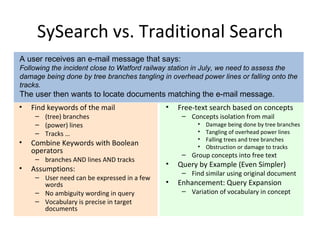
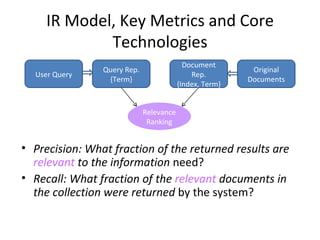
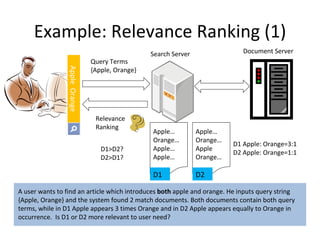
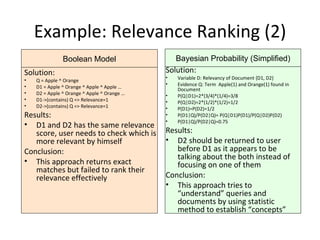
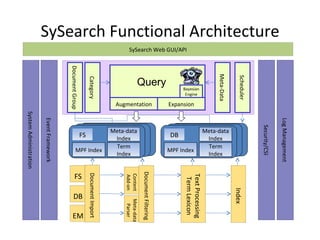
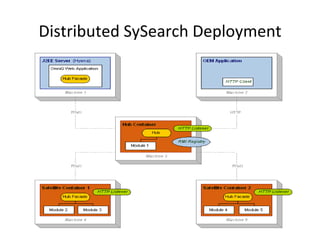
The document compares and contrasts concept-based search using SySearch versus traditional keyword search. SySearch uses concepts extracted from documents and queries to understand information needs better than keyword matching alone. It ranks results by estimating the probability of relevance using a Bayesian approach rather than binary keyword matching. This allows it to better support natural language queries and retrieve more relevant results.