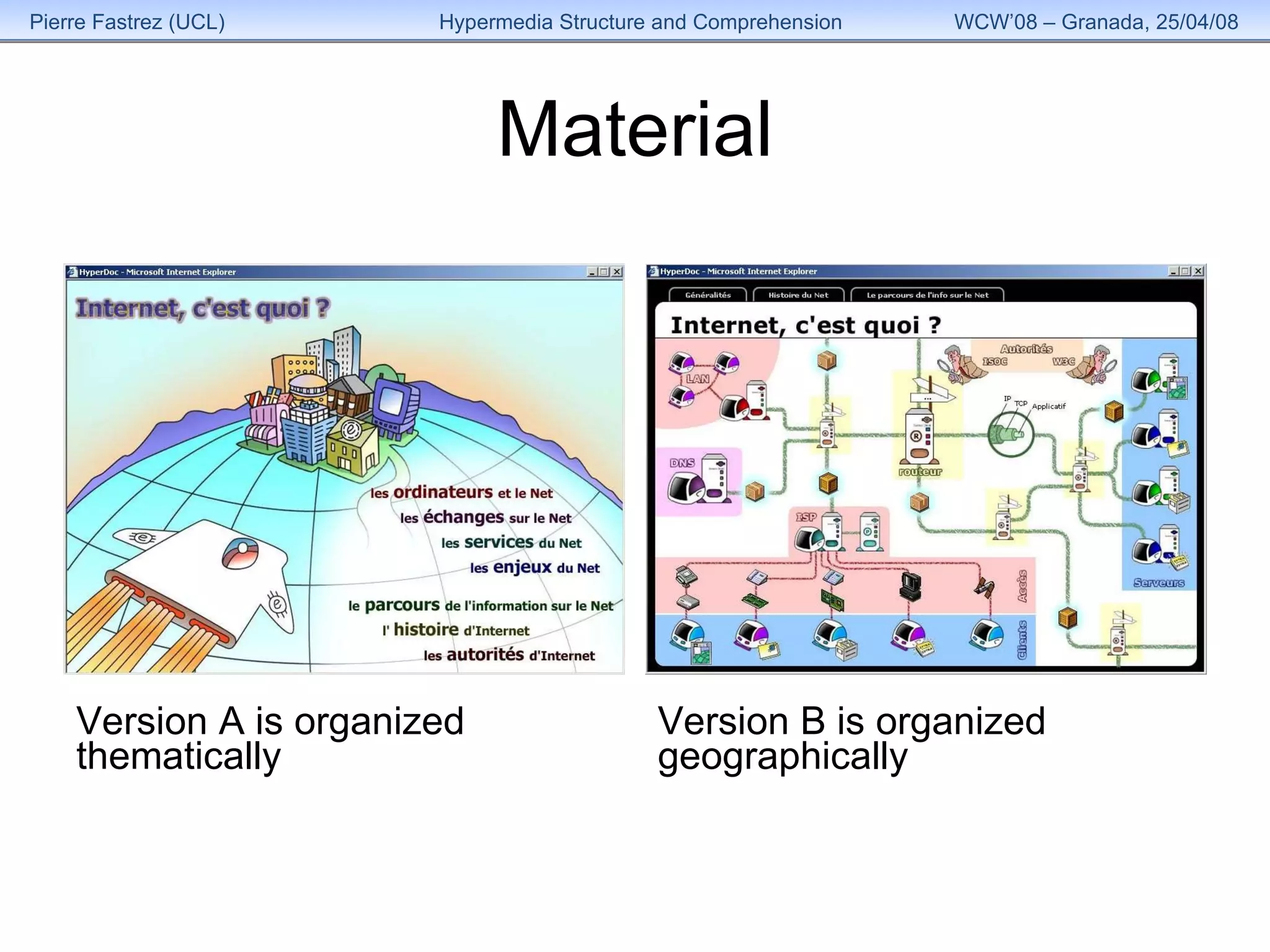
2) Participants used one of two versions of HyperDoc, which had the same information but different structural organizations, over 4 sessions of browsing and note-taking.
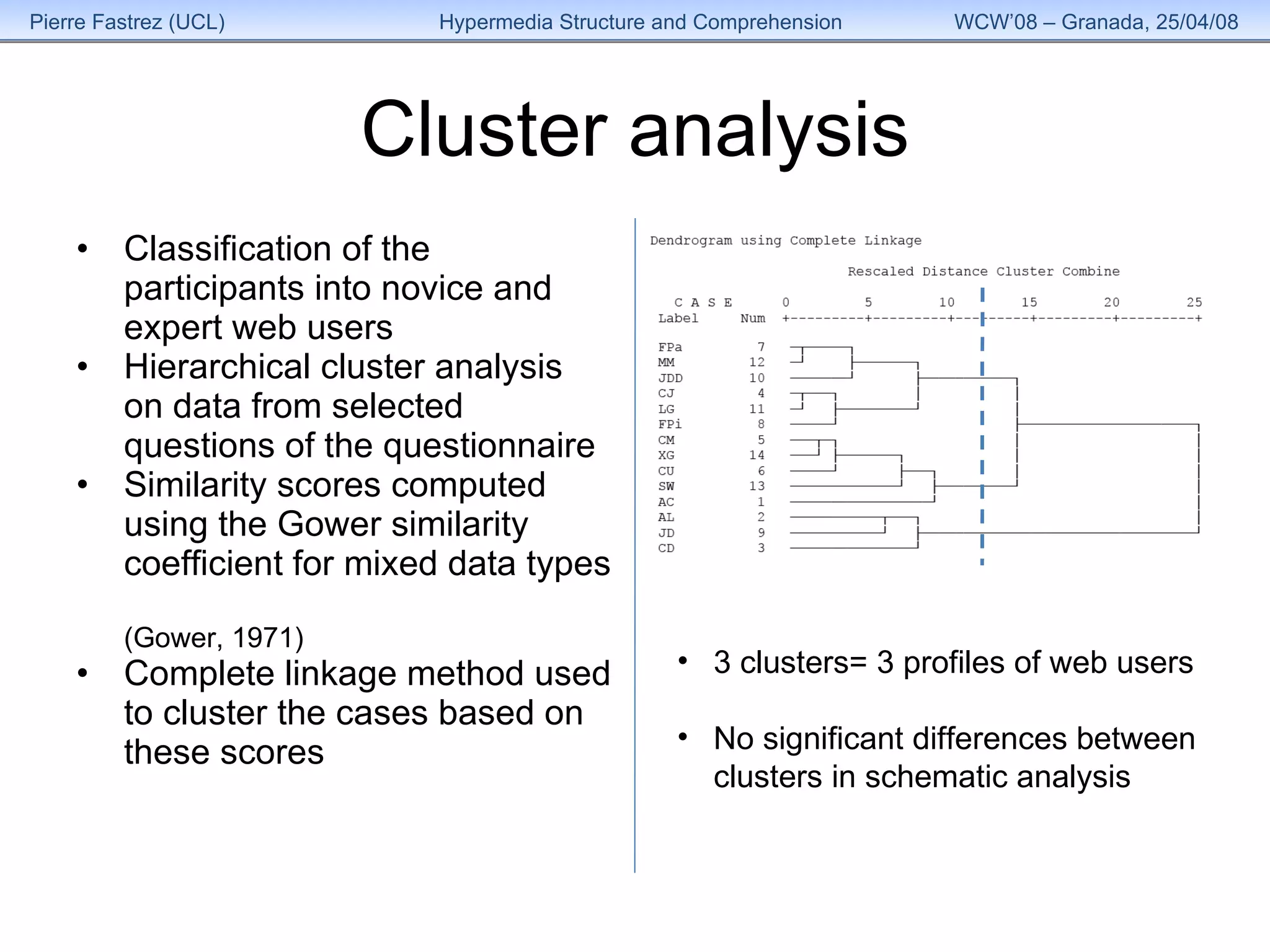
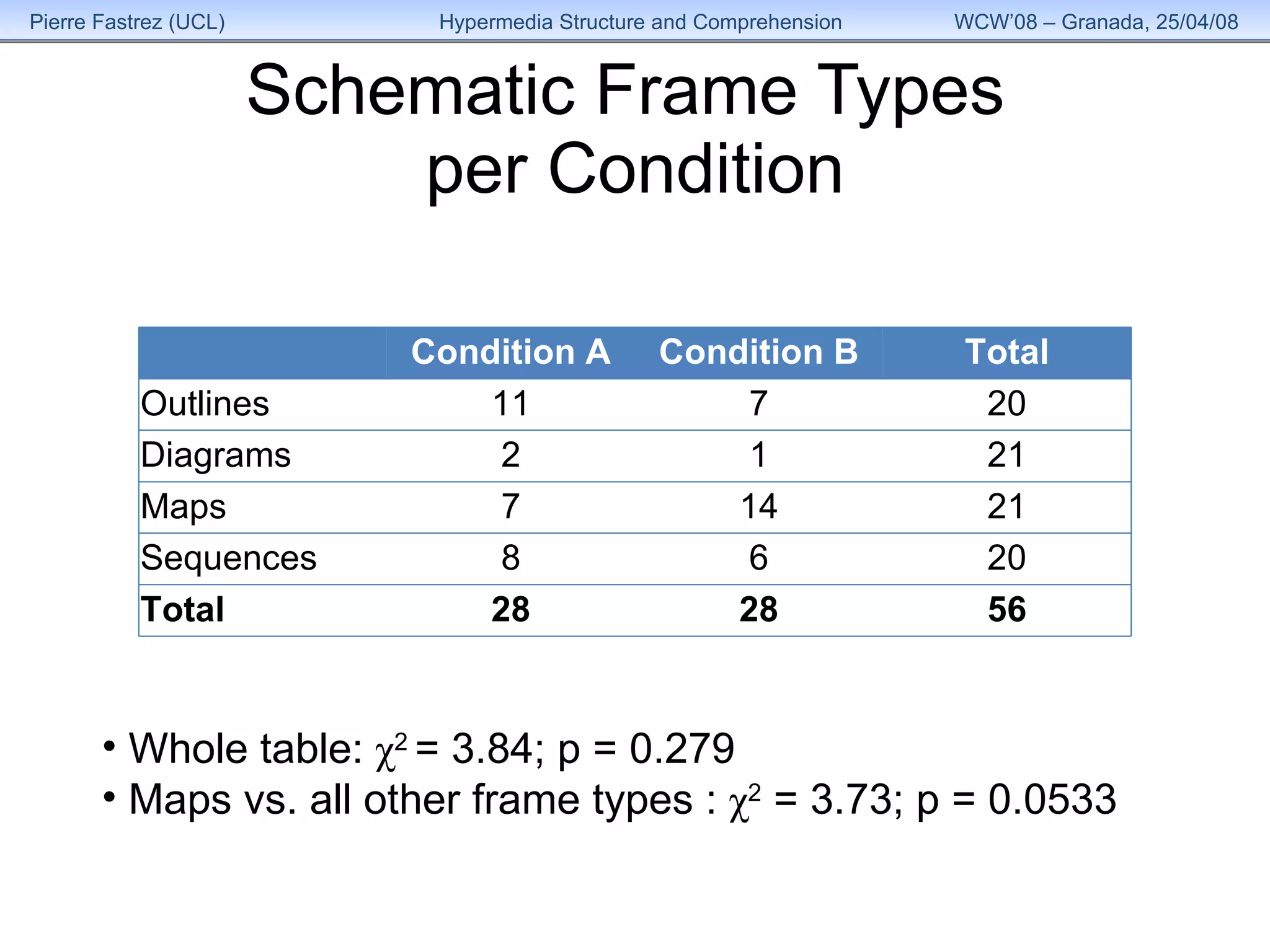
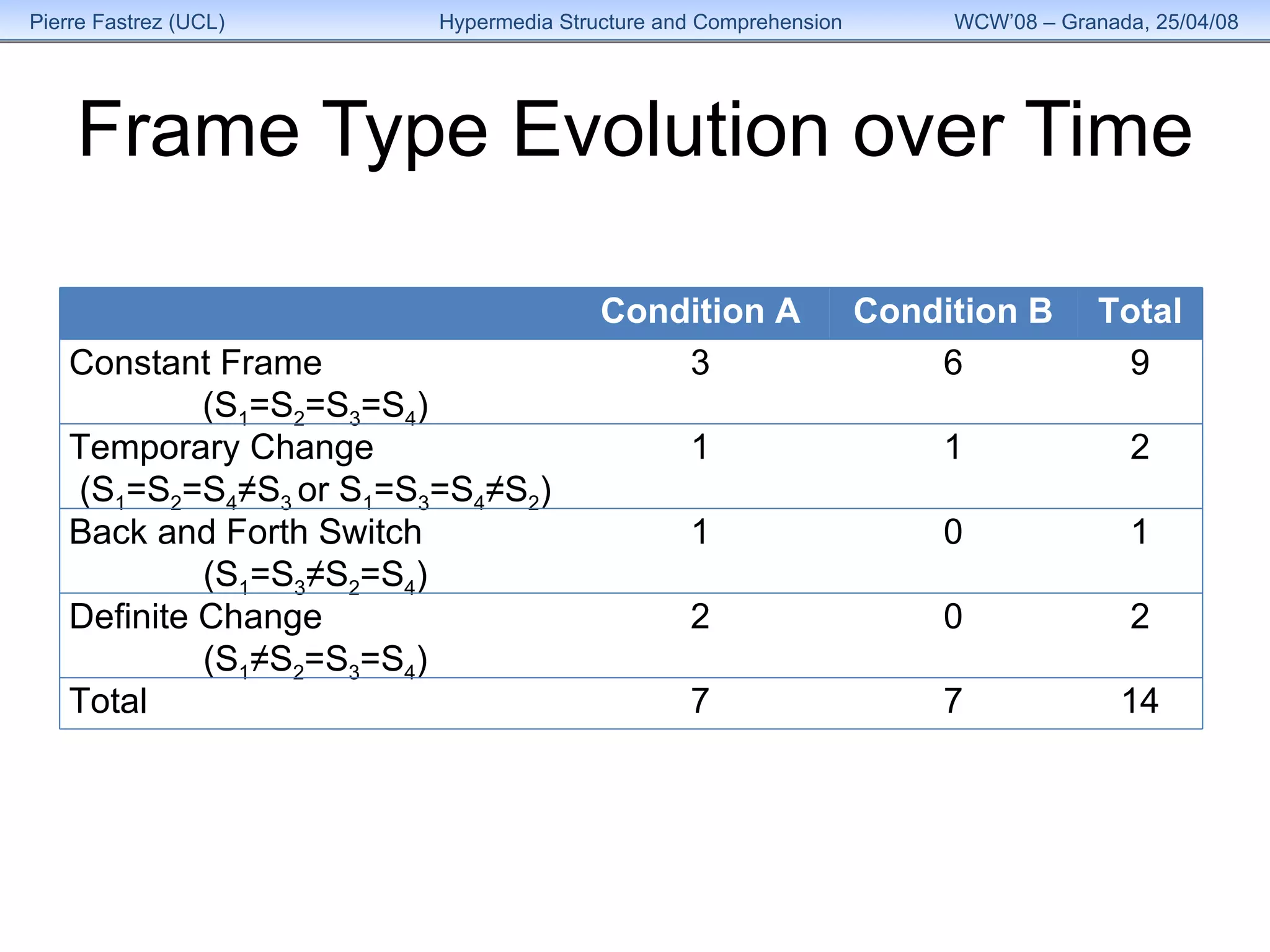
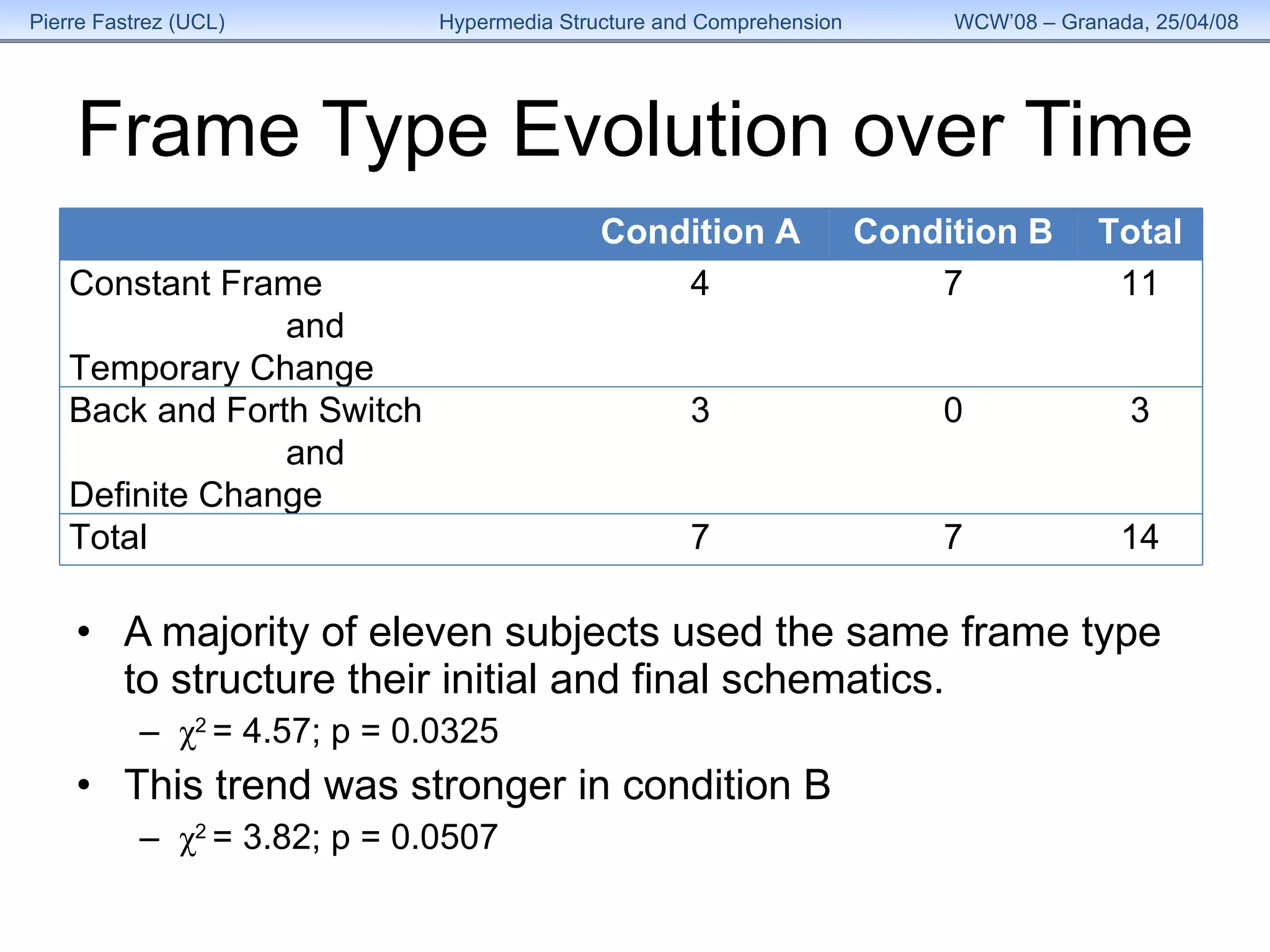
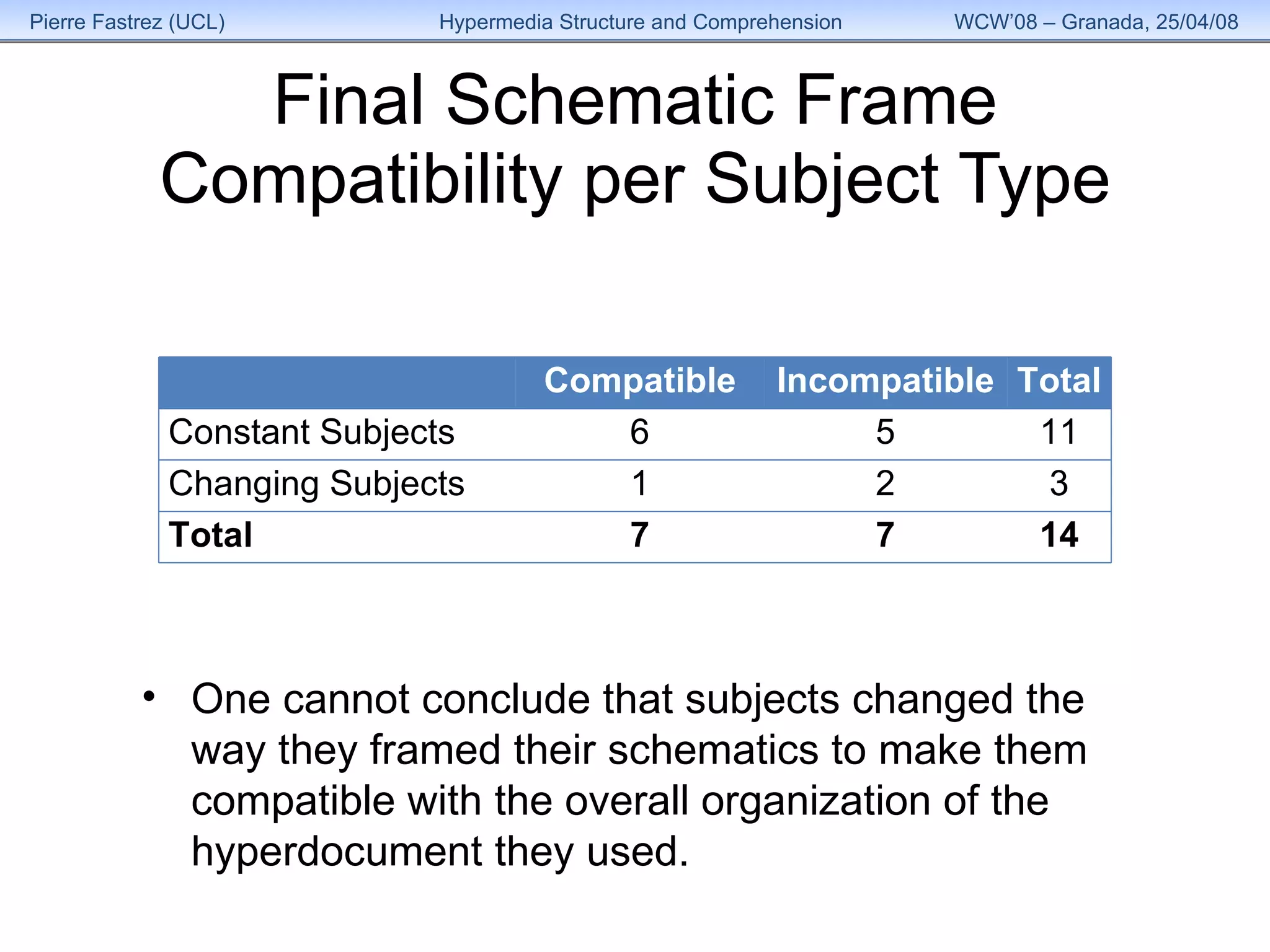
3) Analysis found the overall structure of participants' summaries did not significantly change to match the version of HyperDoc they used, and remained stable over time as their expertise grew.