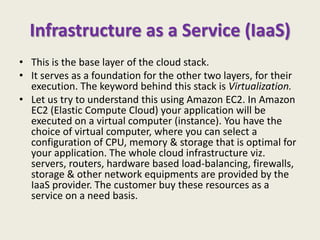
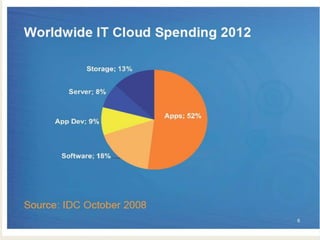
Cloud computing allows users to access computational resources like software, data storage, and computing power without needing to know details of the physical systems delivering those resources. It provides dynamism through flexible scaling of resources to meet fluctuating demand, abstraction by hiding technical details from end users, and resource sharing to improve utilization. The three main types of cloud computing services are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Cloud computing spending is growing much faster than traditional IT spending and is projected to become a large market.