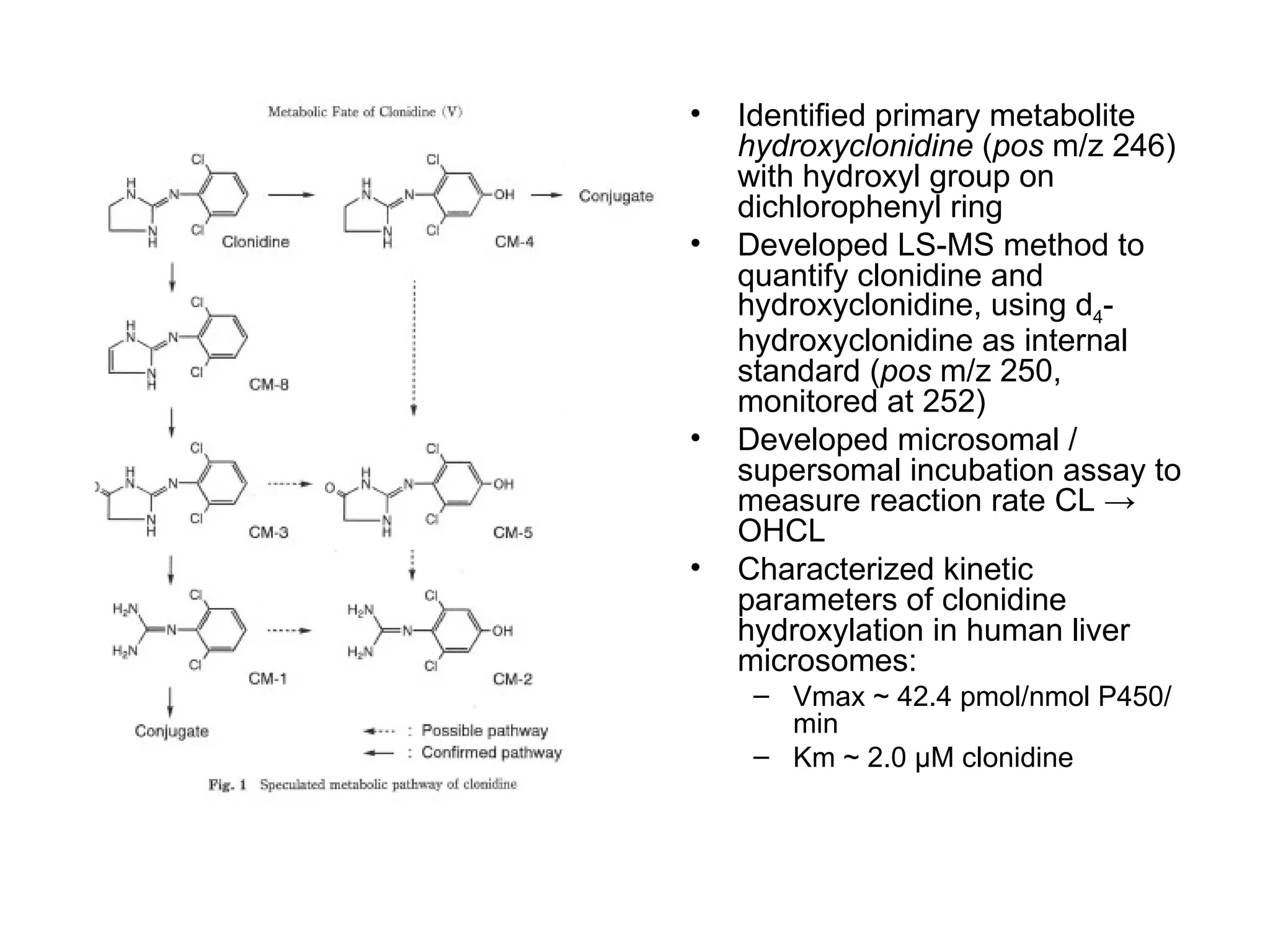
1. The document identifies the primary metabolite of clonidine as hydroxyclonidine and develops an LC-MS method to quantify both compounds using a deuterated internal standard.
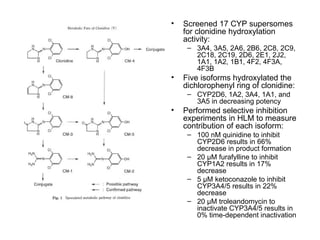
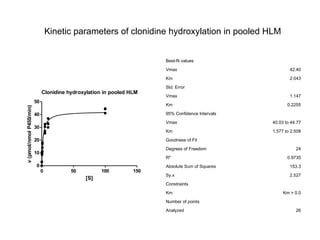
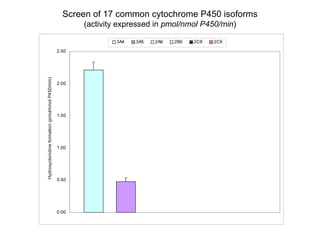
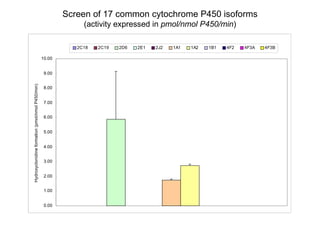
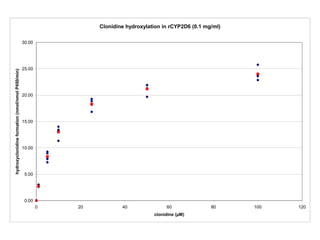
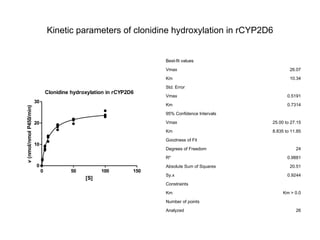
2. It characterizes the kinetic parameters of clonidine hydroxylation in human liver microsomes and screens 17 cytochrome P450 isoforms, finding five that hydroxylate clonidine with varying potency.
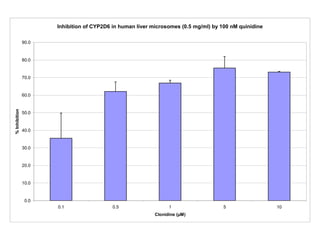
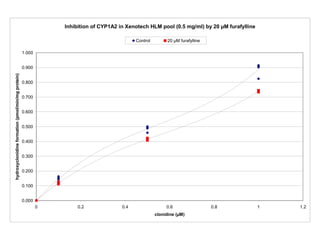
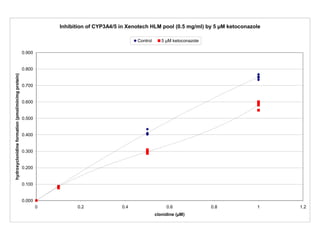
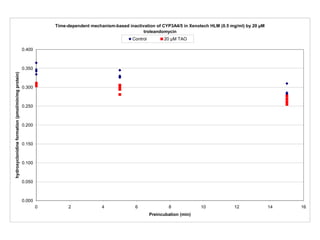
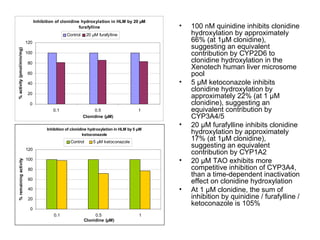
3. Selective inhibition experiments show that CYP2D6, CYP1A2, and CYP3A4/5 contribute most to clonidine hydroxylation in human liver microsomes.