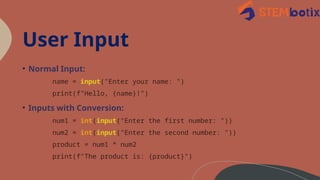
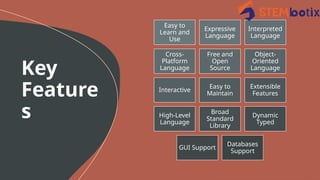
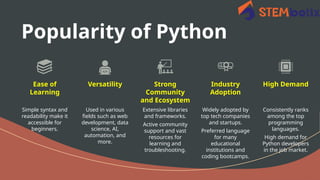
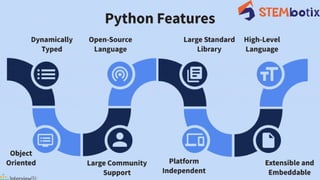
Python is a versatile, high-level programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991, known for its readability and efficiency. It is widely used in web development, data analysis, and artificial intelligence, with a strong community and extensive libraries. Python's user-friendly nature and broad applications have led to its continued growth and demand in the tech industry.







![Python vs Java Codes:
• Python
print("Hello, world!")
• Java
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-english-240818102238-1ec67de3/85/A-Brief-Introduction-to-Python-English-11-320.jpg)