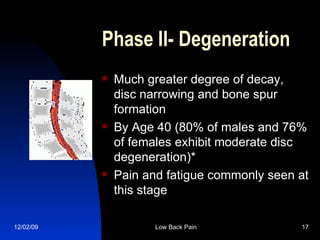
This document discusses low back pain, including its causes, risk factors, and treatments. It notes that 80% of people will experience low back pain in their lifetime. Common causes include mechanical issues like spinal degeneration or disc herniations that put pressure on nerves. Chiropractic care can help by improving spinal balance and mobility to reduce pain and prevent further issues. Maintaining good posture and exercising are also recommended for prevention and treatment.