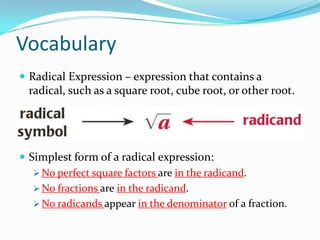
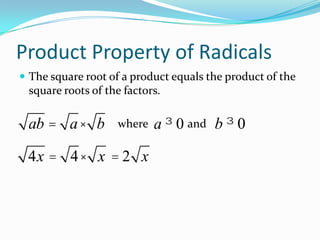
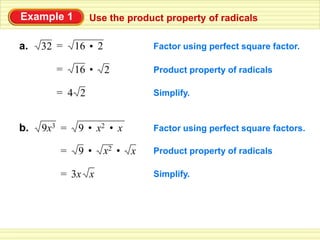
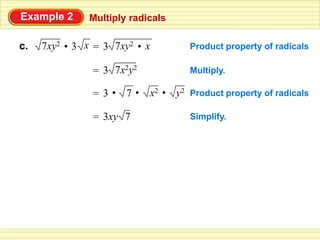
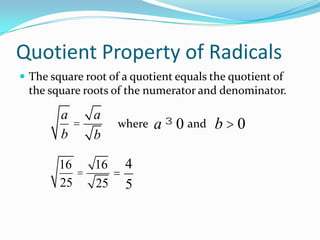
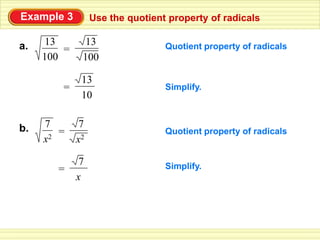
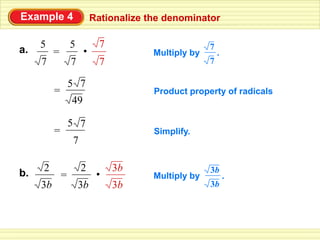
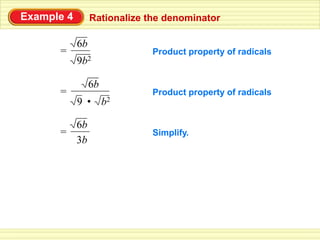
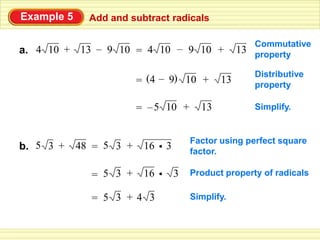
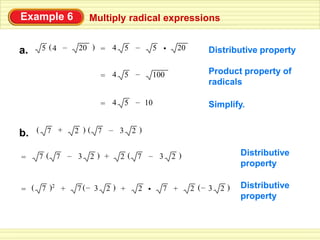
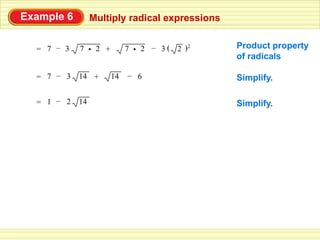
The document defines key terms related to radical expressions, including radical expressions, radicands, and simplest form. It then outlines several properties of radicals: the product property, which allows multiplying radicals by splitting them into factors; the quotient property, which allows simplifying radicals in fractions; and rationalizing denominators, which removes radicals from denominators. Finally, it provides examples applying these properties to simplify, add, subtract, and multiply radical expressions.