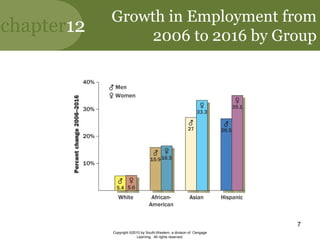
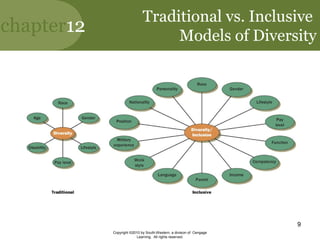
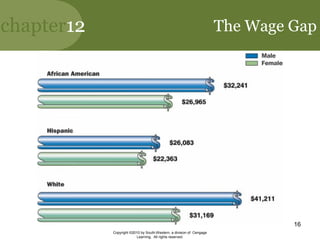
This document discusses managing diversity in the workplace. It covers topics like the changing demographics in the US and globally, defining diversity, the benefits of a diverse workforce, and challenges like biases and stereotypes. It also discusses initiatives companies use to promote diversity through training, policies, and programs. The goal is to create a culturally competent workplace that values all employees.