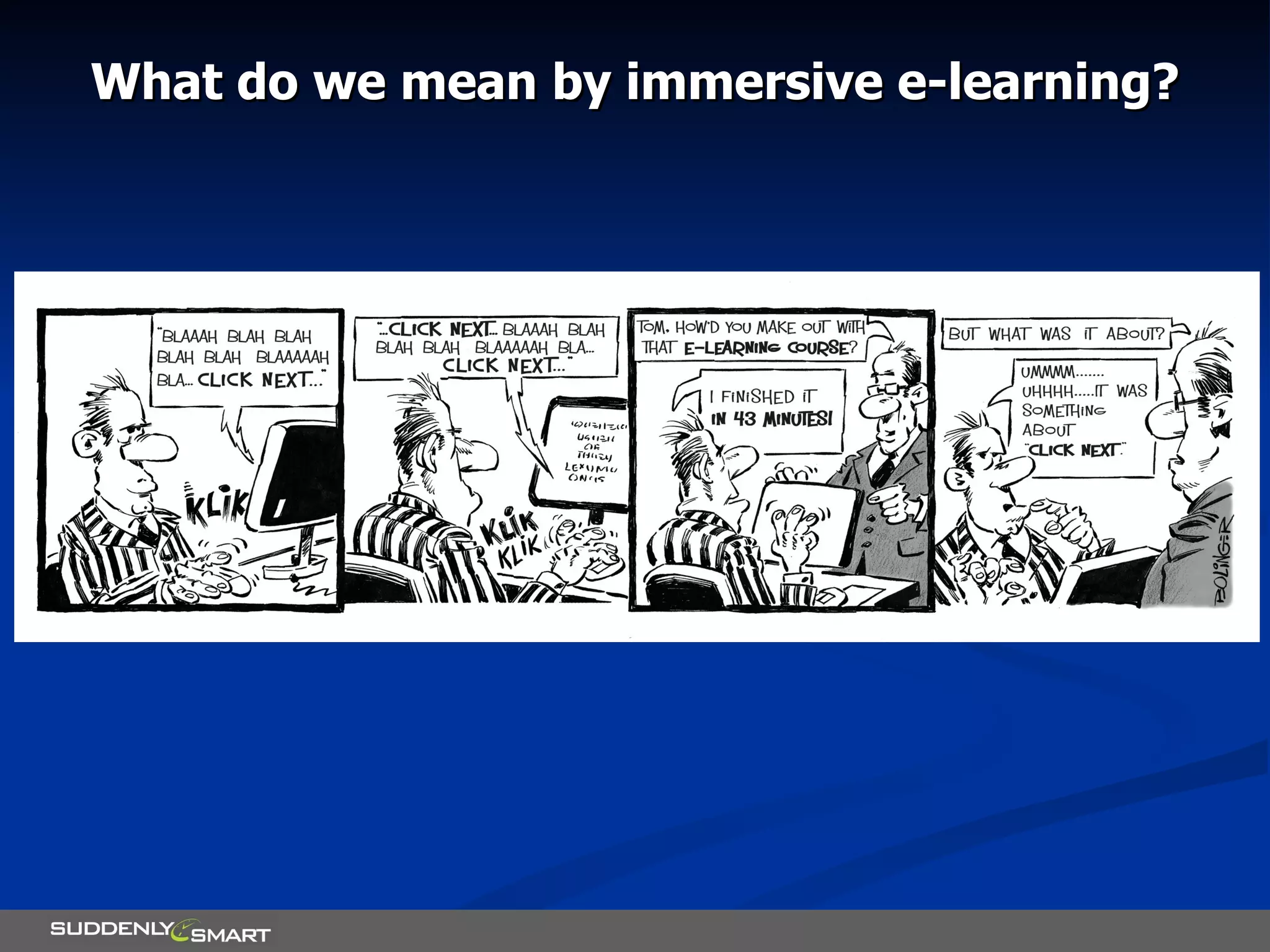
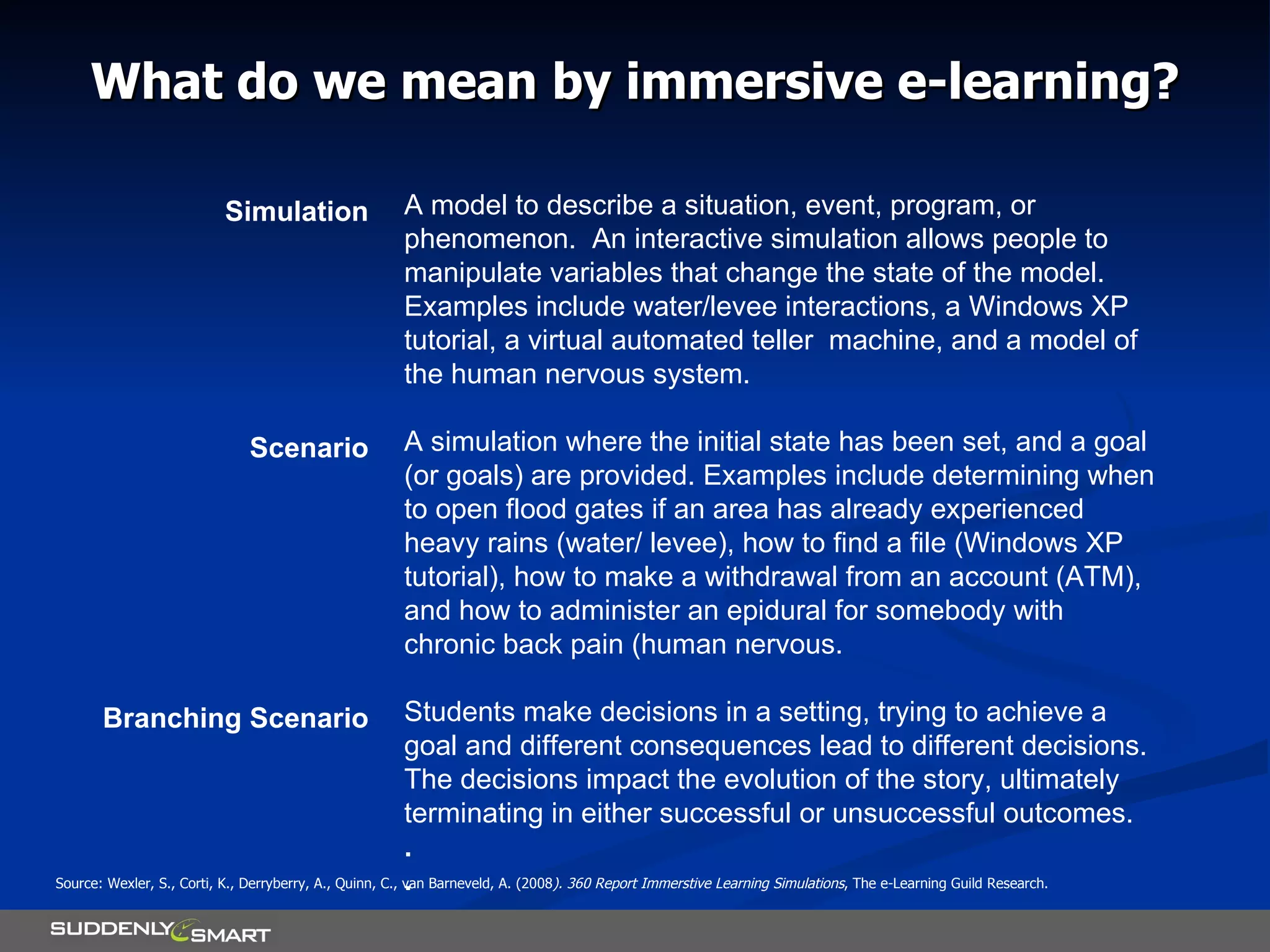
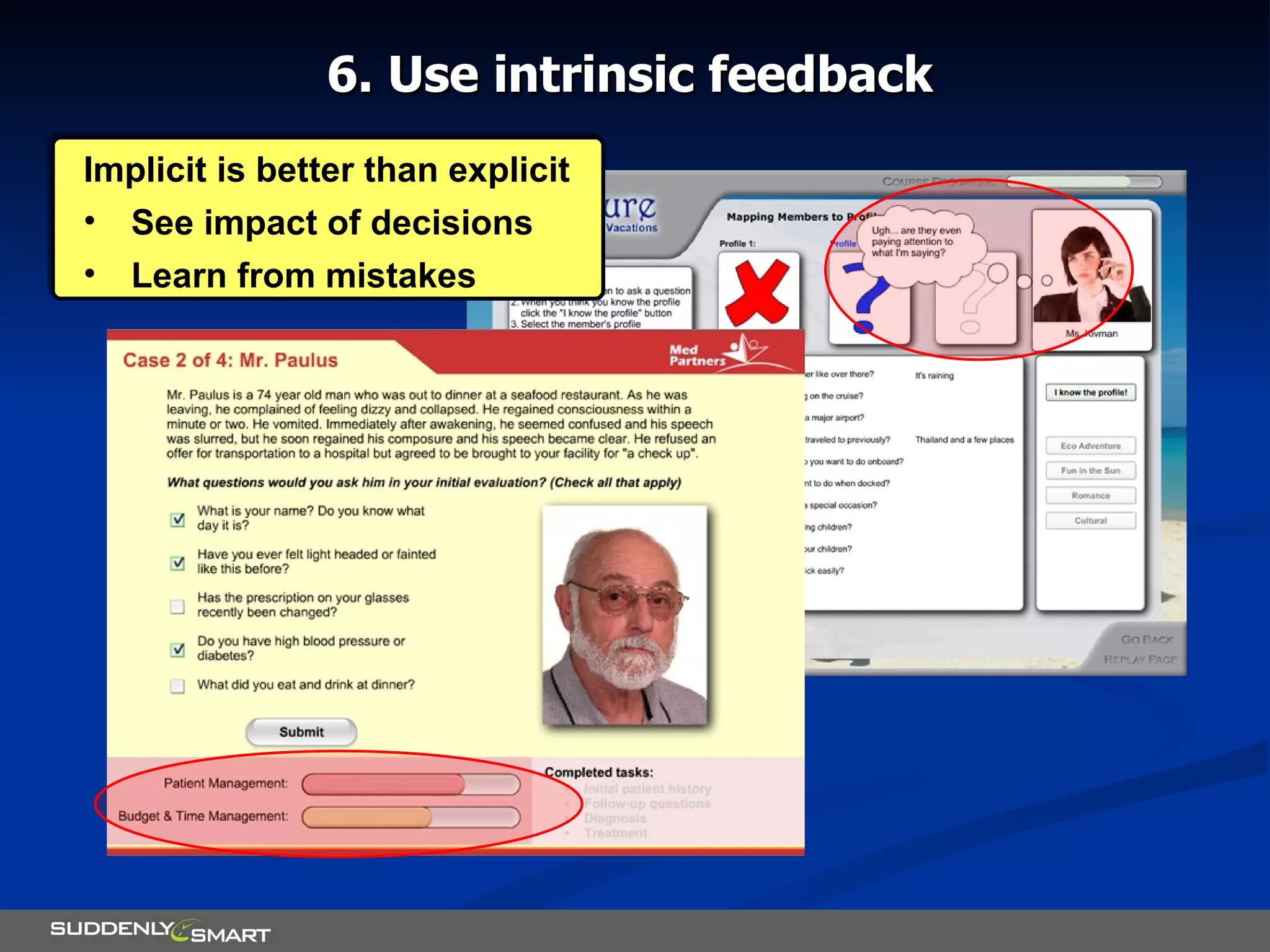
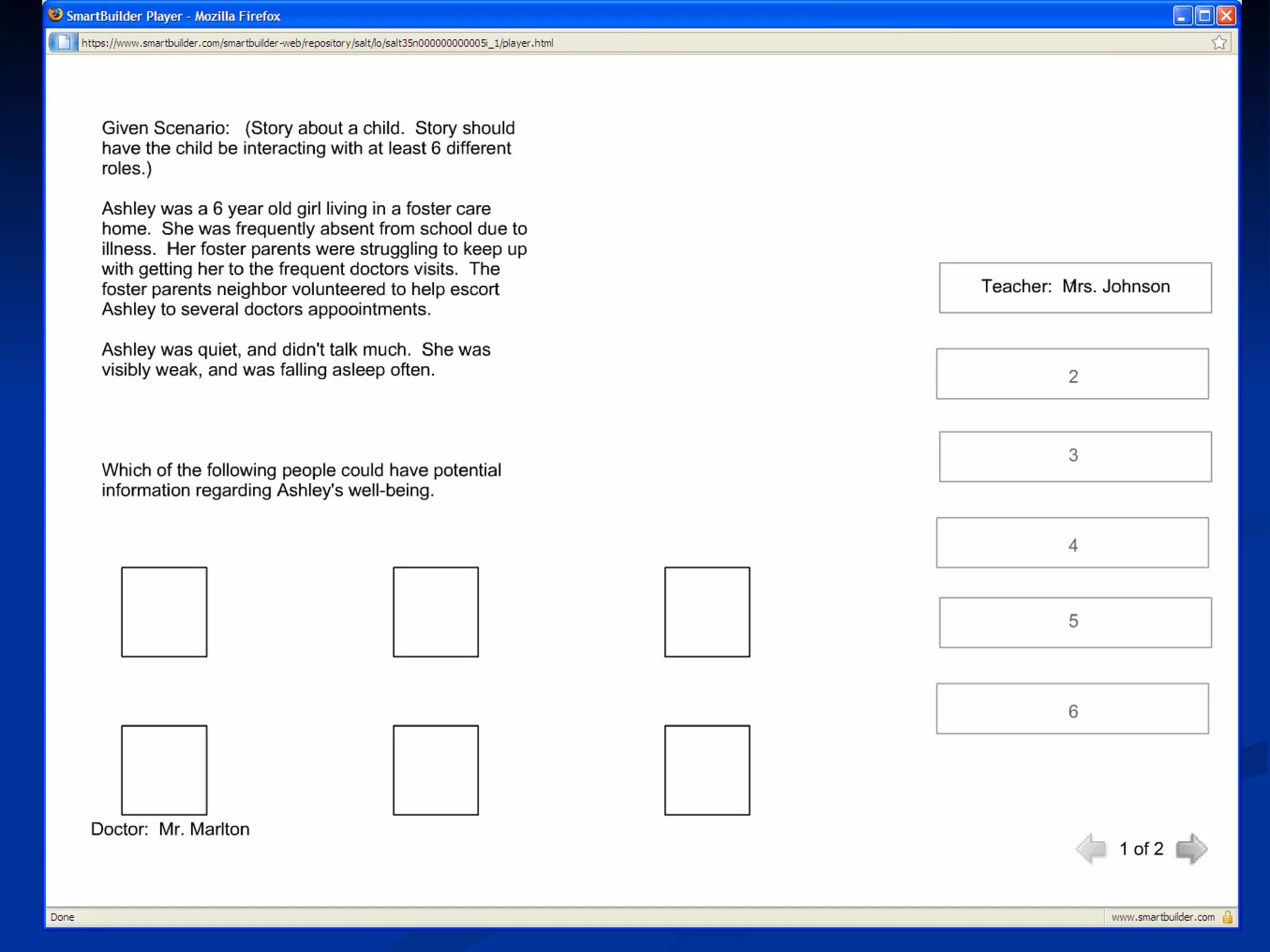
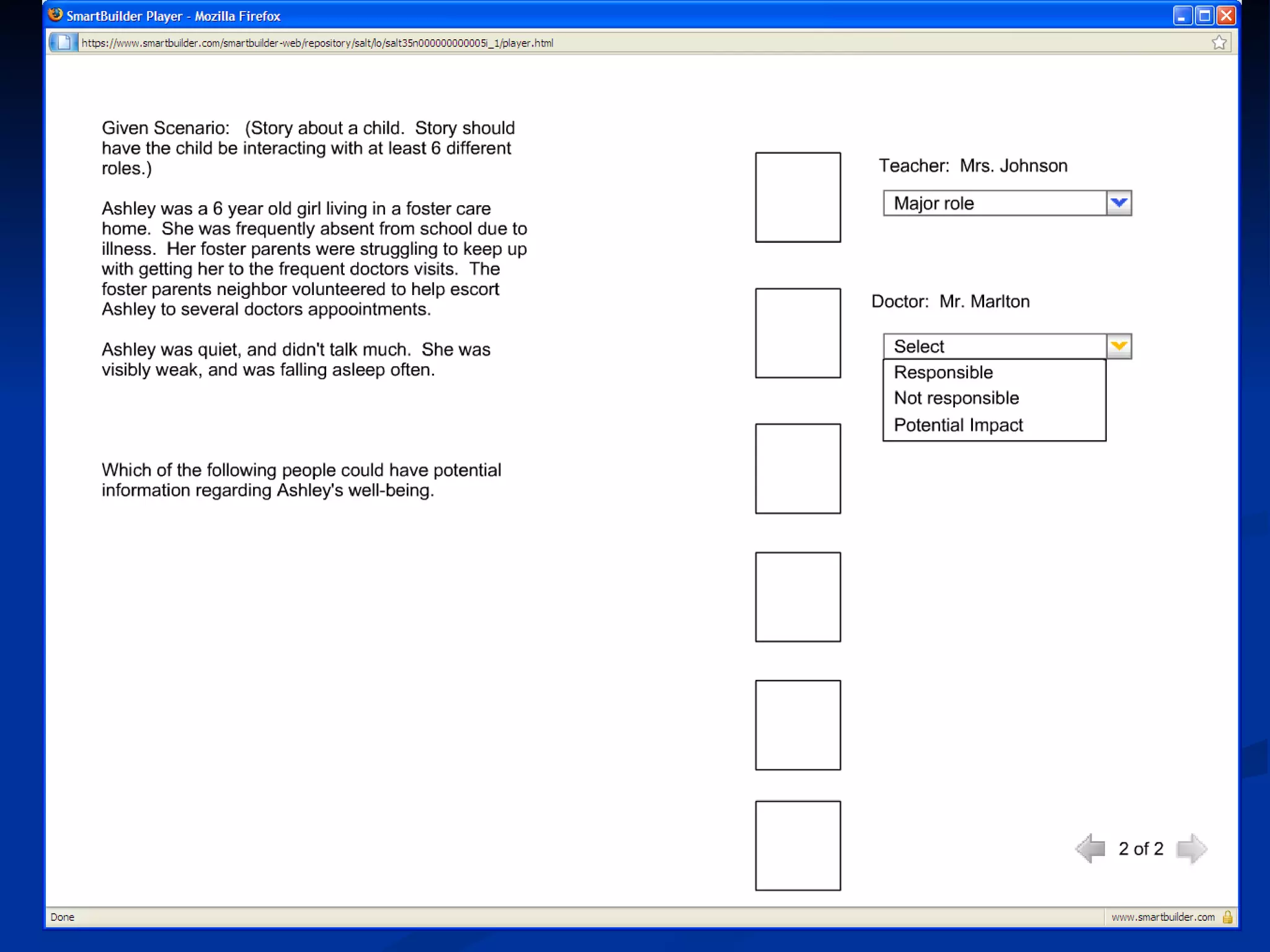
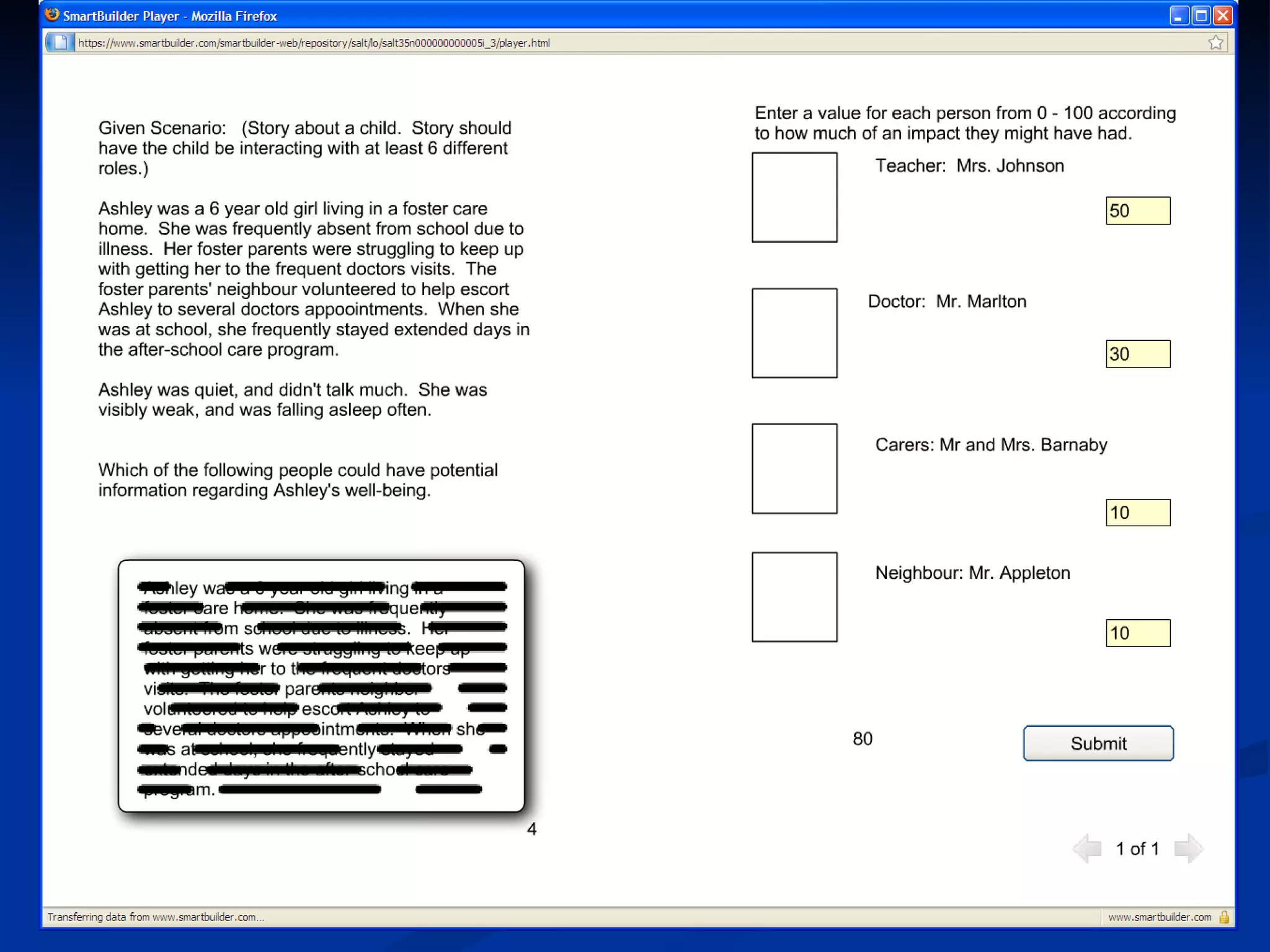
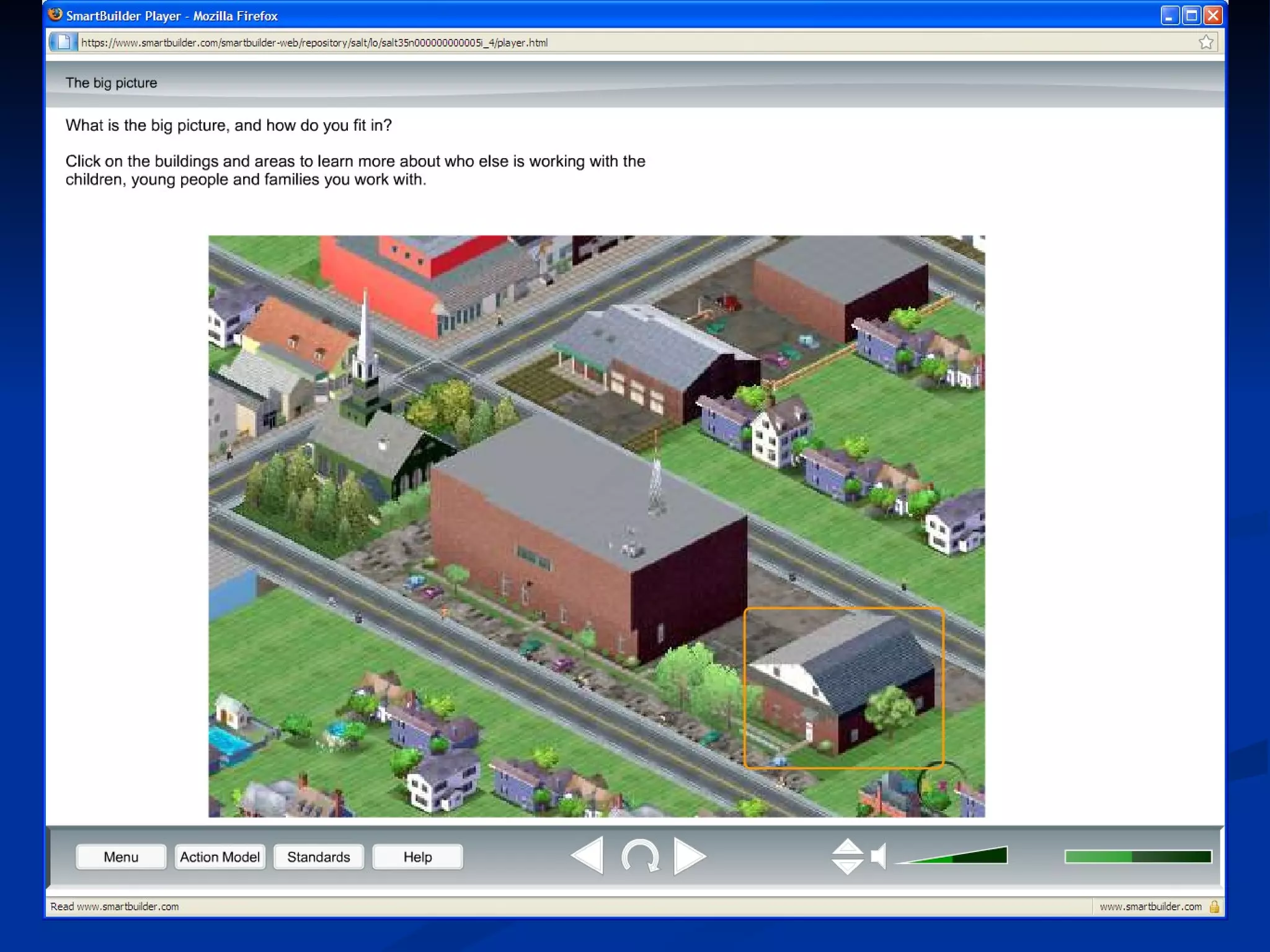
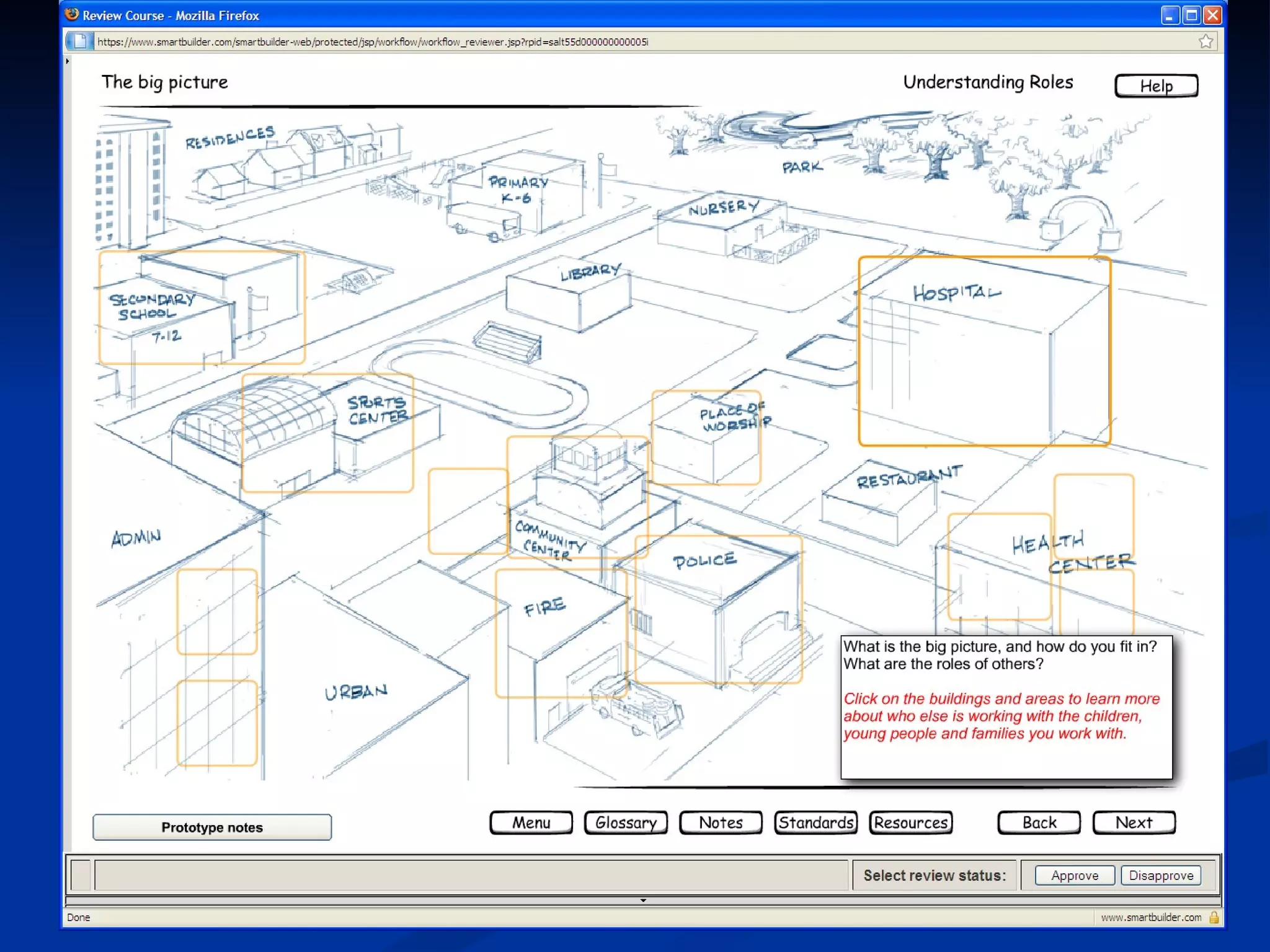
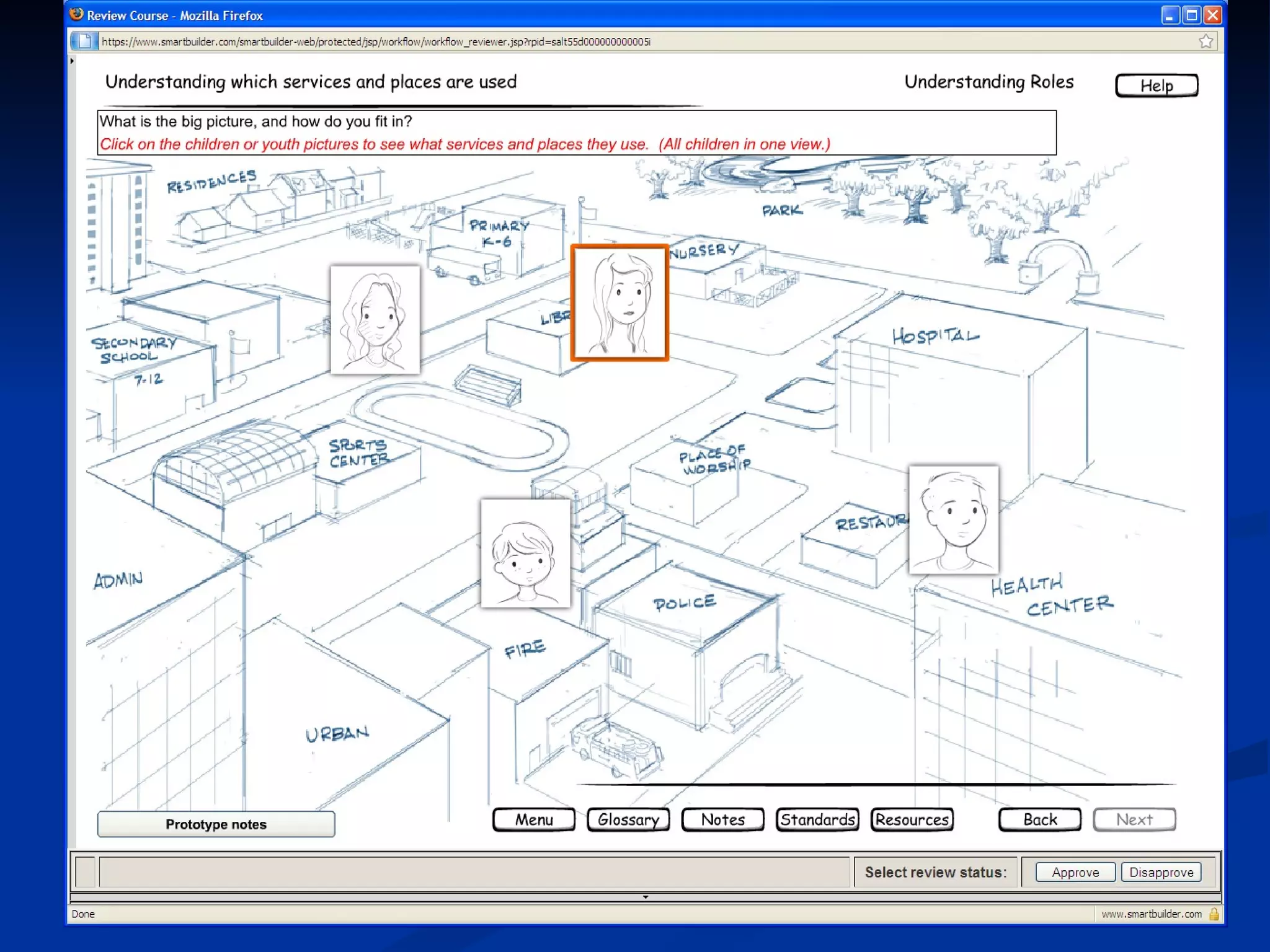
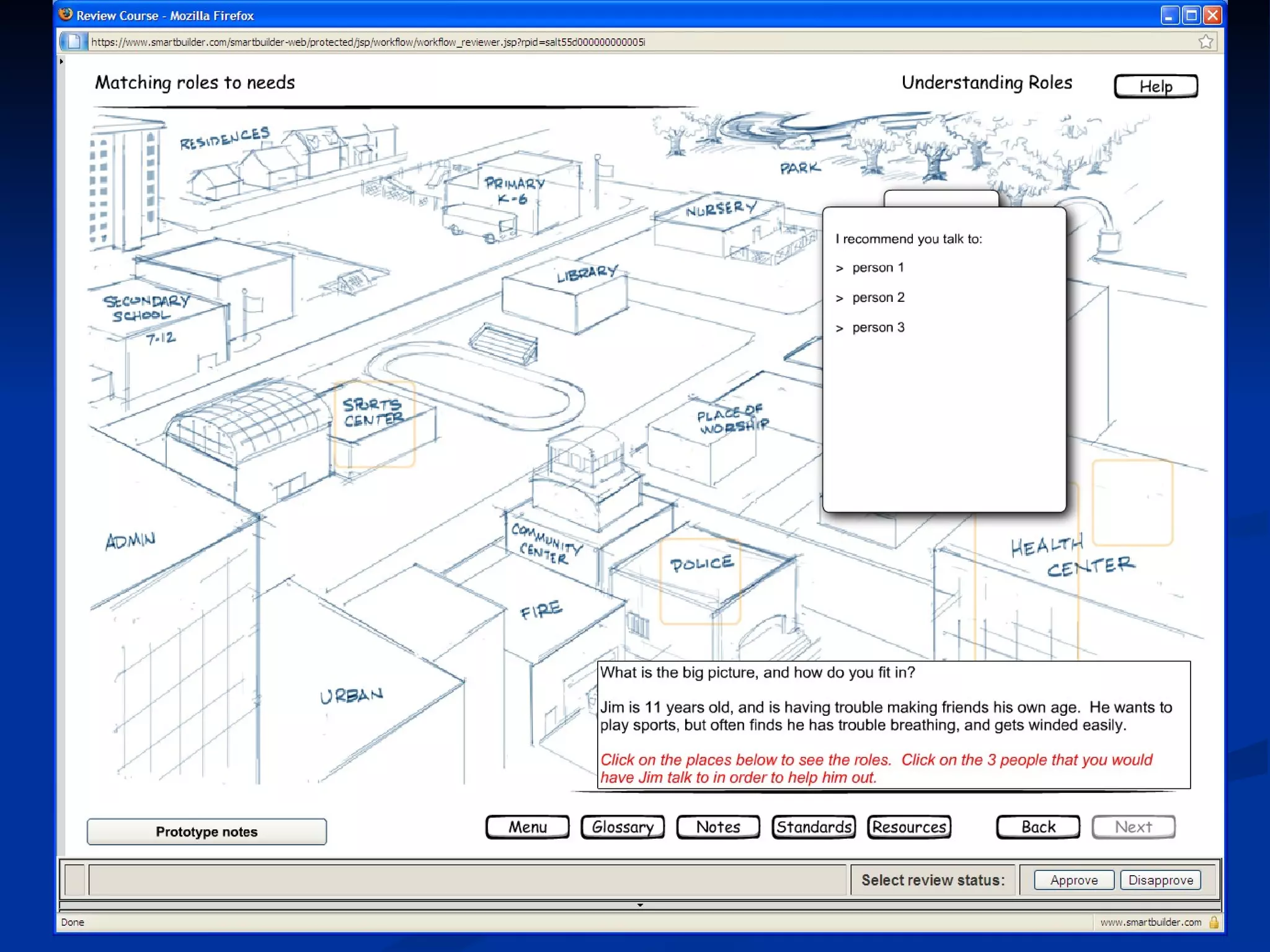
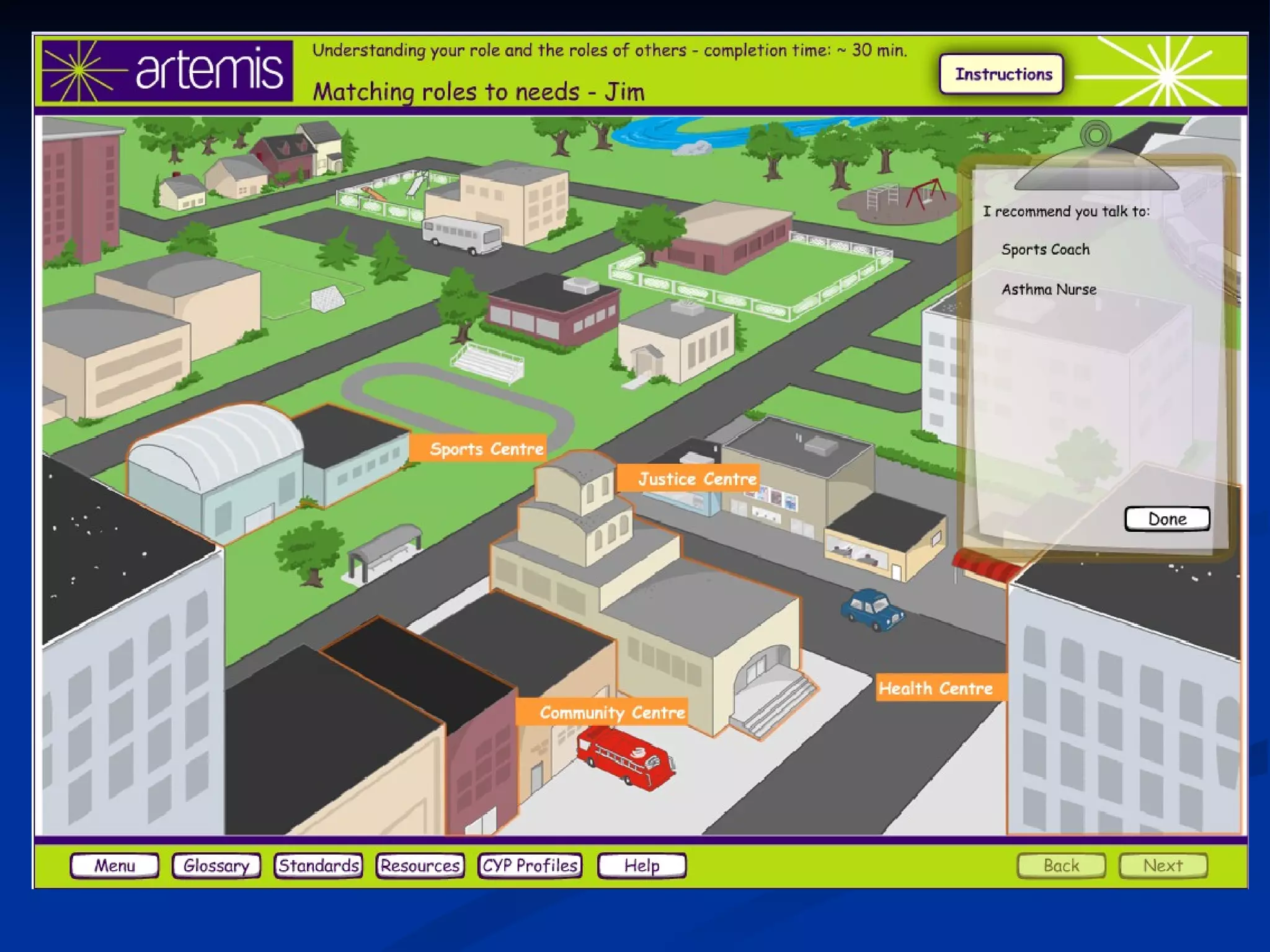
The document discusses principles for designing effective immersive e-learning experiences. It outlines 6 key design principles: focusing on applied knowledge over facts, hooking learners with engaging introductions, making content relevant to learners' contexts, providing exercises where learners make meaningful choices, introducing an element of risk, and using intrinsic feedback. It also discusses prototyping content through successive iterations to get the right level of instructional interactivity.
![A Better Way to Design and Build Immersive e-Learning Robert Penn [email_address] (800) 690-4259 x203](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abetterwaytocreateimmersiveelearningforastd-090723161806-phpapp01/75/A-Better-Way-to-Design-Build-Immersive-E-Learning-1-2048.jpg)