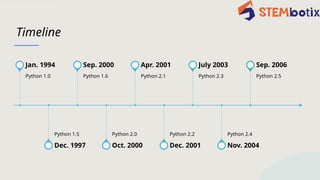
Python, created by Guido van Rossum between 1989 and 1991, has evolved from an easy-to-read language into a versatile tool widely used in web development, data science, and automation. Major versions, including Python 2.0 and Python 3.0, introduced significant features like garbage collection and enhanced Unicode support, alongside backward-incompatible changes. With a rich ecosystem and an active community, Python continues to develop, anticipating advancements in performance and functionality in areas like data science and AI.